Previous: Exercise 11 | Next: Exercise 12
Iso Surfaces
An iso surface is a surface of constant value. This is an example of a velocity magnitude iso surface colored by static pressure. The iso-surface shape indicates everywhere in the model that has a specific velocity magnitude. The colors indicate the static pressure at these locations.
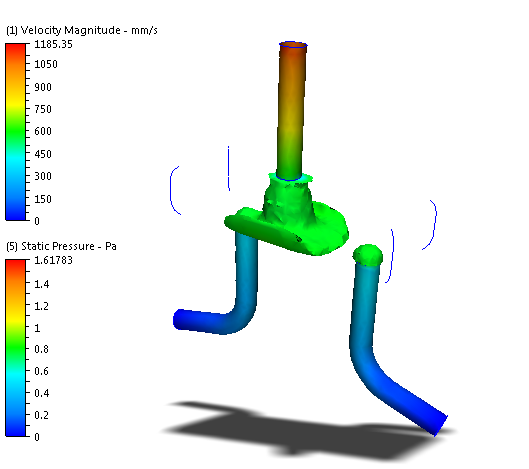
Iso surfaces are a three dimensional visualization tool that show a value as well as the physical shape of the flow characteristics. They are useful for visualizing velocity distributions in complicated flow paths as well as temperature distributions in thermal simulations. You can also use iso surfaces to determine the locations of the maximum and minimum values of a quantity.
Using Iso Surfaces
There are multiple ways to perform most Iso Surface tasks:
- On-model: Click directly on the model or the iso surface (as indicated). This is useful for maintaining focus on the model.
- Off-model: Use the Iso Surfaces branch of the Design Study bar or the Iso Surfaces context panel. This is useful for complex models in which it is easier to work away from geometry.
To Create an Iso Surface
- On-model: Right click on or near the model (not on an existing Iso Surface). Click Add Iso Surface.
- Off-model: Click Add on the Iso Surface context panel.
To rename an Iso Surface
- Right click on the desired Iso Volume in the Design Study bar, and click Rename.
To select an Iso Surface
- On-model: Left click directly on the iso surface.
- Off-model: Click its name in the Design Study bar.
To Hide an Iso Surface
- Uncheck the box adjacent to the Iso Surface in the Design Study bar. You can also right click on the name, and click Hide iso surface.
To Delete an Iso Surface
- On-Surface: Right click. Click Remove.
- Off-model: Right click on the desired Iso Surface in the Design Study bar, and click Remove
To Change the Appearance of an Iso Surface
- On-Surface: Right click. Select an option.
- Off-model: Click Edit from the Iso Surface context panel, and select from the Appearance menu.
To change the Iso quantity and the Color by Result quantity
- On-Surface: Right click. Click Iso Quantity or Color by Result, and select from the list.
- Off-model: Select from the Quantity and Color by menus, respectively, on the Iso Surfaces context panel.
To change the value of the Iso quantity
- Drag the slider bar on the Controls dialog.
To vary the vector length
- By default, all vectors are displayed with the Same length. To change vector length, drag the Length slider.
- To display vectors with different lengths, click Length range. Drag the Min and Max sliders to vary the range.
- To scale all vectors by the same amount, modify the value of the Scale factor in the Attributes section.
Iso Volumes
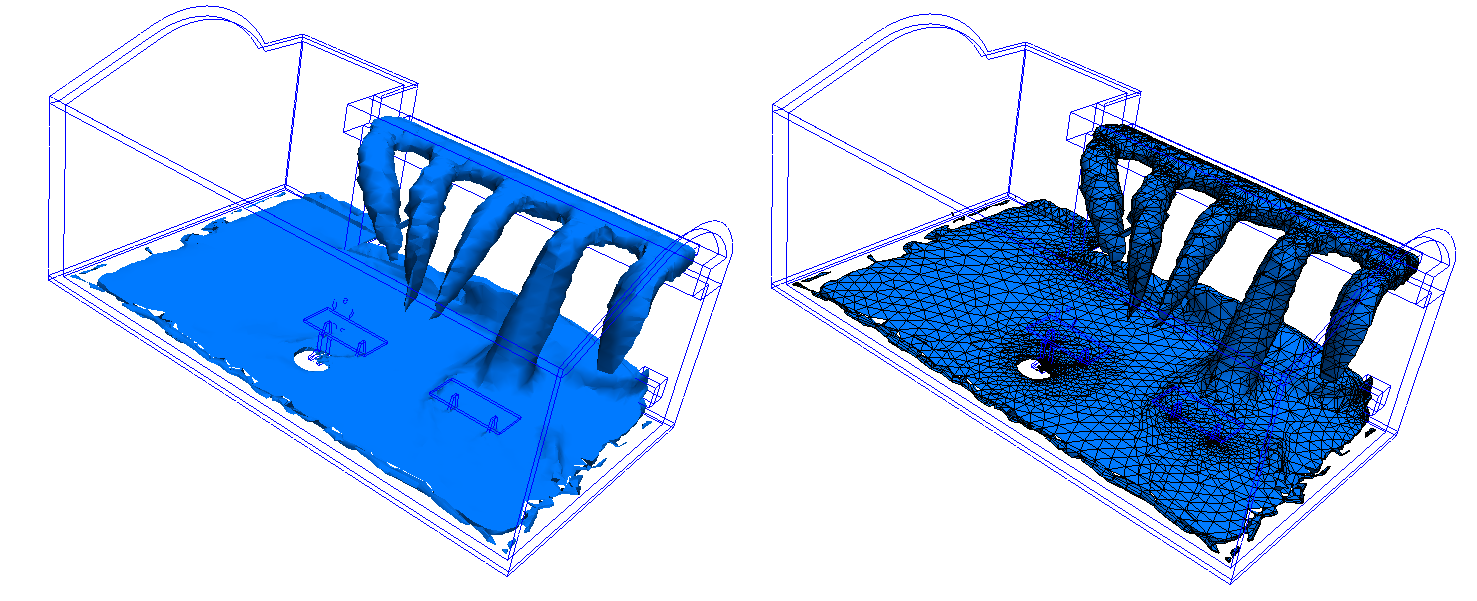
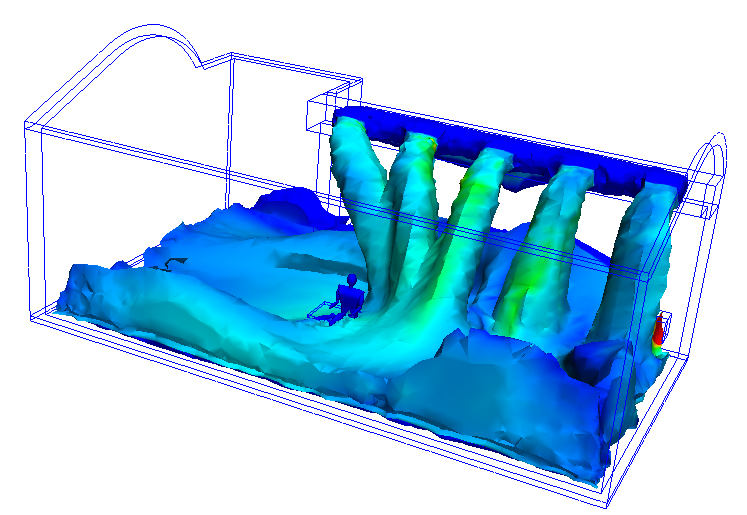
An Iso Volume is the volume of a model that falls within a specified range of a result quantity value. Unlike an Iso Surface which shows everywhere in the model that has a single, specified value, an Iso Volume shows everywhere that falls within a range of that result value.
The following shows an velocity magnitude Iso Volume colored by temperature. The shape of the Iso Volume indicates everywhere in the model that falls within a specified range of velocity magnitude. The colors indicate the temperature.
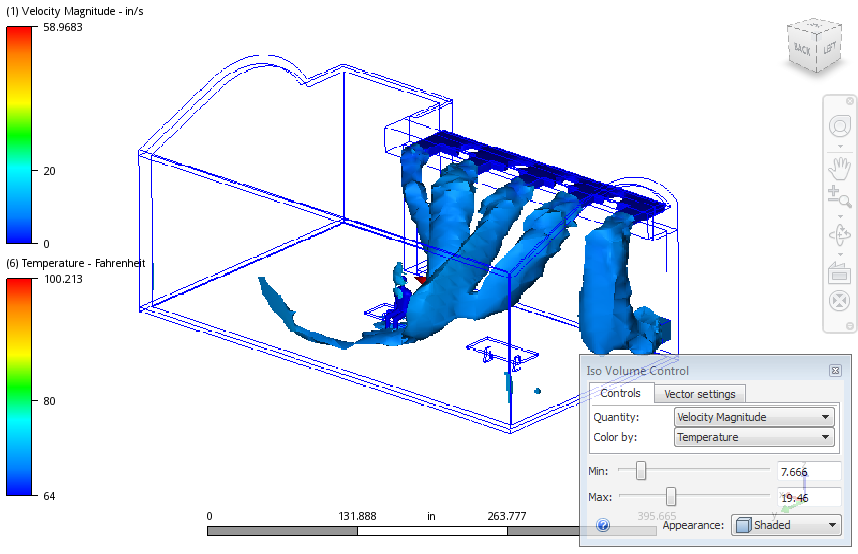
You can create and interact with Iso Volumes by clicking the Iso Volume command on the ribbon. The workflows for using Iso Volumes are very similar to those of Iso Surfaces.