Display one or more scaled views of your design on a standard-size drawing sheet called a layout.
After you finish creating a model at full size, you can switch to a paper space layout to create scaled views of the model, and to add notes, labels, and dimensions. You can also specify different linetypes and line widths for display in paper space.
Specifying the Paper Size of a Layout
The first thing that you should do when you access a layout tab (1) is right-click the tab (2) and rename it (3) to something more specific than Layout 1. For a D-size layout, ARCH D or ANSI D might be a good choice.
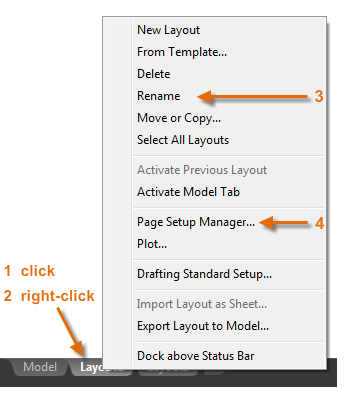
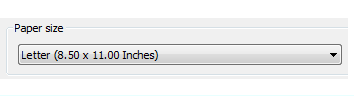
Next, open the Page Setup Manager (4) to change the paper size displayed in the layout tab. There are a lot of controls here, but you only need to change a few. The first is to specify the size of your sheet.
Model Space and Paper Space
As you know, you create the geometry of your model in model space.
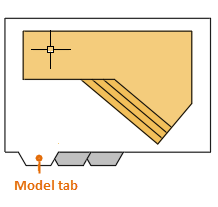
Originally, this was the only space available in AutoCAD. All notes, labels, dimensions, and the drawing border and title block were also created and scaled in model space. For some applications, this method is still entirely sufficient.
With the paper space feature, you can click a layout tab designed specifically for displaying multiple views, automatic scaling, and electronic or printing output.
For example, a layout tab is selected in the following illustration. There are currently two objects in paper space: a block object for the title and drawing border, and a single layout viewport, which displays a scaled view of model space.
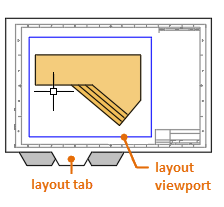
By default, a single layout viewport object is initially included on each layout tab, but your organization might be using customized drawing template (DWT) files that include several predefined layouts, layout viewports, and title blocks.
Let's learn more about layout viewport objects.
Layout Viewports
A layout viewport is an object that's created on a layout tab to display a scaled view of model space. You can think of it as a closed-circuit TV monitor that displays part of model space. You can select a layout viewport as you would any other object. When you select it, several grips display that provide a way to adjust the size of the viewport, move the viewport, and specify the scale of the view that's contained in it.
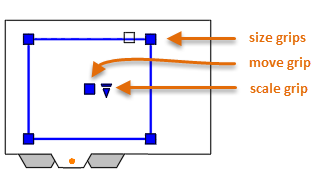
Several editing commands such as Move, Erase, and Copy can be used on layout viewports. When you select a layout viewport, you can use the Properties palette to provide a complete list of options and settings.
Switch between Model Space and Paper Space
When you're working on a layout tab, you can switch between paper space and model space without returning to the Model tab. Here's how. As shown in the illustration, you move your cursor and double-click either inside a layout viewport to access model space or you double-click outside the layout viewport to return to paper space. When you're in model space, the border of the layout viewport becomes thicker.
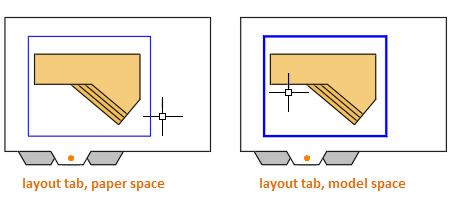
The primary reasons that you might want to access model space through the layout viewport is to pan the view or to make minor adjustments to the objects, especially those that display only in that viewport.
Create a New Viewport
You can use the New option of the MVIEW (make view) command to create additional layout viewports in paper space. With several layout viewports, you can display different views of model space at the same scale or at different scales.
- From a layout tab, enter MVIEW in the Command window and choose the New option.
- A maximized view of model space displays temporarily and you can click two points as shown to define an area.
- Back in the layout, right-click to display a list of scales and click the one that you want to use.
- Click a location to place the new layout viewport containing the scaled view.
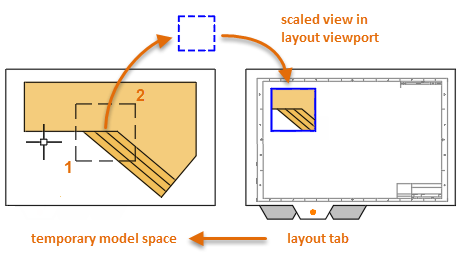
If you later need to set a different scale, select the layout viewport and click the triangular scale grip. This action displays a list of scales to choose from.
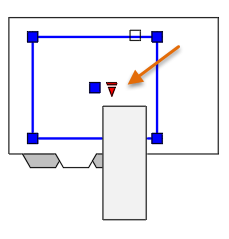
By default, scaled viewports are automatically locked to prevent accidental zooming or panning, which would change the scale or the clipping boundaries. You can lock and unlock a layout viewport by selecting it, right-clicking to display the shortcut menu, and choose Display Locked > On or Off.
Trans-Spatial Annotation
After you create one or more scaled layout viewports on a layout tab, follow these steps to use the trans-spatial method of annotating your drawing:
- Move the layout viewport as needed, and adjust its edges using the size grips.
- Turn off the layer on which you created the layout viewport object. This hides the edges of the layout viewport.
- Create notes, labels, and dimensions directly in paper space. They automatically appear at the correct size.
- Print the drawing to paper or as a DWF or PDF file.

Four Methods for Scaling Views and Annotating Drawings (Optional)
There are four different methods in AutoCAD for scaling views, notes, labels, and dimensions. Each method has advantages depending on how the drawing will be used. Here's a brief summary of each of the methods:
- The Original Method. You create geometry, annotate, and print from model space. Dimensions, notes, and labels must all be scaled in reverse. You set the dimension scale to the inverse of the plot scale. With this method, scaling requires a little math. For example, a commonly used imperial scale in architecture is 1/4" = 1'-0" which is 1:48 scale. If a note is to be printed 1/4" high, then it must be created 48 times as large, or 12" high in model space. The same scale factor also applies to dimensions, and an ARCH D drawing border at that scale is 144 feet long. When the drawing is printed as a D-size sheet, everything scales down to the correct size.
Note: Many AutoCAD drawings were created with this method, and many companies still use it. Once everything is set up, the method works well for 2D drawings with single views and inserted details.
- The Layout Method. You create geometry and annotations in model space, and then print from the layout. Set the dimension scale to 0 and the dimensions will scale automatically.
- The Annotative Method. You create geometry in model space, create annotative dimensions, notes, and labels, which use a special annotative style, in model space from the layout, and then you print from the layout. Annotative objects display only in layout viewports that share the same scale. The dimension scale is automatically set to 0 and all annotative objects scale automatically.
- The Trans-Spatial Method. You create geometry in model space, create annotations in paper space on a layout with the dimension scale set to 1, and then you print from the layout. This is arguably the simplest, most direct method, which is why it is the method of choice for this guide.