|
Operator |
Function |
Example |
Explanation |
|---|---|---|---|
|
eq |
Equal |
[eq(<TOOL>, 0)] |
True if <TOOL> ≡ 0 Also works for strings. |
|
neq |
Not Equal |
[neq(<TOOL>, 0)] |
True if <TOOL> ≠ 0 Also works for strings. |
|
lt |
Less Than |
[lt(<TOOL>, 0)] |
True if <TOOL> < 0 Also works for strings. |
|
gt |
Greater Than |
[gt(<TOOL>, 0)] |
True if <TOOL> > 0 Also works for strings. |
|
le |
Less Than or Equal |
[le(<TOOL>, 0)] |
True if <TOOL> ≤0 Also works for strings. |
|
ge |
Greater Than or Equal |
[ge(<TOOL>, 0)] |
True if <TOOL> ≥ 0 Also works for strings. |
|
and |
And |
[and(<Z-UP>, <INDEX>)] |
True if both <Z UP> and <INDEX> are true. |
|
or |
Or |
[or(<Z-UP>, <INDEX>)] |
True if either <Z UP> or <INDEX> is true. |
|
not |
Not |
[not(<Z-CHANGED>)] |
True if <Z CHANGE> is false. |
|
apxeq |
Approximately Equal (if tolerance is not given, the default is 1e-6.) |
[apxeq(<Z-COORD>, 0)] [apxeq(<Z-COORD>, 0, 1e-6)] |
True if
<Z COORD> ≡ 0 within
|
More examples of logical operators in expressions
To output Z as 0 if Z is within 0.0001 of zero:
<IF>[apxeq(<Z-COORD>, 0, 0.0001)]<THEN> N<SEQ> G00 X<X-COORD> Y<Y-COORD> Z0<EOB> <ENDIF>
To make Rapid Move use polar coordinates:
N<SEQ> I0 J0<EOB> N<SEQ> G10 R[sqrt(pow(<X-COORD>, 2) + pow(<Y-COORD>, 2))] H[D|3.2|1.0:atan2d(<Y-COORD>, <X-COORD>)] <EOB>
To output Z as 15 if Z is between 10 and 20 inclusively:
<IF>[and(ge(<Z-COORD>, 10), le(<Z-COORD>, 20))] <THEN> N<SEQ> G00 X<X-COORD> Y<Y-COORD> Z15<EOB> <ENDIF>
If P1 variable is not set, set it to the string G0:
<IF>[eq(<P1>,"")]<THEN> [<P1>=”G0”] <ENDIF>
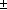 1e-6.
1e-6.