Create a WebEngine to add an interactive website or html content to a VRED scene. The content streams into a material texture channel in real-time and uses the properties of the material for display.
Create a WebEngine
- Select to open the Media Editor.
- Select the + icon in the bottom icon bar to create a WebEngine.
- Name the WebEngine.
- Set the Width and Height:
- If using html content in the URL, enter the known width and height from the code.
- If using a website in the URL, adjust the width and height when the website is displayed on an object.
- Add a URL for the content:
- To add a website, enter it in the URL field (for example, www.Autodesk.com).
- To add a local html file use the Browse icon. Html can contain audio and video. The html file can refer to audio and video files that are embedded. Supported media formats are WebM (.webm), OGG (.ogg/.ogv) and WAV (.wav).
- From the Material Editor, drag the material assigned to the object that the WebEngine is to be applied, to Material.
- Set the Texture type:
- Diffuse:
The environment is reflected in this texture.
- In the Material Editor Material tab, set the Diffuse Color to white.
- In the Material Editor Diffuse tab, set the Mapping type to UV. Rotate the Diffuse Texture as needed.
- Incandescence:
In raytracing, the material emits light into the scene when Use as Light Source is activated.
- In the Material Editor Material tab, set the Diffuse Color to black.
- In the Incandescence tab, set the intensity to 1.00 and the color to white.
- Set the Mapping type to UV. Rotate the Incandescence Texture as needed.
- Diffuse + Incandescence:
This texture is used when the properties of incandescence and an alpha channel, that is only available in diffuse, are needed.
HTML example code to set the background of a webpage transparent (alpha):
<style>
body{
background-color: rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);
}
</style>
- In the Material Editor Material tab, set the Diffuse Color to white.
- In the Diffuse Texture tab, select Use Alpha.
- In the Incandescence tab, set the intensity to 1.00 and the color to white.
- In either the Diffuse or Incandescence tab, set the Mapping type to UV. Rotate the Texture as needed.
- Diffuse:
VRED to HTML5 communication
Interaction between VRED and HTML5 is a two-way communication. Here is an example of VRED to HTML5.
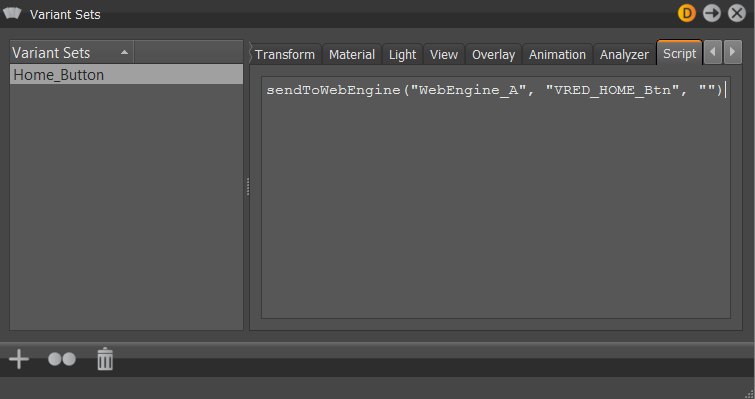
Executing the Variant Set (Home_Button) with an associated python script (sendToWebEngine), triggers a specific WebEngine (Webengine_A) and sends an html event (VRED_HOME_Btn) to the web page. The web page must have an Event Listener to receive the message.
The following is an example of HTML code to receive a message:
<script>
document.addEventListener("VRED_HOME_Btn", Icon_HomeClick);
</script>
HTML5 to VRED communication
An img element and a URL can be used to send python commands from the webpage to VRED using the webserver. For example, src = "http://localhost:8888?..... The webserver must be enabled in the preferences.
HTML code to set the Switch Material to choice 0:
<script>
function r(){
var i = document.createElement("img");
i.src = "http://localhost:8888/python?value=setSwitchMaterialChoice('SwitchColor', 0)";
};
</script>
HTML code to trigger a VarianSet named Icon_Anim:
<script>
Icon_Click = function(event) {
var i = document.createElement("img");
i.src = "http://localhost:8888/variants?value=selectVariantSet('Icon_Anim')";
};
</script>