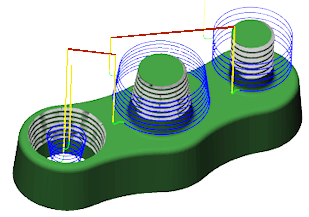
Thread is used for milling threads into a hole or a boss, with straight or tapered walls. Select any internal or external circular Face to create single or multi-lead threads. The heights and depths are automatically derived from the selected Face.
|
|
|
Access: |
Ribbon:
CAM tab
 2D Milling panel
2D Milling panel
 Thread
Thread

|
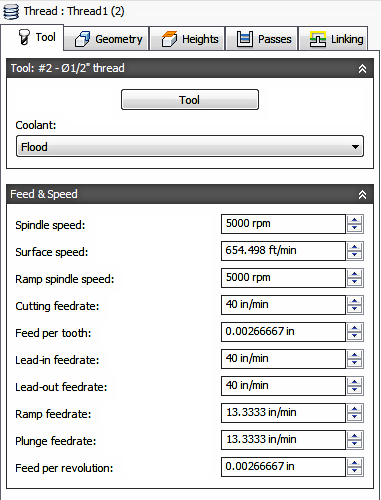
 Tool tab settings
Tool tab settings
Coolant
Select the type of coolant used with the machine tool. Not all types will work with all machine postprocessors.
Feed & Speed
Spindle and Feedrate cutting parameters.
- Spindle Speed - The rotational speed of the spindle expressed in Rotations Per Minute (RPM)
- Surface Speed - The speed which the material moves past the cutting edge of the tool (SFM or m/min)
- Ramp Spindle Speed - The rotational speed of the spindle when performing ramp movements
- Cutting Feedrate - Feedrate used in regular cutting moves. Expressed as Inches/Min (IPM) or MM/Min
- Feed per Tooth - The cutting feedrate expressed as the feed per tooth (FPT)
- Lead-In Feedrate - Feed used when leading in to a cutting move.
- Lead-Out Feedrate - Feed used when leading out from a cutting move
- Ramp Feedrate - Feed used when doing helical ramps into stock
- Plunge Feedrate - Feed used when plunging into stock
- Feed per Revolution - The plunge feedrate expressed as the feed per revolution
 Geometry tab settings
Geometry tab settings
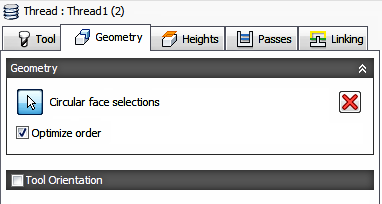
Geometry
Select any internal or external circular Face. This can be straight walled or tapered.
Circular Face Selection
Select any internal or external circular Face. The heights and depths are automatically derived from the selected Face.

Optimize Order
Enable to order the selected Faces for the shortest distance between cuts
Tool Orientation
Specifies how the tool orientation is determined using a combination of triad orientation and origin options.
The Orientation drop-down menu provides the following options to set the orientation of the X, Y, and Z triad axes:
- Setup WCS orientation - Uses the workpiece coordinate system (WCS) of the current setup for the tool orientation.
- Model orientation - Uses the coordinate system (WCS) of the current part for the tool orientation.
- Select Z axis/plane & X axis - Select a face or an edge to define the Z axis and another face or edge to define the X axis. Both the Z and X axes can be flipped 180 degrees.
- Select Z axis/plane & Y axis - Select a face or an edge to define the Z axis and another face or edge to define the Y axis. Both the Z and Y axes can be flipped 180 degrees.
- Select X & Y axes - Select a face or an edge to define the X axis and another face or edge to define the Y axis. Both the X and Y axes can be flipped 180 degrees.
- Select coordinate system - Sets a specific tool orientation for this operation from an Inventor User Coordinate System (UCS) in the model. This uses both the origin and orientation of the existing coordinate system. Use this if your model does not contain a suitable point & plane for your operation.
The Origin drop-down menu offers the following options for locating the triad origin:
- Setup WCS origin - Uses the workpiece coordinate system (WCS) origin of the current setup for the tool origin.
- Model origin - Uses the coordinate system (WCS) origin of the current part for the tool origin.
- Selected point - Select a vertex or an edge for the triad origin.
- Stock box point - Select a point on the stock bounding box for the triad origin.
- Model box point - Select a point on the model bounding box for the triad origin.
 Heights tab settings
Heights tab settings
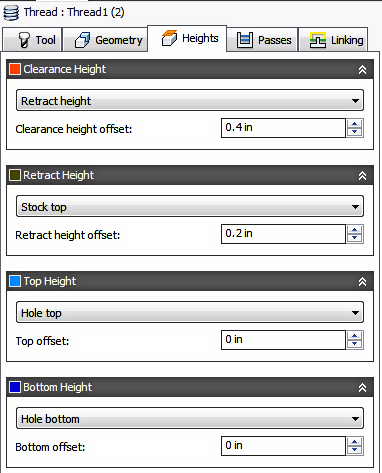
Clearance Height
The Clearance height is the first height the tool rapids to on its way to the start of the toolpath.

Clearance Height
- Retract height: incremental offset from the Retract Height.
- Top height: incremental offset from the Top Height.
- Bottom height: incremental offset from the Bottom Height.
- Model top: incremental offset from the Model Top.
- Model bottom: incremental offset from the Model Bottom.
- Stock top: incremental offset from the Stock Top.
- Stock bottom: incremental offset from the Stock Bottom.
- Hole top: incremental offset from the Hole Top.
- Hole bottom: incremental offset from the Hole Bottom.
- Selection: incremental offset from a Point (vertex), Edge or Face selected on the model.
- Origin (absolute): absolute offset from the Origin that is defined in either the Setup or in Tool Orientation within the specific operation.
Clearance height offset:
The Clearance height offset is applied and is relative to the Clearance height selection in the above drop-down list.
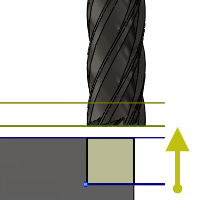
Retract Height
Retract height sets the height that the tool moves up to before the next cutting pass. Retract height should be set above the Feed height and Top. Retract height is used together with the subsequent offset to establish the height.
Retract Height
- Clearance height: incremental offset from the Clearance Height.
- Top height: incremental offset from the Top Height.
- Bottom height: incremental offset from the Bottom Height.
- Model top: incremental offset from the Model Top.
- Model bottom: incremental offset from the Model Bottom.
- Stock top: incremental offset from the Stock Top.
- Stock bottom: incremental offset from the Stock Bottom.
- Hole top: incremental offset from the Hole Top.
- Hole bottom: incremental offset from the Hole Bottom.
- Selection: incremental offset from a Point (vertex), Edge or Face selected on the model.
- Origin (absolute): absolute offset from the Origin that is defined in either the Setup or in Tool Orientation within the specific operation.
Retract height offset:
Retract height offset is applied and is relative to the Retract height selection in the above drop-down list.
Top Height
Top height sets the height that describes the top of the cut. Top height should be set above the Bottom. Top height is used together with the subsequent offset to establish the height.

Top Height
- Clearance height: incremental offset from the Clearance Height.
- Retract height: incremental offset from the Retract Height.
- Bottom height: incremental offset from the Bottom Height.
- Model top: incremental offset from the Model Top.
- Model bottom: incremental offset from the Model Bottom.
- Stock top: incremental offset from the Stock Top.
- Stock bottom: incremental offset from the Stock Bottom.
- Hole top: incremental offset from the Hole Top.
- Hole bottom: incremental offset from the Hole Bottom.
- Selection: incremental offset from a Point (vertex), Edge or Face selected on the model.
- Origin (absolute): absolute offset from the Origin that is defined in either the Setup or in Tool Orientation within the specific operation.
Top offset:
Top offset is applied and is relative to the Top height selection in the above drop-down list.
Bottom Height
Bottom height determines the final machining height/depth and the lowest depth that the tool descends into the stock. Bottom height needs to be set below the Top. Bottom height is used together with the subsequent offset to establish the height.

Bottom Height
- Clearance height: incremental offset from the Clearance Height.
- Retract height: incremental offset from the Retract Height.
- Top height: incremental offset from the Top Height.
- Model top: incremental offset from the Model Top.
- Model bottom: incremental offset from the Model Bottom.
- Stock top: incremental offset from the Stock Top.
- Stock bottom: incremental offset from the Stock Bottom.
- Hole top: incremental offset from the Hole Top.
- Hole bottom: incremental offset from the Hole Bottom.
- Selection: incremental offset from a Point (vertex), Edge or Face selected on the model.
- Origin (absolute): absolute offset from the Origin that is defined in either the Setup or in Tool Orientation within the specific operation.
Bottom offset
Bottom offset is applied and is relative to the Bottom height selection in the above drop-down list.
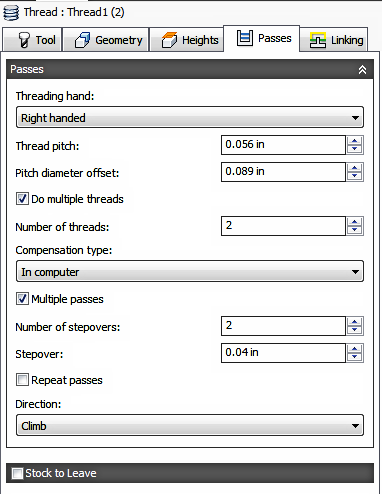
 Passes tab settings
Passes tab settings
Threading Hand
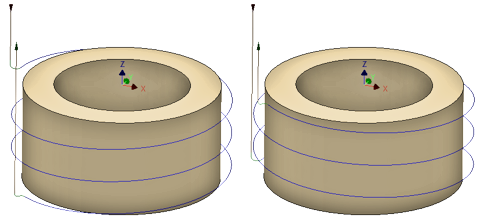
Right handed threads --- Left handed threads
Thread Pitch
The distance traversed for 1 complete thread. For Inch threads, it's the 1/Threads Per Inch (TPI). For Metric it's just the pitch as stated.
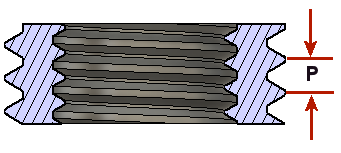
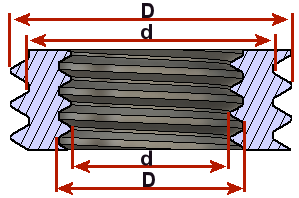
Pitch Diameter Offset
The difference between the Major "D" and the Minor "d" thread diameters. This is the thread depth and the value is always positive.
Do multiple threads
Enable to enter the number of threads.
Number of threads:
Specifies the number of thread leads.
Compensation type:
Specifies the compensation type.
- In computer - Tool compensation is calculated automatically by Autodesk HSM based on the selected tool diameter. The post-processed output contains the compensated path directly, instead of G41/G42 codes.
- In control - Tool compensation is not calculated, but rather G41/G42 codes are output to allow the operator to set the compensation amount and wear on the machine tool control.
- Wear - Works as if In computer was selected, but also outputs the G41/G42 codes. This lets the machine tool operator adjust for tool wear at the machine tool control by entering the difference in tool size as a negative number.
- Inverse wear - Identical to the Wear option, except that the wear adjustment is entered as a positive number.
Multiple Passes
Enable to enter a value for multiple depth cuts when Thread Milling.
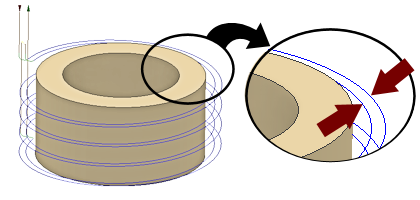
Number of Stepovers
Enter the number of roughing steps. 2 Steps shown above.
Stepover
The maximum distance between finishing passes. (See the illustration shown above)
Repeat Passes
Enable to perform the final finishing pass twice to remove stock left due to tool deflection.
Direction:
The Direction option lets you control if Autodesk HSM should try to maintain either Climb or Conventional milling.
Climb
Select Climb to machine all the passes in a single direction. When this method is used, Autodesk HSM attempts to use climb milling relative to the selected boundaries.
Left (climb milling)
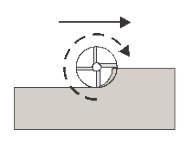 Climb Milling |
Right (conventional milling)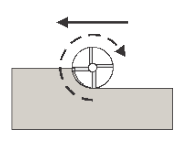 Conventional Milling |
Stock to Leave
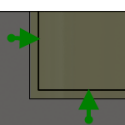 Positive Positive Stock to Leave - The amount of stock left after an operation to be removed by subsequent roughing or finishing operations. For roughing operations, the default is to leave a small amount of material. |
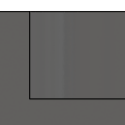 None No Stock to Leave - Remove all excess material up to the selected geometry. |
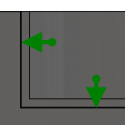 Negative Negative Stock to Leave - Removes material beyond the part surface or boundary. This technique is often used in Electrode Machining to allow for a spark gap, or to meet tolerance requirements of a part. |
Negative Stock to Leave - Removes material beyond the part surface or boundary. This technique is often used in Electrode Machining to allow for a spark gap, or to meet tolerance requirements of a part.
Radial (wall) Stock to Leave
The Radial Stock to Leave parameter controls the amount of material to leave in the radial (perpendicular to the tool axis) direction, i.e. at the side of the tool.
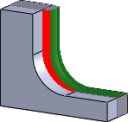 Radial stock to leave |
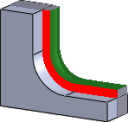 Radial and axial stock to leave |
Specifying a positive radial stock to leave results in material being left on the walls of the part.
For finishing operations, the default value is 0 mm / 0 in, i.e. no material is left.
For roughing operations, the default is to leave a small amount of material that can then be removed later by one or more finishing operations.
 Linking tab settings
Linking tab settings
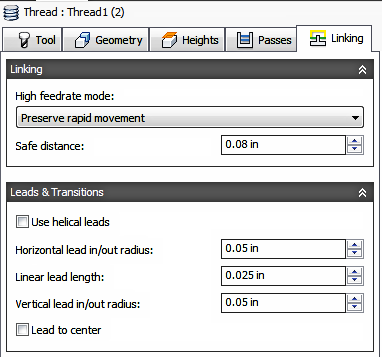
High feedrate mode:
Specifies when rapid movements should be output as true rapids (G0) and when they should be output as high feedrate movements (G1).
- Preserve rapid movement - All rapid movements are preserved.
- Preserve axial and radial rapid movement - Rapid movements moving only horizontally (radial) or vertically (axial) are output as true rapids.
- Preserve axial rapid movement - Only rapid movements moving vertically.
- Preserve radial rapid movement - Only rapid movements moving horizontally.
- Preserve single axis rapid movement - Only rapid movements moving in one axis (X, Y or Z).
- Always use high feed - Outputs rapid movements as (high feed moves) G01 moves instead of rapid movements (G0).
This parameter is usually set to avoid collisions at rapids on machines which perform "dog-leg" movements at rapid.
High feedrate:
The feedrate to use for rapids movements output as G1 instead of G0.
Safe distance:
Minimum distance between the tool and the part surfaces during retract moves. The distance is measured after stock to leave has been applied, so if a negative stock to leave is used, special care should be taken to ensure that safe distance is large enough to prevent any collisions.
Use helical leads
Enable to use helical lead in/out movements instead of circular lead in/out movements.
Horizontal lead-in radius:
Specifies the radius for horizontal lead-in moves.
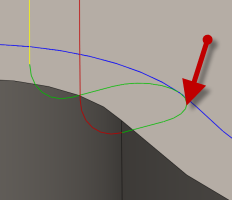
Horizontal lead-in radius
Horizontal lead-out radius:
Specifies the radius for horizontal lead-out moves.
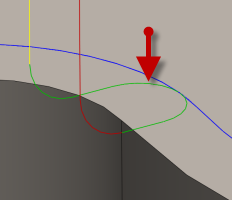
Horizontal lead-out radius
Linear lead length:
Specifies the length of the linear leads.
Vertical lead-in radius:
The radius of the vertical arc smoothing the entry move as it goes from the entry move to the toolpath itself.
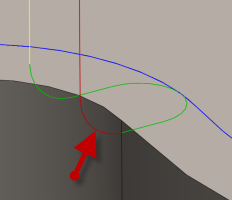
Vertical lead-in radius
Vertical lead-out radius:
Specifies the radius of the vertical lead-out.
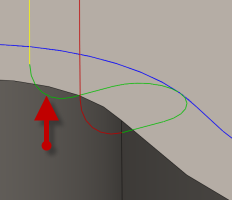
Vertical lead-out radius
Lead to center
Specifies that the lead in/out movement should be into the center of the geometry.