The Strain tensor (warp) result shows the residual strain in the selected direction throughout the part, after the ejected part has cooled to room temperature, in the midplane and in the 3D solutions.
 Midplane
Note: This result is only available if you have selected an appropriate option in the Stress result(s) to output drop-down menu in the Process Settings Wizard. The result is in the laminate through the thickness of the part shown by the Normalized Thickness value in the legend, and the load factor shown in the legend. Note the Normalized Thickness value, where -1 is the bottom of the element, 0 is the centerline through the element, and +1 is the top of the element.
Midplane
Note: This result is only available if you have selected an appropriate option in the Stress result(s) to output drop-down menu in the Process Settings Wizard. The result is in the laminate through the thickness of the part shown by the Normalized Thickness value in the legend, and the load factor shown in the legend. Note the Normalized Thickness value, where -1 is the bottom of the element, 0 is the centerline through the element, and +1 is the top of the element.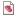 3D
Note: This result is only available if you have used the default Uncorrected residual stress model, and if you have turned off Use mesh aggregation. The result is an elemental value.
3D
Note: This result is only available if you have used the default Uncorrected residual stress model, and if you have turned off Use mesh aggregation. The result is an elemental value.
- Fill+Pack+Warp
- Cool+Fill+Pack+Warp
In the case of a Warp analysis, the values represent residual strains, which are the actual strains due to warp minus the unhindered strains at an element level. Positive strain values indicate extension; negative strain values denote contraction.
Using this result
This result, together with the Stress tensor (warp) result, can be used to understand, at an element level, what stresses (or tendencies to shrink) remain in the part after warpage deflection. These may be useful to understand in the context of subsequent cracking, or failure, due to environmental or loading factors.
You can display strains in the three principal directions, or one of the 6 tensor components, using the options provided on the Tensor tab of the Plot Properties dialog.
This result displays the strain distribution within the part as a tensor plot. You can also display the strains as a contour plot using either the Strain in the principal directions.