 Generate a parametric part from a mesh using the boundary representation model
Generate a parametric part from a mesh using the boundary representation model
 When launching the BREP function on a part,
Netfabb offers to check for flaws which can cause the BREP generation to fail. If it suspects there may be such flaws, it offers to send the part to repair instead of BREPping. If you choose to forgo the repair despite
Netfabb indicating the part may be flawed, a message will be posted to the crash logger whenever entering a loaded
Mesh to BREP instance to remind you of this. To re-test, close the
When launching the BREP function on a part,
Netfabb offers to check for flaws which can cause the BREP generation to fail. If it suspects there may be such flaws, it offers to send the part to repair instead of BREPping. If you choose to forgo the repair despite
Netfabb indicating the part may be flawed, a message will be posted to the crash logger whenever entering a loaded
Mesh to BREP instance to remind you of this. To re-test, close the
 Mesh to BREP tree node on the part by clicking
Mesh to BREP tree node on the part by clicking
 Remove Mesh to BREP.
Remove Mesh to BREP.
Generally, we recommend to use Mesh to BREP only on sane meshes, free from mesh flaws such as self-intersections, holes, overlapping or inverted triangles, and other issues.
Mesh to BREP is a module.
- Select the part.
- From the main menu, choose .
- Make adjustments as needed.
- Click Calculate.
- Click Apply to accept the result, or click Reset to return to making more adjustments.
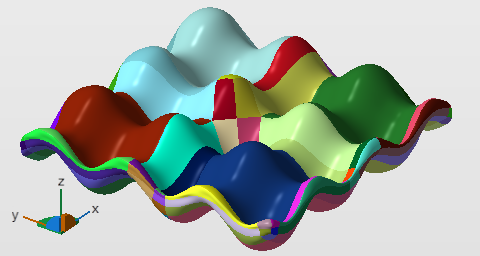
BREP patches are highlighted during the conversion
Settings Reference
Preprocessing
Preprocessing retriangulates the part surface into a more even mesh before the actual BREP generation is launched. You can choose to not do this. Depending on your choice, different preprocessing options regarding the handling of sharp corners are available:
Retriangulate input mesh disabled:
- Preserve given face groups as sharp edges: Provided the part actually has any face groups (otherwise this checkbox remains disabled), ticking this will cause the preprocessing to recognize the lines where face groups meet as sharp edges and will attempt to avoid smoothing these through the remeshing.
Retriangulate input mesh enabled:
- Target Edge Length: The remesher will try to adhere to this edge length but may deviate if the geometry requires it.
- Resolution: Lower values significantly increase generation of triangles and lead to increased calculation times.
- Detect and preserve sharp edges and Critical angle: This is the threshold of the smaller angle between triangles forming the edge, ranging from 90 ° up to 180 °. Blunt edges of this angle or greater will be smoothed. This ignores the signs of the triangles' normals, so both types of edges, concave or convex, can be addressed by this.
Surface generation
- Approximation: Sets a distance threshold for permitted deviation from the original surface
- Number of surfaces: Allows to set a target for the amount of BREP patches to be used for surface approximation.
Display settings
- Tessellation settings: Provides selection from the Retessellation Library.
- Show triangle mesh: Switches triangle borders to be highlighted by a black line.
 Mesh To BREP
Mesh To BREP