This method places a space where its volume is constrained from the base level to a ceiling or plenum level. Use this method when the space above a ceiling will serve as a plenum or otherwise have different parameters from the occupied spaces.
In the Project Browser, open a floor plan that contains the area where you want to place a space. Next, you create a section view to verify the space as you place it.
Create a section view
-
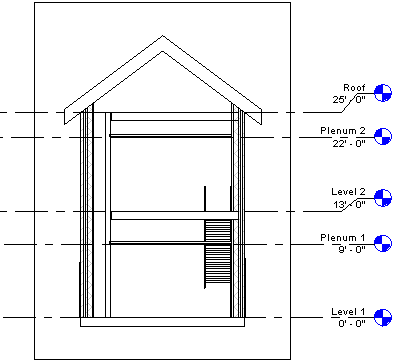
You can use an existing section view but make certain that the section line intersects the area in which you are placing the space. In the following examples, only one section view is needed because each level consists of a single space. You may need additional section views depending on the complexity of your design.
Note: Spaces do not display in elevation views.Place the section in the floor plan so that the section line intersects the area in which you are placing the space as shown.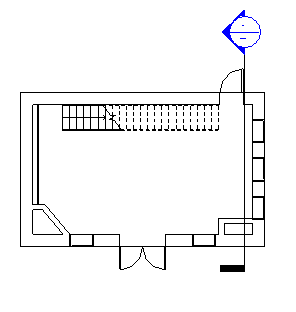
- Double-click the section to open it.
Create plenum levels
- If the project contains levels that are located at the ceiling height, select these levels, and in the Type Selector, select Level : Plenum.
This changes these standard levels to the plenum levels.
Note: If you change the level type, you need to create new floor plan views based on the plenum levels. See Create a plan view. You can delete the old floor plan views in the Project Browser. - If the project contains plenum levels, you can skip this section.
However, you need to confirm in the Project Browser that floor plan views based on the plenum levels exist. See the note above, if you need to create the floor plan views based on plenum levels.
- If the project does not contain levels at the ceiling height, click Architect tab
 Datum panel
Datum panel
 (Level).
(Level).
- In the Type Selector, select Level : Plenum.
- On the Options Bar, do the following:
- Verify that Make Plan view is selected.
- Click Plan View Types, and in the Plan View Types dialog, select only Floor Plan, and click OK.
This creates a new floor plan view based on the plenum level that you create. You need this floor plan view to place spaces in the plenum areas.
- For Offset, verify that 0' 0" (0.00 mm) is specified.
- Add plenum levels at the height of the ceiling.
- Click Modify.
- In the Project Browser, under the working discipline, double-click ???
 Floor Plans, right-click a new plenum floor plan view, and click Properties.
Floor Plans, right-click a new plenum floor plan view, and click Properties.
- On the Properties palette, specify the Sub-Discipline for the view.
This lists the new plenum floor plan view under its sub-discipline in the Project Browser.
You use plenum levels when placing spaces in areas that contain ceilings. Plenum levels are special levels that allow you to place spaces in the plenum areas above the ceiling by using a floor plan view based on the plenum level. You must place spaces in all plenum areas in order to perform an accurate heating and cooling loads analysis.
Activate spaces visibility
- Close all views, except the section view and the floor plan view where you want to place the space, and type
w t on the keyboard to tile the 2 views.
You can also click View tab
 Windows panel
Windows panel
 (Tile Views).
(Tile Views).
- With the section view active, type v g on the keyboard.
- On the Model Categories tab of the Visibility Graphics dialog, scroll down to Spaces.
- Expand Spaces, select Interior and Reference (if you want to display reference crosshairs), and click OK.
- Repeat to make spaces visible in the floor plan view.
Place a space
- With the floor plan view active, click Analyze tab
 Spaces and Zones panel
Spaces and Zones panel
 (Space).
Note: You may need to load space tags in the project, if they are not already loaded.
(Space).
Note: You may need to load space tags in the project, if they are not already loaded. - On the Options Bar, do the following:
- For Upper Limit, specify the level above the level of the space.
- For Offset, enter
0' 0" (0.00 mm).
These 2 options specify the vertical extent or height of the space.
Note: If the upper limit and offset are specified beyond the ceiling level, the vertical boundary of the space will snap to the ceiling, even though the upper limit is higher than the ceiling. This is because with the Areas and Volumes option selected (default setting), the vertical boundary of the space will snap to room-bounding components, such as ceilings. The volume of the space will be calculated up to the room-bounding component. The Areas and Volumes option is located on the Architect tab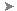 Room & Area panel drop-down
Room & Area panel drop-down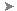 Area and Volume Computations.
Area and Volume Computations.
- In the Space box, either verify that New is selected if placing a new space, or select an unplaced space from the list to place it.
- Tag on placement: Places a space tag upon placement of the space.
Tag on placement is selected by default. If Tag on placement is selected, you can select the tag type from the Type Selector.
- Tag location box: specifies either Horizontal, Vertical, or Model as the space tag location.
Applicable only if Tag on placement is selected.
- Leader: Creates a leader line for the space tag.
Applicable only if Tag on placement is selected.
- Show Bounding Elements: Highlights the room-bounding elements in the building model for immediate recognition.
Select the following options as needed:
- In the floor plan view, move the cursor over an area in the building model, and click to place a space.
Note: Spaces can only be placed in floor plan views.
- Click Modify.
- Select the space.
- On the Properties palette, under Energy Analysis, do one of the following:
- Select Occupiable, if the space will be occupied.
- Clear Occupiable, if the space will be unoccupied.
- Click OK.
Note: If you place a space in an area that contains a room, the Occupiable parameter is automatically selected. This defines the space as occupied. If the area does not contain a room, the Occupiable parameter is automatically cleared. This defines the space as unoccupied. You can always redefine the space by selecting or clearing this parameter. The Occupiable parameter affects the heating and cooling loads analysis.
- In the section view, verify that the shaded area representing the volume of the space is constrained from the base level to the ceiling level above, and that unshaded areas (caused by such things as cavities or shafts) do not exist. This provides for a more accurate volume calculation.
Notice that unshaded areas exist for the gaps (left) and the chase (lower right). These need to be resolved.
- If the space is not constrained as specified, in the section view, verify that the upper limit of the space is specified to the level above, and
redefine the space vertically, if necessary.
You must also resolve all unshaded areas.