Objects in Free Motion react with walls and solids when they collide, thereby preventing penetration with other objects.
As an object in free motion moves through a flow field, Autodesk® CFD tracks the forces and torque acting on it, and uses this information to update its position. When a collision occurs, the forces, torque, and location of impact are computed, and are used to determine the reaction. A coefficient of restitution of 0.5 is used to compute the momentum exchange between objects as they collide. Reactions include bouncing, glancing, and spinning:
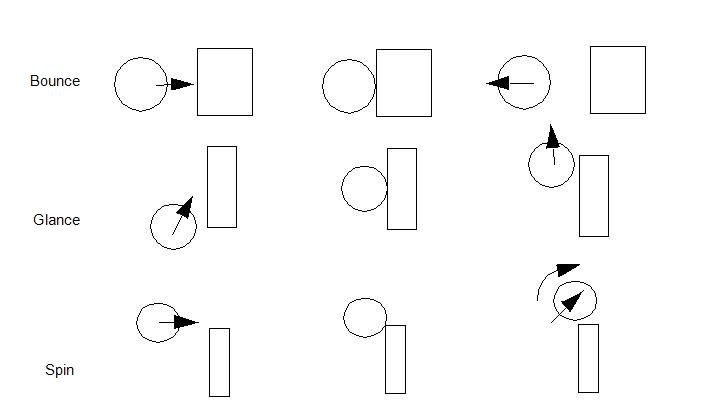
- Collision detection is enabled only for collisions involving at least one object in free motion.
- If a free motion object strikes another object in free motion, both objects will adjust their paths to avoid penetration. The impulse exchanged during the collision as well as a contact path are calculated. The contact force (which is the impulse divided by the time step) is applied to both objects at their respective contact points.
- If a free motion object strikes an object in user-specified motion, the free motion object will adjust to avoid penetrating the other object. The forces from the collision are applied to both objects, respectively, but will not affect the motion of the object in user-specified motion. (The collision force is included in the motion output data for both parts, however.)
- If a free motion object strikes an object in fluid-driven motion, the free motion object will adjust to avoid penetrating the other object. Forces from the collision are applied to both objects, and will move the fluid-driven part in its constrained path of motion.
- The mesh must follow the guidelines described in the User’s Manual for the motion path. If the mesh is too coarse, the moving object may pass through an obstruction instead of colliding with it.
- Collision detection is sensitive to the time step size. If the time step is too large, moving objects may pass through an obstruction instead of colliding. A good guideline is the time step size indicated by the Estimate function on the Analyze dialog.
If an object in free motion strikes a wall or static solid, a collision will also occur, and the object will bounce or deflect appropriately.