You can create blocks by associating objects and giving them a name or by creating a drawing to be used as a block.
Block Definitions
Whenever you create a block or insert a drawing as a block, all of the block information in the block definition, which includes its geometry, layers, colors, linetypes, and block attribute objects, is stored within the drawing file as non-graphic information as part of what's called the block table. Every block you insert is a block reference to a block definition. Block references are often simply called blocks.
Blocks can be defined and saved in several places:
- Within a drawing file intended for use only within that drawing
- Within a drawing template file intended for use by any drawing that starts with it
- As separate drawing files intended to be inserted into other drawings as blocks
- As multiple blocks within a drawing file intended to serve as a block library drawing to be accessed from other drawings
- As online block definitions provided by one of several vendors and services. These blocks are often associated with specific parts or products.
How Blocks are Referenced
Block definitions can be created directly in the current drawing using the BLOCK command or they can be inserted from a different drawing. Several methods are available for inserting blocks from other drawing files or inserting the drawing file itself:
- Autodesk DesignCenter
- The Blocks palette, Other Drawing tab
- Dragged and dropped from a file folder
- Defined in the Tools Palette window
Create a Block Within a Drawing
A block definition typically includes the following information:
- The block name
- Objects that are included
- A base point that's used for placing the block in a drawing
- Optionally, block attribute objects used to store data such as the part number, vendor name, service information, and so on.
Create Drawing Files for Use as Blocks
You can create drawing files for the purpose of inserting them into other drawings as blocks. Individual drawing files are easy to create and manage as the source of block definitions. Related drawings can be stored in a folder as a library of blocks.
- Specify the name of the block
The drawing name serves as the name of the block.
-
Specify the base point of the drawing
By default, the WCS (world coordinate system) origin (0,0,0) is used as the base point for drawing files inserted as blocks. You can reset the base point to specify a different base point for insertion using the BASE command.
- Create the objects
These objects typically include geometric objects, text, and block attribute objects. When you're finished, save the drawing in a folder with other drawings that you intend to use as blocks.
There are several methods of creating blocks so that they inherit one or more properties such as layers, colors, or linetypes from the current setting.
Create a Block Library Drawing
Collections of related blocks can be stored in a drawing file or set of drawings files. These are called block library drawings. In block library drawings, related block definitions are saved in an otherwise empty drawing file. When that drawing file is inserted as a block into the current drawing, all of its block definitions are added to the block table of the current drawing.
Create Nested Blocks
Block references that are included in a block definition are called nested blocks. Using blocks within blocks can simplify the organization of a complex block definition.
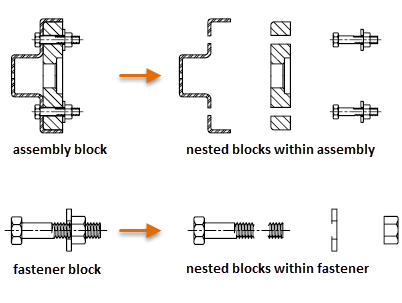
Blocks that try to reference themselves are called circular references, and are not allowed.