You can create work features in parts or assemblies.
Part work features and assembly work features differ in the following ways:
- In part files, part work features are nested beneath consuming work features in the browser. In assembly files, work features are depending on the components from which they were created; assembly work features are listed at the bottom of the browser.
- Work features can’t be created in-line in assembly files.
- Projected geometry can’t be used in assembly files because an assembly constraint is not available to control the work feature position.
- Midpoints can’t be selected in assembly files.
- The 3D Move/Rotate tool is not available in assembly files.
- The User Coordinate System cannot be position relatively to existing geometry in assembly files.
- Assembly constraints are created when you create a part in-place using another part to position a work feature.
- You can set selection priority to Select Features when selecting assembly work features.
Create Work Planes
In a part, a work plane is an infinite construction plane that is parametrically attached to a feature. In an assembly, a work plane is constrained relative to an existing component.
- On the ribbon, click 3D Model tab
 Work Features panel . Then, choose the type of plane you want to create and select the appropriate geometry:
Work Features panel . Then, choose the type of plane you want to create and select the appropriate geometry: -
 Plane. Creates a construction plane through selected objects. Select vertices, edges, or faces to define the plane.
Plane. Creates a construction plane through selected objects. Select vertices, edges, or faces to define the plane.  Offset from Plane. Creates a work plane parallel to the selected face at the specified offset distance. Select a planar face and drag in the direction of the offset. Enter a value in the edit box to specify the offset distance.
Offset from Plane. Creates a work plane parallel to the selected face at the specified offset distance. Select a planar face and drag in the direction of the offset. Enter a value in the edit box to specify the offset distance.  Parallel to Plane Through Point. Creates a work plane parallel to a selected point, face, or plane through a point. Select a planar face or work plane and any point, in either order. The work plane coordinate system is derived from the selected plane.
Parallel to Plane Through Point. Creates a work plane parallel to a selected point, face, or plane through a point. Select a planar face or work plane and any point, in either order. The work plane coordinate system is derived from the selected plane.  Midplane Between Two Planes. Creates a work plane in the middle of two planar faces or planes. Select two parallel planar faces or work planes. The new work plane is oriented to the coordinate system and has the same outward normal of the first selected plane.
Midplane Between Two Planes. Creates a work plane in the middle of two planar faces or planes. Select two parallel planar faces or work planes. The new work plane is oriented to the coordinate system and has the same outward normal of the first selected plane.  Midplane of Torus. Creates a work plane through the center, or midplane, or a torus. Select a torus.
Midplane of Torus. Creates a work plane through the center, or midplane, or a torus. Select a torus. 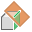 Angle to Plane Around Edge. Creates a work plane at a 90-degree angle from a part face or plane. Select a part face or plane and any edge or line parallel to the face. Enter the desired angle in the edit box.
Angle to Plane Around Edge. Creates a work plane at a 90-degree angle from a part face or plane. Select a part face or plane and any edge or line parallel to the face. Enter the desired angle in the edit box. 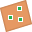 Three Points. Creates a work plane through three endpoints, midpoints, intersections, or work points. Select any three endpoints, midpoints, intersections, or work points. The positive X axis is directed from the first point to the second point. The positive Y axis is perpendicular to the positive X axis through the third point.
Three Points. Creates a work plane through three endpoints, midpoints, intersections, or work points. Select any three endpoints, midpoints, intersections, or work points. The positive X axis is directed from the first point to the second point. The positive Y axis is perpendicular to the positive X axis through the third point.  Two Coplanar Edges. Creates a work plane through two coplanar work axes, edges, or lines. Select two coplanar work axes, edges, or lines. The positive X axis is oriented along the first selected edge.
Two Coplanar Edges. Creates a work plane through two coplanar work axes, edges, or lines. Select two coplanar work axes, edges, or lines. The positive X axis is oriented along the first selected edge.  Tangent to Surface Through Edge. Creates a work plane through an edge and tangent to a curved surface. Select a curved face and a linear edge, in either order. The X axis is defined by the line of tangency to the face. The positive Y axis is defined from the X axis to the edge.
Tangent to Surface Through Edge. Creates a work plane through an edge and tangent to a curved surface. Select a curved face and a linear edge, in either order. The X axis is defined by the line of tangency to the face. The positive Y axis is defined from the X axis to the edge.  Tangent to Surface Through Point. (Part files only.) Creates a work plane through an endpoint, midpoint, or work point and tangent to a curved surface. Select a curved face and an endpoint, midpoint, or work point. The X axis is defined by the line of tangency to the face. The positive Y axis is defined from the X axis to the point.
Tangent to Surface Through Point. (Part files only.) Creates a work plane through an endpoint, midpoint, or work point and tangent to a curved surface. Select a curved face and an endpoint, midpoint, or work point. The X axis is defined by the line of tangency to the face. The positive Y axis is defined from the X axis to the point.  Tangent to Surface and Parallel to Plane. Creates a work plane tangent to a curved surface and parallel to a plane. Select a curved face and a planar face or work plane, in either order. The new work plane coordinate system is derived from the selected plane. This method can also be used to create a work plane tangent to a face or plane that is normal to a plane.
Tangent to Surface and Parallel to Plane. Creates a work plane tangent to a curved surface and parallel to a plane. Select a curved face and a planar face or work plane, in either order. The new work plane coordinate system is derived from the selected plane. This method can also be used to create a work plane tangent to a face or plane that is normal to a plane. 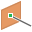 Normal to Axis Through Point. Creates a work plane perpendicular to an edge or work axis and through an endpoint, midpoint, or work point. Select a linear edge or axis and a point, in either order. The positive X axis is oriented from the intersection of the plane and axis to the point. Specify the direction of the positive Y axis.
Normal to Axis Through Point. Creates a work plane perpendicular to an edge or work axis and through an endpoint, midpoint, or work point. Select a linear edge or axis and a point, in either order. The positive X axis is oriented from the intersection of the plane and axis to the point. Specify the direction of the positive Y axis. 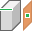 Normal to Curve at Point. (Part files only.) Creates a work plane perpendicular to a curve and through a vertex, edge midpoint, sketch point, or work point. Select a nonlinear edge or sketch curve (arc, circle, ellipse, or spline) and a vertex, edge midpoint, sketch point, or work point on the curve. The new work plane is normal to the curve and passes through the point.
Normal to Curve at Point. (Part files only.) Creates a work plane perpendicular to a curve and through a vertex, edge midpoint, sketch point, or work point. Select a nonlinear edge or sketch curve (arc, circle, ellipse, or spline) and a vertex, edge midpoint, sketch point, or work point on the curve. The new work plane is normal to the curve and passes through the point.
-
- If applicable, click the check mark in the edit box to accept the preview and create the plane.
Create Work Plane Through Axis
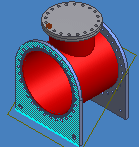
- In a part file, select Work Plane
 , or in an assembly file (not available in Inventor LT), click 3D Model tab
, or in an assembly file (not available in Inventor LT), click 3D Model tab  Work Features panel
Work Features panel  Plane
Plane - Select a PLANE and a LINE. Note: The selection order does not matter. The PLANE and LINE must be parallel to each other.
The PLANE can be a:
- Planar face in the graphics window
- Work plane in the graphics window or browser
- Sketch in browser
The LINE can be a:
- Linear edge in the graphics window
- Work axis in the graphics window or browser
- 2D sketch line in the graphics window
- 3D sketch line in the graphics window
- Enter an angle in the Angle dialog box. As you change the angle, the preview updates automatically.
- Click the check mark in the Angle dialog box or press Enter.
Create Work Axes
- On the ribbon, click 3D Model tab
 Work Features panel . Then, choose the type of axis you want to create and select the appropriate geometry.
Work Features panel . Then, choose the type of axis you want to create and select the appropriate geometry.  Axis. Creates a construction line that is parametrically attached to other objects. Select edges, lines, planes, or points to create the work axis through the selected objects.
Axis. Creates a construction line that is parametrically attached to other objects. Select edges, lines, planes, or points to create the work axis through the selected objects.  On Line or Edge. Creates a work axis that is collinear with a linear edge or sketch line. Select a linear edge or a 2D or 3D sketch line.
On Line or Edge. Creates a work axis that is collinear with a linear edge or sketch line. Select a linear edge or a 2D or 3D sketch line.  Parallel to Line Through Point. Creates a work axis through a point and parallel to a linear edge. Select an endpoint, midpoint, sketch point, or work point. Then, select a linear edge or sketch line.
Parallel to Line Through Point. Creates a work axis through a point and parallel to a linear edge. Select an endpoint, midpoint, sketch point, or work point. Then, select a linear edge or sketch line.  Through Two Points. Creates a work axis through two endpoints, intersections, midpoints, sketch points, or work points. Select two endpoints, intersections, midpoints, sketch points, or work points. (You can’t select midpoints in an assembly.) The positive direction of the new work axis is oriented from the first point to the second point.
Through Two Points. Creates a work axis through two endpoints, intersections, midpoints, sketch points, or work points. Select two endpoints, intersections, midpoints, sketch points, or work points. (You can’t select midpoints in an assembly.) The positive direction of the new work axis is oriented from the first point to the second point.  Intersection of Two Planes. Creates a work axis coincident with the intersection of two planes. Select two nonparallel work planes or planar faces.
Intersection of Two Planes. Creates a work axis coincident with the intersection of two planes. Select two nonparallel work planes or planar faces.  Normal to Plane Through Point. (Part files only.) Creates a work axis through a point and perpendicular to a plane. Select a planar face or work plane and a point.
Normal to Plane Through Point. (Part files only.) Creates a work axis through a point and perpendicular to a plane. Select a planar face or work plane and a point.  Through Center of Circular or Elliptical Shape. Creates a work axis coincident with the axis of a circle, ellipse, or fillet. Select the edge of a circle, ellipse, or fillet.
Through Center of Circular or Elliptical Shape. Creates a work axis coincident with the axis of a circle, ellipse, or fillet. Select the edge of a circle, ellipse, or fillet.  Through Revolved Face or Feature. Creates a work axis coincident with the axis of a face or feature. Select a revolved face or feature.
Through Revolved Face or Feature. Creates a work axis coincident with the axis of a face or feature. Select a revolved face or feature.
Create Work Points
- On the ribbon, click 3D Model tab
 Work Features panel . Then, choose the type of point you want to create and click or select the appropriate geometry.
Work Features panel . Then, choose the type of point you want to create and click or select the appropriate geometry.  Point. Creates a construction point that is parametrically attached to other objects. Select model vertices, edge and axis intersections, or intersections of three nonparallel faces or planes to create a work point. In an assembly, in-line work features are not available and midpoints can’t be selected.
Point. Creates a construction point that is parametrically attached to other objects. Select model vertices, edge and axis intersections, or intersections of three nonparallel faces or planes to create a work point. In an assembly, in-line work features are not available and midpoints can’t be selected.  On Vertex, Sketch Point, or Midpoint. Creates a work point on a 2D or 3D sketch point, vertex, or the endpoint or midpoint of a line or linear edge. Select a 2D or 3D sketch point, vertex, or the endpoint or midpoint of a line or linear edge.
On Vertex, Sketch Point, or Midpoint. Creates a work point on a 2D or 3D sketch point, vertex, or the endpoint or midpoint of a line or linear edge. Select a 2D or 3D sketch point, vertex, or the endpoint or midpoint of a line or linear edge.  Intersection of Three Planes. Creates a work point at the intersection of three work planes or planar faces. Select three work planes or planar faces.
Intersection of Three Planes. Creates a work point at the intersection of three work planes or planar faces. Select three work planes or planar faces.  Intersection of Two Lines. Creates a work point at the intersection of two lines. Select any two lines including linear edges, 2D or 3D sketch lines, and work axes.
Intersection of Two Lines. Creates a work point at the intersection of two lines. Select any two lines including linear edges, 2D or 3D sketch lines, and work axes.  Intersection of Plane/Surface and Line. (Part files only.) Creates a work point at the intersection of a planar face or work plane and a work axis or line. Select a planar face or work plane and a work axis or line. Or, select a surface and a sketch line, straight edge, or work axis.
Intersection of Plane/Surface and Line. (Part files only.) Creates a work point at the intersection of a planar face or work plane and a work axis or line. Select a planar face or work plane and a work axis or line. Or, select a surface and a sketch line, straight edge, or work axis.  Center Point of Loop of Edges. (Part files only.) Creates a work point on any closed loop when the Loop Select option is active. First, right-click and select Loop Select from the pop-up context menu. Then select one edge of a closed loop of edges.
Center Point of Loop of Edges. (Part files only.) Creates a work point on any closed loop when the Loop Select option is active. First, right-click and select Loop Select from the pop-up context menu. Then select one edge of a closed loop of edges.  Center Point of Torus. Creates a work point through the center, or midplane, of a torus. Select a torus.
Center Point of Torus. Creates a work point through the center, or midplane, of a torus. Select a torus.  Center Point of Sphere. Creates a work point at the center of a sphere. Select a sphere.
Center Point of Sphere. Creates a work point at the center of a sphere. Select a sphere.
Create a Grounded Work Point in a Part
To create a grounded work point, you must specify the point’s X, Y, and Z coordinates. The point remains fixed in space regardless of changes to model geometry. In-line work features are not available for grounded work points.
- On the ribbon, click 3D Model tab
 Work Features panel
Work Features panel  Grounded Point
Grounded Point  .
. - Click a work point, midpoint, or vertex.
A pushpin cursor symbol indicates the selection is grounded and the 3D Move/Rotate tool displays with its axes aligned with the principal axes of the part.
- Click or drag an axis or center of the tool, then enter values in the 3D Move/Rotate dialog box and click Apply. Repeat until the X, Y, and Z coordinates are defined. Note: You can ground an associative work point, and then unground it if the point is not moved. If you move the point using the triad, you cannot change it back to an associative work point.
 Show Me How to Create a Grounded Work Point
Show Me How to Create a Grounded Work Point
Create a Grounded Work Point in an Assembly
- On the ribbon, click 3D Model tab
 Work Features panel
Work Features panel  Point
Point  .
. - Click geometry to position the work point.
- In the browser, right-click the work point symbol and choose Grounded.