Use these options to set what happens when you select File > Import. See also Import files.
General options
- Group
-
Specifies whether the imported objects are grouped under a single transform when you import the file. Grouping makes it easier to work on the nodes of imported objects. The default is off.
- Remove duplicate shading networks
-
This setting prevents the duplication of geometry and shading networks if you import a file more than once into Maya.
- File type
-
Select from the drop-down list the file type you are importing. If you aren’t sure what type of file you are importing, you can select Best Guess.
Depending on the file type you select, various file type specific options may be displayed.
Playback options
- Always Override if Scene is Empty
- This setting is active by default if the scene is empty, and all timing options in the scene (framerate, animation range, animation playback range) are replaced by the settings in the incoming, imported file. If the scene is already populated, this option is automatically disabled so that the Framerate Import section becomes active, letting you choose what playback elements you want to import or override.
- Framerate Import
- These options let you choose how Maya LT treats imported framerates.
-
- Maintain Original
- Imposes the Maya scene framerate on the imported file.
- Override to Match Source
- Replaces the Maya scene framerate with the framerate of the imported file.
-
Note: When you import a framerate, keys are placed absolutely on the Timeline. If you import into a scene that has a different frame rate from your imported scene, you may encounter fractional values, which are represented by an asterisk.
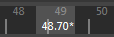
This also occurs when the Time Slider preferences Snap to Whole Frames option is disabled.
- Animation Range
- Choose a setting to specify whether to import the time and play range of the imported file, or impose the ranges used in the current Maya scene.
-
- Maintain Original
- Imposes the playback and time range of the current Maya scene onto the imported file.
- Override to Match Source
- Replaces the current Maya scene playback and time range with the playback and time range of the imported file.
- Combine to Include Source
- Incorporates both the Maya scene's ranges and the ranges of the imported file to create a hybrid range that can contain all timings. For example, if you import a scene with a animation range of 10 to 100 into a Maya scene with a range of 0 to 120, this setting creates a animation range of 0 to 120 so that it can include both timings.

Namespace Options
- Use namespaces
-
When you reference or import a scene with Use namespaces on, Maya creates a new namespace that contains the referenced data. Turning on Use namespaces ensures that all nodes are uniquely named. See Namespaces and Create namespaces when referencing or importing.
Tip:Before referencing a file, make sure that the renaming prefix contains no invalid characters.
The currently set namespace is indicated in the Namespace Options section by the
 icon. Namespaces that are parents of the currently set namespace are indicated by an
icon. Namespaces that are parents of the currently set namespace are indicated by an
 icon. You can set the current namespace in the
Namespace Editor by clicking
Set Current. See
Namespace Editor Overview and
Edit namespaces.
icon. You can set the current namespace in the
Namespace Editor by clicking
Set Current. See
Namespace Editor Overview and
Edit namespaces.
Namespaces do not effect selection, the DAG, the Dependency Graph, or any other aspect of Maya.
- Use selected namespace as parent and add new namespace (file name)
-
Specifies that the referenced file name is added to the beginning of object namespace.
For example, if you are referencing or importing a scene named foo.ma that contains an object named ball, its namespace is foo:ball.
- Use selected namespace as parent and add new namespace string:
-
Specifies that a text string is added to the beginning of the object namespace. Type the string in the field that appears.
- Merge into selected namespace and rename incoming objects that match
-
Merges the object's namespace wih an existing, selected namespace.
If duplicate namespaces occur, the namespaces are merged and duplicate object names are incrementally suffixed with a number. Use this option to avoid an accumulation of new namespaces each time your referenced or imported objects have the same namespace.