Correct a condition in which the cant region of one curve overlaps with the cant region of an adjacent curve.
Overlapping cant curves may be resolved manually, by either changing the chainage values of the overlapping chainages, or deleting critical chainages.
Overlapping cant curves may also be resolved automatically, either during the cant calculation or after the calculation is complete. When cant overlap is automatically resolved, the solution depends on whether the overlapping curves are compound or reverse.
Overlapping Compound Curves
In compound curve cases, overlapping critical chainages are deleted, and applied cant continues from one curve to the next.
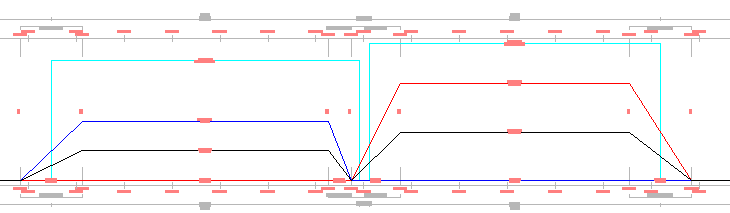
In the following example, the End Level Rail of first curve overlaps with the Begin Level Rail of the second curve. The  is displayed in the cant view at the location of overlap.
is displayed in the cant view at the location of overlap.
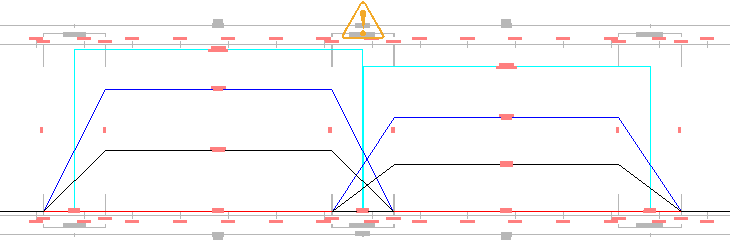
When the  is clicked, the Overlap Detected task dialog box is displayed. When “Automatically resolve overlap” is clicked, the overlapping End Level Rail and Begin Level Rail chainages are removed from the cant view and the tabular editor, and the applied cant transitions from the first curve to the second curve.
is clicked, the Overlap Detected task dialog box is displayed. When “Automatically resolve overlap” is clicked, the overlapping End Level Rail and Begin Level Rail chainages are removed from the cant view and the tabular editor, and the applied cant transitions from the first curve to the second curve.
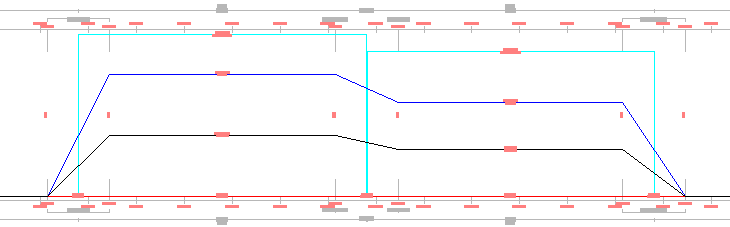
Overlapping Reverse Curves
In the following example, the End Level Rail of the second curve overlaps with the Begin Level Rail of the first curve. The  is displayed in the cant view at the location of overlap.
is displayed in the cant view at the location of overlap.
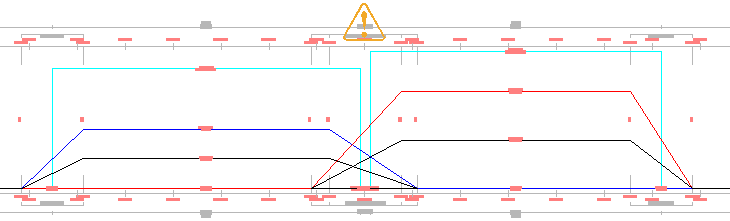
When the  is clicked, the Overlap Detected task dialog box is displayed. When “Automatically resolve overlap” is clicked, the chainage at which critical chainages overlap is located, the chainage value is applied to both critical chainages, and then the Applied Cant value is changed to zero at both critical chainages.
is clicked, the Overlap Detected task dialog box is displayed. When “Automatically resolve overlap” is clicked, the chainage at which critical chainages overlap is located, the chainage value is applied to both critical chainages, and then the Applied Cant value is changed to zero at both critical chainages.
After overlap has been resolved, the shared chainage value can be manipulated separately using either the tabular editor or grips in the cant view.