The HI Solver is a history-independent solver that doesn't rely on the calculations from previous frames for the IK solution, so it is fast to use no matter the length of your animation. The history-independent solver uses a goal to manipulate the end of the chain. It uses a preferred angle that specifies a preference regarding which direction the link will rotate: positive or negative. The preferred angle can also be considered as the initial angle; that is, the angle at which the link was rotated at the time the solver was applied.
The IK solution takes place in a plane, known as the solver plane. The angle of the solver plane is controlled by a parameter called the swivel angle.
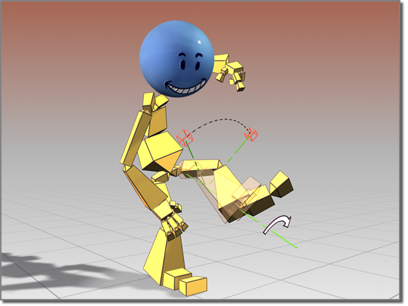
Changing the swivel angle
The angle of the solver plane is actually calculated in one of two coordinate systems: the Start Joint Parent space or the IK Goal Parent space. World space is not an explicit option; however, you can easily configure the IK chain to work in world space by choosing the IK Goal Parent option and making sure that the IK goal is unlinked (that is, has no hierarchical parent). In this case, the IK goal’s parent is the world, and therefore, the solver plane will be computed in world space.
The swivel angle is animatable. You can adjust it directly, or with a manipulator. Or you can target the swivel angle to a object and animate that to affect the swivel angle. These parameters are on the IK Solver Properties rollout.
The HI Solver is designed to let the animator jump back and forth between forward and inverse kinematics quickly and conveniently, with tools to automatically enable IK and snap the goal to the end effector.
Procedures
To turn off IK on a chain:
-
 Select the goal of a chain with an HI Solver.
Select the goal of a chain with an HI Solver. - On the
 Motion panel
Motion panel  IK Solver rollout, turn off Enabled.
IK Solver rollout, turn off Enabled. IK is now off, so you can select and rotate any of the objects in the chain. Turning IK on and off is animatable using the Auto Key button.
To mix IK and forward kinematics (FK) in a single animation track:
- Apply an HI IK Solver to a hierarchy or bone system.
- Turn on
 and move the time slider ahead in time.
and move the time slider ahead in time. -
 Select the goal of the IK Chain, and open the
Select the goal of the IK Chain, and open the  Motion panel.
Motion panel. -
 Move the goal to animate the IK chain with Inverse Kinematics.
Move the goal to animate the IK chain with Inverse Kinematics. - Advance the time slider again.
- On the IK Solver Rollout, turn off Enabled and IK for FK Pose.
-
 Rotate the root. The entire hierarchy rotates freely. You are now adding keyframes using forward kinematics.
Rotate the root. The entire hierarchy rotates freely. You are now adding keyframes using forward kinematics.
To match the goal and the end effector positions:
- If the goal and end effector become separated, click IK/FK Snap and the goal will move to match the end link of the chain.
- If AutoSnap is turned on, clicking the goal will automatically perform the snap action, matching the goal and end effector positions.
Interface
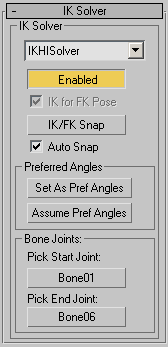
IK Solver group
The items in this group provide the ability to set the start and end points of the selected HI IK solver chain. There are also controls in this rollout that allow you to use IK manipulation to create forward kinematic rotational keyframes on the hierarchy objects, and there are buttons to align the goal and the end effector.
- Solver drop-down list
- Choose between the HI IK Solver and the IK Limb Solver here. Any HI IK plug-in solver present at startup will appear in this list, as well.
- Enabled
- Turns IK control of the chain on and off.
The HI IK Controller has an FK subcontroller. When Enabled is selected, the FK subcontroller values are overwritten by the IK controller. When Enabled is turned off, the FK values are used. You can animate Enabled On and Off.
Use this to turn off the chain control by the goal, when you want to do forward rotations.
- IK for FK Pose
- Lets you turn on IK in middle of FK manipulation. When Enabled is off and IK for FK Pose is on, moving the goal will turn on IK automatically in the middle of an FK manipulation. The result of this is that all the FK subcontrollers receive values from the IK solution. Keys are placed on the hierarchy objects or the bones, not on the goal. When both Enabled and IK for FK Pose are turned off, moving the goal does not affect the chain at all.
- IK/FK Snap
- Performs an IK snap when in FK mode, and an FK snap in IK mode.
IK Snap If the goal has moved away from the end of the chain, clicking IK/FK Snap moves the goal to coincide with the end link position.
FK Snap The values of FK subcontrollers are suppressed by the solution of IK when IK is on (Enabled is on). Their values don't always correspond to the current pose of the chain. If you turn off Enabled, the values of FK subcontrollers will suddenly take over. This can cause the chain to jump. FK Snap, before Enabled is turned on, forces the FK subcontrollers to assume values from the current pose (which is determined by the IK.) This eliminates the jump in the chain's animation.
- Auto Snap
-
When Auto Snap is on, 3ds Max automatically applies an IK/FK snap before you turn Enabled on or off. If Auto Snap is not on, you need to click IK/FK Snap before toggling Enabled, otherwise the chain will jump.
Preferred Angles group
- Set As Pref Angles
- Sets the preferred angle for each bone in the HI IK chain. The current parent-space rotation of each bone is placed into its X, Y, and Z Preferred Angle rotation channels as seen in the Rotational Joint rollout of the Hierarchy|IK panel. This is useful for establishing a perfect match frame when transitioning between forward and inverse kinematics.
- Assume Pref Angles
- Copies the X, Y, and Z preferred angle channels of each bone and places them into its FK rotation subcontroller. This essentially performs the inverse operation of the Set As Pref Angles function.
Bone Joints group
Allows you to change the ends of the IK chain.
- Pick Start Joint
- Defines one end of the IK chain. Select from the viewport or by name (press H).
- Pick End Joint
- Defines the other end of the IK chain. The direction of the chain is defined by the hierarchy, not by Start and End Joint. Select from the viewport or by name (press H). Warning: If you change the Start or End Joints so the IK Limb Solver so there are more than two bones between the start and end, the solver will not work. Moving the IK goal does not affect the bones.Tip: The order of the hierarchy determines the direction of the chain. You cannot reverse the direction of the chain by picking Bone 10 as the start and Bone 1 as the end.