You can use a bitmap file or procedural map to alter the intensity of specular highlights, based on the intensity of the bitmap. White pixels in the map produce full specular highlights. Black pixels remove the specular highlights completely, and intermediate values reduce the specular highlights accordingly.
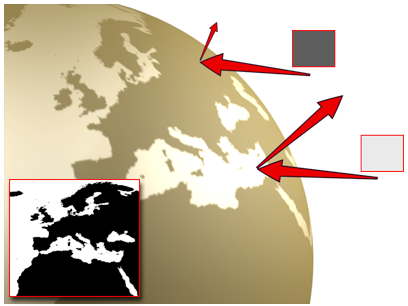
Using a map for the specular level: The sea is more reflective than the land.
The specular level component is different from specular color. Specular level affects the intensity of highlights, while specular color alters the color of highlights.
A specular level is generally most effective when you assign the same map to both Specular Level and Glossiness. (On the Maps rollout for a Standard or Raytrace material, you can do this by dragging from one map button to another; in the Slate Material Editor, you can wire a single map node to both components.)
Procedures
To use a Specular Level map:
- Click the map button for the Specular Level value.
3ds Max opens the Material/Map Browser.
- Choose from the list of map types, and then click OK.
(If you choose Bitmap as the map type, 3ds Max opens a file dialog that lets you choose the image file.)
- Use the map controls to set up the map.
Alternatively, you can use the ![]() Slate Material Editor to wire a map node to the Specular Level component.
Slate Material Editor to wire a map node to the Specular Level component.