3ds Max gives you a wide variety of options for designing materials. If you’re new to designing and using materials, read these topics for a general idea about working with materials, and what the most important options are.

Materials make objects look more convincing.
Workflow Outline
In general, when you create a new material and apply it to an object, you follow these steps:
- Choose the renderer you plan to use, and make it the active renderer.
It is a good idea to design materials with a particular renderer in mind, as the materials available depend on the renderer.
- Choose the material type.
- When you have decided on a material type, open the Slate Material Editor.
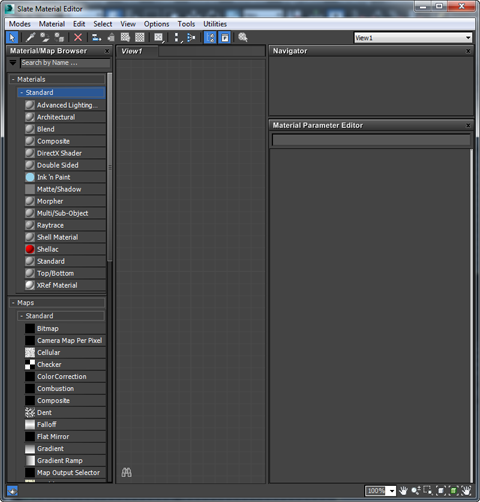
Slate Material Editor window
Left: Material/Map Browser panel
Middle: The active View (you can set up more than one View)
Lower right: Parameter Editor panel
- Drag a material of the type you want from the Material/Map Browser panel to the active View.
3ds Max displays the material as a node in the active View.
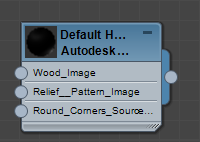
Example of a material node
- Double-click the material node to display its parameters in the Parameter Editor panel.
- Use the Parameter Editor to enter settings for the various material components: diffuse color, glossiness, opacity, and so on.
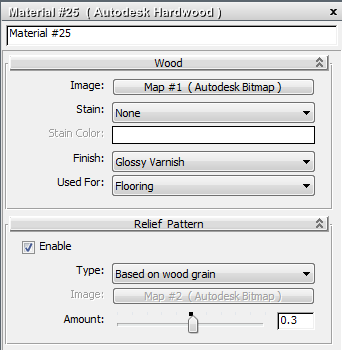
Material parameters in the Parameter Editor
(Double-click a node to display the node’s parameters)
- Assign maps to the components you want to map, and adjust the map parameters.
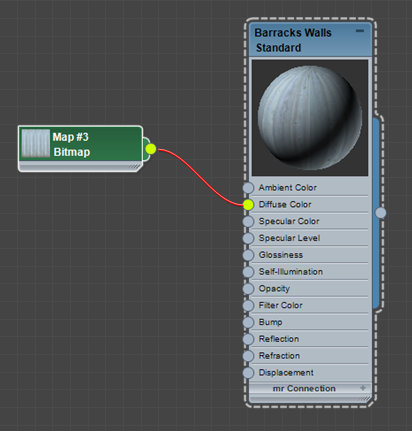
You assign a map to a material by “wiring” the map and material nodes together.
- On the Slate Material Editor toolbar, click
 (Assign Material To Selection) to apply the material to the object.
(Assign Material To Selection) to apply the material to the object.
- Also on the Slate Material Editor toolbar, if the material is mapped, turn on
 (Show Shaded Material in Viewport) so you can view the mapping interactively.
(Show Shaded Material in Viewport) so you can view the mapping interactively.
- If necessary, adjust the UV mapping coordinates in order to orient maps with objects correctly.
- Save the material.