On the Surface Parameters rollout, you control smoothing of the surface of the loft as well as designate if texture mapping is applied along the loft object.
Interface
Smoothing group

Left: Smoothing the length
Right: Smoothing the width
Rear: Smoothing both length and width
- Smooth Length
- Provides a smooth surface along the length of the path. This type of smoothing is useful when your path curves or when shapes on the path change size. Default=on.
- Smooth Width
- Provides a smooth surface around the perimeter of the cross-section shapes. This type of smoothing is useful when your shapes change the number of vertices or change form. Default=on.
Mapping group
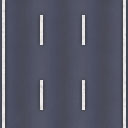
Bitmap used to create the lines on the road

Mapped roadway showing U and V dimensions for the loft
- Apply Mapping
- Turns lofted mapping coordinates on and off. Apply Mapping must be on in order to access the remaining items.
- Real-World Map Size
- Controls the scaling method used for texture mapped materials that are applied to the object. The scaling values are controlled by the Use Real-World Scale settings found in the applied material's Coordinates rollout. Default=off.
- Length Repeat
- Sets the number of times a map repeats along the length of the path. The bottom of the map is placed at the first vertex of the path.
- Width Repeat
- Sets the number of times a map repeats around the perimeter of cross-section shapes. The left edge of a map is aligned with the first vertex of each shape.
- Normalize
- Determines how path vertex spacing affects a map along both the path length and shape width. When on, vertices are ignored. Map coordinates and Repeat values are applied evenly along the length of the path and around the shapes. When off, major path divisions and shape vertex spacing affects map coordinate spacing. Map coordinates and Repeat values are applied proportionally according to the path division spacing or shape vertex spacing.

Before and after applying Normalize to loft
Materials group
- Generate Material IDs
- Creates Material IDs during the loft process.
- Use Shape IDs
- Offers the choice of using the spline material IDs to define the material IDs. Note: Prior to version 3 of 3ds Max, splines could not hold material IDs.Note: Shape IDs are inherited from shape cross sections, not from the path spline.
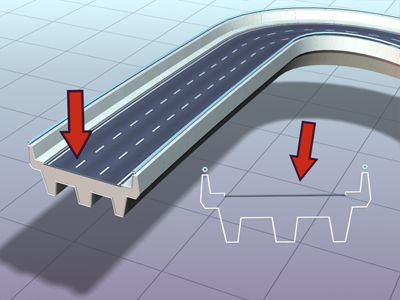
Shape material IDs used to give the roadway two materials: concrete for supports and railings, asphalt with white lines for the traffic lanes
Output group
- Patch The lofting process produces a patch object.
- Mesh The lofting process produces a mesh object. This is the default, and was the only output type available with Loft in versions prior to version 3 of 3ds Max.
You can also create NURBS objects from lofting by choosing Convert To: NURBS from the modifier stack right-click menu.