VRED NURBS Analysis diagnostic shader
Sends the current model to VRED NURBS Analysis to perform ray tracing directly on the NURBs surfaces.

You can display different types of virtual lines on the objects in the scene to examine the continuity of surfaces.
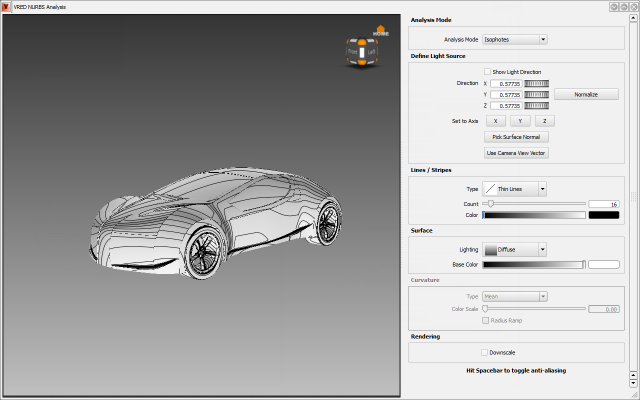
To analyze surfaces in VRED NURBS Analysis
-
Select the surfaces you want to analyze.
-
In the Diagnostic Shade window, click the VRED NURBS Analysis
 diagnostic shader. VRED NURBS Analysis opens.
diagnostic shader. VRED NURBS Analysis opens. -
Select an Analysis Mode and set options.
-
To center the all geometry in the scene in the view (look at), press
 +F
+FTo center selected geometry in the view, select the geometry (
 -click) and press F.
-click) and press F.To toggle anti-aliasing on and off, press the spacebar.
VRED NURBS Analysis Options
Analysis Mode
Activate Surface Analysis
Projects lines on the objects in the scene for analyzing the quality of surfaces.
Analysis Mode
Select the type of lines to display for analysis:
Isophotes – Displays isophotes (lines of equal brightness on the surface). With isophotes you can determine whether a surface is continuous in position, tangency, or curvature. The surface is assumed to be perfectly diffuse reflecting. It is lit from both sides by a directional light emitting parallel light beams. You can set the direction of the light source. The isophote lines are view-independent meaning that the lines do not change when moving the camera (except when using the option Use Camera View Vector).
Highlight Lines – Displays locations on the surface where the extended surface normals intersect the light lines. Highlight lines are view independent.
Reflection Lines – Displays reflections of light lines on the surface. Reflection lines are view independent.
Both Highlight Lines and Reflection Lines need light lines to be defined as a kind of virtual light source. You can choose between two different shapes on which the light lines appear.
Longitudinal Lines on a Sphere – The lines are meridians on a sphere (lines from pole to pole) which encloses the scene and is of infinite size. You can set the axis of the sphere.
Parallel Linear Lines on a Plane – The lines are parallel and straight on a plane. You can set their position and rotation.
Curvature (NURBS only) – Color-codes the curvature of the surfaces.
Define Light Source
Not applicable to Curvature (NURBS only) analysis mode.
For Isophotes
Show Light Direction
Displays the light direction as an orange arrow in the render view. You can change the light direction by  -dragging the rotation manipulator or by entering precise X, Y, Z direction values. The translation manipulator does not change the direction of the light and therefore does not affect the isophotes.
-dragging the rotation manipulator or by entering precise X, Y, Z direction values. The translation manipulator does not change the direction of the light and therefore does not affect the isophotes.
Direction
Change the direction of the light by setting X, Y, and Z coordinates.
Normalize
Scales the direction vector to a length of 1.0.
Set to Axis
Sets the direction to X (1, 0, 0), Y (0, 1, 0), or Z (0, 0, 1).
Pick Surface Normal
Enters a mode where you can pick a surface normal as the light direction, sphere axis, or plane normal, depending on which analysis mode is selected.
-
 +
+  to pick a surface normal.
to pick a surface normal. - To exit the mode, click the button again.
Use Camera View Vector
Uses the current camera view vector for the direction of the light. To select a different light direction, click the button again.
For Highlight/Reflection Lines with Longitudinal Lines on a Sphere
Show Sphere with Light Lines
Displays the light sphere with its light lines in the render window.
The sphere used for mapping the lines on the surfaces is of infinite size.
You can change the axis of the sphere by  -dragging the rotation manipulator.
-dragging the rotation manipulator.
Sphere Rotation
Change the direction of the light by setting X, Y, and Z coordinates.
Set to Axis
Sets the direction to X (1, 0, 0), Y (0, 1, 0), or Z (0, 0, 1).
Pick Surface Normal
Enters a mode where you can pick a surface normal as the light direction, sphere axis, or plane normal, depending on which analysis mode is selected.
-
 +
+  to pick a surface normal.
to pick a surface normal. - To exit the mode, click the button again.
For Highlight/Reflection Lines with Parallel Linear Lines on a Plane
Show Plane with Light Lines
Displays the light sphere with its light lines in the render window.
The sphere used for mapping the lines on the surfaces is of infinite size.
You can change the axis of the sphere using the rotation manipulator.
Light Plane Origin
Set coordinates of the origin of the light plane.
Light Plane Rotation
Specify the number of degrees to rotate the plane around the X, Y, and Z axes.
Lines Spacing
Specify the spacing between the lines on the plane. The default is 10.00.
Limited Lines Length
Limits the length of the lines to the number you specify. The default is 1000.00.
Pick Surface Normal
Enters a mode where you can pick a surface normal as the light direction, sphere axis, or plane normal, depending on which analysis mode is selected.
-
 +
+  to pick a surface normal.
to pick a surface normal. - To exit the mode, click the button again.
Lines / Stripes
Not applicable to Curvature (NURBS only) analysis mode.
Type
Select the style of analysis line to display:
Thin Lines – Displays thin sharp lines.
Stripes – Displays stripes. You can modify the Sharpness and Thickness of the stripes.
Zebra – Uses a classical zebra pattern.
Count
The number of isoline highlight bands on the surface.
Color
The color of the highlight bands. Click to open the Choose a Color dialog box and select a color.
Surface
Not applicable to Curvature (NURBS only) analysis mode.
Lighting
Select the surface lighting to render the surface:
Ambient – The surfaces are displayed single-colored. The color is defined by Base Color.
Diffuse – The surfaces are assumed to be diffuse. Set the diffuse reflection color using Base Color.
Phong – The surfaces are lit with the phong lighting model. You can use Base Color to set the diffuse reflection color, the glossy reflection color using Glossy Color, and Roughness.
NURBS UV – Show the parameterization of NURBS surfaces. Triangle meshes are displayed in Ambient mode.
Base Color
The color of the surface. Click to open the Choose a Color dialog box and select a color.
Curvature
Applicable only to Curvature (NURBS only) analysis mode.
Type
The method of calculating curvature on the surface. Mean averages the two principal curvatures at each point on the surface.
Color Scale
Scales the radius ramp to show finer details of curvature variation.
Radius Ramp
Select this option to show the range of colors that will be applied to the curvature map (and their corresponding curvature radius values).
If the +/- band is set to 0.0, the curvature map is relative, and the ramp colors, from left to right, represent increasing curvature values. (The colors are not associated with specific values.)
If you adjust the Color Scale, the radius ramp updates interactively.
Rendering
Downscale
Select this option to turn off anti-aliasing. Press the spacebar to toggle anti-aliasing on and off.