Creates a shape definition based on selected objects.
Shapes display relatively simple geometry quickly. The size of a single shape is limited to 2200 bytes of data. If you create a shape that exceeds that limit, MKSHAPE creates complex geometry shapes to form a single shape. To list these "sub-shapes," start the SHAPE command, specify the ? option, and enter *.
Neither points nor zero-length line segments are used by MKSHAPE. However, you can get the effect of a point by drawing a very short line segment and using a resolution that is high enough to prevent the segment from being converted to a 0 length. If the short segment does not appear in the shape that results, try again, using a higher resolution value or a longer line segment.
Use the SHAPE command to place shapes in your drawing.
If you load two or more shape files containing one or more shapes with the same shape definitions, the shape definition from the first file loaded is used.
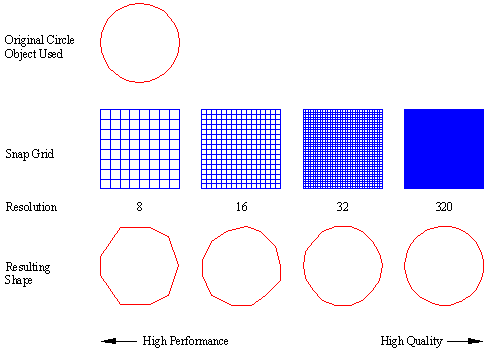
Resolution Values
Large resolution values create shapes that are more accurate representations of the selected geometry. However, large resolution values tend to create shapes that contain more coordinate data and place a higher processing burden on AutoCAD during regeneration. Conversely, small resolution values create less accurate shapes that are more quickly processed by AutoCAD. You can experiment with different resolution values to find the balance of performance and accuracy that best fits your needs. Note that the resolution value is rounded off to the nearest factor of 8 and cannot exceed 32,767. The following graphic shows how the resolution factor affects the resulting shape's appearance:
Command: MKSHAPE
Select a ".SHP" file: <drawing.shp>: Enter a shape file name where you would like to save your shape
Enter the name of the shape: Specify the shape name
Enter resolution <124>: Enter a number for the resolution value
Insertion base point: Specify a point
Select objects: Select line, polyline, arc, circle, and/or ellipse objects (for definition purposes, the selected objects are treated as though they are of a continuous linetype)
Example
Create a switch shape.
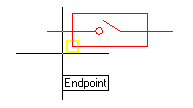
After specifying the file name and shape name, select the insertion point for the shape:
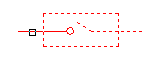
Next, select the objects to be used to define the shape:
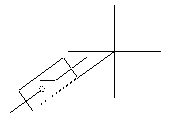
The shape can now be placed using the SHAPE command:
File
mkshape.lsp