From the command line, creates copies of objects arranged in a pattern.
Maintains legacy command line behavior for creating nonassociative, 2D rectangular or polar arrays.
- Most AutoCAD-based products: The limit is set by the MAXARRAY setting in the registry. To reset the limit to 200,000, for example, enter (setenv "MaxArray" "200000") at the Command prompt.
- AutoCAD LT: You can change the maximum number of array elements by setting the MaxArray system registry variable using the SETENV command.
The following prompts are displayed.
Select objects
Select one or more objects to use as a basis for the array.
Type of array
Specifies whether to create a rectangular or polar array.
Rectangular
Creates an array of rows and columns of copies of the selected objects.
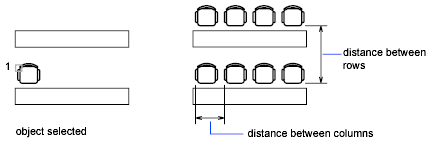
The selected object, or cornerstone element, is assumed to be in the lower-left corner, and generates the array up and to the right.
- Number of rows (---)
- Specifies the number of rows using a nonzero integer. If you specify one row, you must specify more than one column and vice versa.
- Number of columns (|||)
- Specifies the number of columns.
- Distance between rows or specify unit cell
- Specifies the distance between rows, including the length of the object to be arrayed.
To add rows downward, specify a negative value for the distance between rows.
To specify the distance between rows and columns at the same time, specify two sets of coordinates or drawing locations that represent the opposite corners of a rectangle.
- Distance between columns (|||)
- Specifies the distance between columns.
To add columns to the left, specify a negative value for the distance between columns.
Rectangular arrays are constructed along a baseline defined by the current snap rotation. This angle is normally 0, so the rows and columns are orthogonal with respect to the X and Y drawing axes. Use the Rotate option of the SNAP command to change the angle and creates a rotated array. The SNAPANG system variable stores the snap rotation angle.
Polar
Creates an array by copying the selected objects around a specified center point.
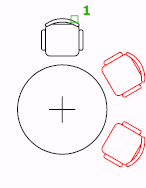
In a polar array, the reference point of the last object in the selection set is used for all objects. If you defined the selection set by using window or crossing selection, the last object in the selection set is arbitrary. Removing an object from the selection set and adding it back forces that object to be the last object selected. You can also make the selection set into a block and replicate it.
The prompt values you enter determine whether the array configuration is based on the number of items or the angle that is filled by the arrayed items.
- Center point of array
- Specifies the central location for the array.
- Base
-
Specifies a new reference (base) point relative to the selected objects that will remain at a constant distance from the center point of the array as the objects are arrayed.
- Number of items in the array
- Specifies the total number of items to be arrayed around the center point.
If you do not enter a value, the array is based on the Angle to Fill and Angle Between Items values.
- Angle to fill (+=ccw, -=cw) (+=ccw, -=cw)
- Specifies the included angle between the base points of the first and last arrayed objects. Enter a positive number for a counterclockwise rotation or a negative number for a clockwise rotation.
- Angle between items (+=ccw, -=cw) (+=ccw, -=cw)
- Specifies the included angle between objects, based on the center point of the array and the base points of the arrayed objects. Enter a positive number for a counterclockwise rotation or a negative number for a clockwise rotation. Note: To display this option, press Enter at the Number of items prompt or enter 0 at the Angle to fill prompt.
- Rotate arrayed objects?
- Controls whether items are rotated as they are arrayed. Enter Yes or No.