3D Cartesian coordinates specify a precise location by using three coordinate values: X, Y, and Z.
Entering 3D Cartesian coordinate values (X,Y,Z) is similar to entering 2D coordinate values (X,Y). In addition to specifying X and Y values, you also specify a Z value using the following format:
X,Y,Z
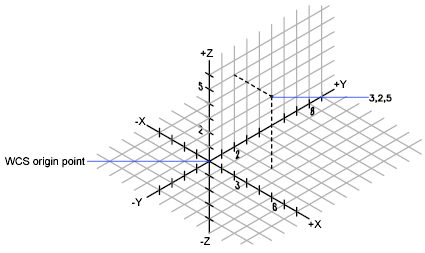
In the illustration below, the coordinates 3,2,5 specifies a point 3 units along the positive X axis, 2 units along the positive Y axis, and 5 units along the positive Z axis.
Use Default Z Values
The initial default value of Z in any drawing is 0. When you specify a point, the Z value is retained as the default. For example, if you enter the following coordinates for a line
From point: 0,0,5
To point: 3,4
both endpoints of the line will have a Z value of 5.
Absolute and Relative Cartesian Coordinates
As with 2D coordinates, you can enter absolute coordinate values, which are based on the origin, or you can enter relative coordinate values, which are based on the last point entered.
To enter relative coordinates, use the @ sign as a prefix. For example, @1,0,0 specifies a point 1 unit in the positive X direction from the previous point. To enter absolute coordinates, no prefix is necessary.