When you select a supply system to size, the plumbing module highlights all plumbing lines, fittings, and fixtures connected to, and downstream from the specific plumbing line you select. It then identifies the longest run in the system by calculating the equivalent plumbing line lengths of all connected fixtures, fittings, and valves.
The longest run is defined as the longest run in an entire network of connected runs in a system. It is the main run used to determine the sizing requirements. Typically, it connects the booster pump to the limiting fixture (the fixture located at the highest elevation in the building).
The Calculations for the Longest Run section of the Size Supply Plumbing Line dialog box contains the non-editable, calculated values for the longest run.
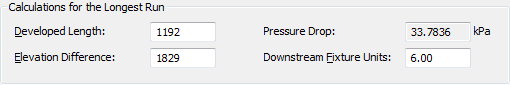
Calculations for the Longest Run section
Developed Length
Developed Length is the length of the longest run, including the equivalent length of the fittings. The plumbing module passes through the entire plumbing system to obtain the plumbing line length of each fixture. The program then refers to the supply plumbing line sizing table (pipe sizing table) that you selected. The sizing table provides the equivalent plumbing line length values associated with each fitting and valve on the run, so that these values can be included in the calculation. The run that has the highest value for the equivalent plumbing line length is considered to be the limiting run, or the run that requires the most resistance.
Elevation Difference
Elevation Difference is the difference in height between the highest elevation and the lowest elevation in the run. For example, if the run is laid out from a fixture at an elevation of 2'-0" to the main run entering the building at an elevation of 6", then the difference in elevation is 1'-6".
Pressure Drop
Pressure Drop displays the loss of pressure between the limiting fixture and the source, typically a booster pump.
The pressure drop uses the calculated elevation difference, also known as head loss, and adds this value to the total friction loss in the limiting run.
The plumbing module uses the following formula to calculate this value:
Pressure Drop = Head Loss + Friction Drop
The formula is defined as follows:
- Pressure Drop is head loss plus friction drop.
- Head Loss is the elevation difference.
- Friction Drop is the friction loss for the limiting run.
To calculate the friction loss, the plumbing module uses the Hazen-Williams formula:
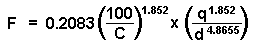
The Hazen-Williams formula is defined as follows:
- F is friction drop for the longest run per 100 feet (or per 100 meters) of pipe (plumbing line).
- C is the inside pipe roughness or friction loss coefficient. The default value is 100.
- q is the total flow of the downstream fixture units measured in gpm (or L/s).
- d is the inside diameter of the pipe.
Downstream Fixture Units
Downstream Fixture Units displays the calculated value of all connected fixtures in the selected system.
To calculate the downstream fixture units value, the plumbing module totals the required fixture units for all connected fixtures on the run that you select.