When you select a plumbing line in the supply run to size, you specify the point on the run at which the software calculates the flow rate, velocity, and plumbing line diameter. For example, to find the flow rate of the source, you would select the plumbing line closest to the booster pump.
The Calculations at Selected Component section of the Size Supply Plumbing Line dialog contains the non-editable, calculated values for the selected component.
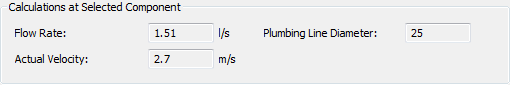
Calculations at Selected Component section
Flow Rate
Flow Rate represents the amount of fluid that travels through the plumbing line that you selected over a period of one minute. The plumbing module calculates the flow rate using the plumbing line diameter and friction loss values. The plumbing module estimates the flow rate using Hunter’s Curve (mixed), which takes into consideration fixtures that only periodically require a specific amount of flow. Therefore, the plumbing line is not sized based on the total amount of flow required by all fixtures, but rather on the expected flow based on the probability that each fixture is being used. The calculated value is then used as a basis for the Hazen-Williams formula. The result is the flow rate displayed in the Size Supply Plumbing Line dialog.
Following is the Hazen-Williams formula:
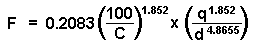
The Hazen-Williams formula is defined as follows:
- F is friction drop for the longest run per 100 feet (or per 100 meters) of pipe (plumbing line).
- C is the inside pipe roughness or friction loss coefficient. The default value is 100.
- q is the total flow of the downstream fixture units measured in gpm (or L/s).
- d is the inside diameter of the pipe.
Actual Velocity
Actual Velocity is the speed at which the fluid travels through the plumbing line you selected and is based on the calculated values for the plumbing line diameter and minimum friction loss.
The plumbing module uses the following formula to calculate the actual velocity:
V = Q/A
The formula is defined as follows:
- V is velocity.
- Q is flow rate.
- A is the inside cross-sectional area of the plumbing line.
The inside cross-sectional area is calculated as follows, where d is the inside diameter of the plumbing line.
Plumbing Line Diameter
Plumbing Line Diameter displays the diameter necessary to accommodate the flow rate and velocity of the selected plumbing line. The plumbing module estimates the size of each plumbing line at 8 feet per second.
The following information outlines how the plumbing line diameter is calculated:
- The plumbing module calculates the pressure available for friction loss throughout the supply system by subtracting Pressure at Source from Pressure of the Highest Fixture, minus Pressure Drop, minus Friction Loss-Water Meter.
- If the available pressure drop is insufficient, then the plumbing module increases the size of all the components in the run by one size (all sizes go up one plumbing line size) and recalculates Pressure Drop.
- If the Restrict Velocity option is enabled and the calculated actual flow velocity exceeds the restricted velocity, then the plumbing module increases the size of the run by one plumbing line size and recalculates Pressure Drop.
Once the plumbing module has found the correct plumbing line size, the corresponding standard nominal size is found from the calculated standard inside diameter. To view the size iterations used by the plumbing module, see the Standard Plumbing Line Sizing table in the following section.
Standard Plumbing Line Sizing Table
Use the following table as a reference for standard sizing calculations of plumbing lines. All values of d, the inside diameter of the pipe (plumbing line), are in inches and are based on a Schedule 40 Steel Pipe gauge. To size the plumbing line, the calculation rounds up to the nearest standard size. The plumbing module assumes that all plumbing lines being sized are similar to Schedule 40 Standard Steel Pipe when determining an inside diameter.
| If the nominal size is… | then the inner diameter is… |
|---|---|
| 0.125 | 0.269 |
| 0.25 | 0.364 |
| 0.375 | 0.493 |
| 0.5 | 0.622 |
| 0.75 | 0.824 |
| 1 | 1.049 |
| 1.25 | 1.380 |
| 1.5 | 1.610 |
| 2 | 2.067 |
| 2.5 | 2.469 |
| 3 | 3.068 |
| 3.5 | 3.548 |
| 4 | 4.026 |
| 5 | 5.047 |
| 6 | 6.065 |
| 8 | 7.981 |
| 10 | 10.02 |
| 12 | 12.000 |
| 14 | 13.250 |
| 16 | 15.250 |
| 18 | 17.250 |
| 20 | 19.250 |
| 22 | 21.250 |
| 24 | 23.250 |
| 26 | 25.250 |
| 28 | 27.250 |
| 30 | 29.250 |
| 32 | 31.250 |
| 34 | 33.250 |
| 36 | 35.250 |