How AutoCAD MEP 2022 toolset performs calculations to size plumbing lines.
- Determine the friction loss.
The plumbing module determines the friction loss of the run using the Hazen-Williams formula.
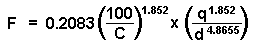
The Hazen-Williams formula is defined as follows:
- F is friction drop for the longest run per 100 feet (or per 100 meters) of pipe (plumbing line).
- C is the inside pipe roughness or friction loss coefficient. The default value is 100.
- q is the total flow of the downstream fixture units measured in gpm (or L/s).
- d is the inside diameter of the pipe.
- Calculate the change in elevation.
The plumbing module calculates the change in elevation for the limiting run by subtracting the value of the Highest Fixture from the Pressure at Source.
- Determine the total pressure drop.
The plumbing module determines the total pressure drop for the run as follows:
Total Pressure Drop = Friction Loss + Elevation Change
- Determine the available pressure for Friction Loss.
The plumbing module determines the pressure available for the Friction Loss by subtracting the Pressure at Source from the Pressure at the Highest Fixture, minus Pressure Drop, minus Friction Loss-Water Meter.
- Compare the Pressure Drop to the Pressure Available.
The plumbing module then compares the Pressure Drop to the Pressure Available. These values need to be equal to or greater than the available pressure. If the values do not match because the pressure available is insufficient, then the plumbing module increases the size of the run by one plumbing line size (all sizes go up one size) and recalculates the pressure drop.
- Display the results.
When the calculations are completed, the plumbing module displays the calculated values in the Size Supply Plumbing Line dialog.