Understand some essential settings for digital elevation models (DEM).
If you have a choice of source data for your existing ground surfaces, create grid surfaces rather than TIN (triangulated irregular network) surfaces when possible. The difference in system memory requirements is significant for large surfaces. As a general rule, a grid surface, such as a DEM, requires about one-sixth (17%) of the memory space required by the same surface in TIN format.
Exporting a DEM File
Autodesk Civil 3D enables you to export DEM files from a surface. At the time of export, you can expand the grid spacing to make the file smaller. Figure 3 shows the menu selection used to start the export process.
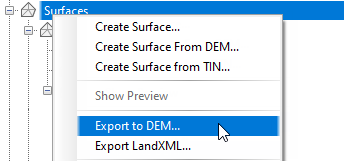
Figure 3: DEM file export
The Export Surface To DEM dialog box, shown in figure 4, is where you can set the grid spacing in the exported DEM file. A grid spacing of 2 covers a given area with one quarter the number of points required by a grid spacing of 1. Use a higher numeric setting here to create a DEM file that is smaller in size, and less detailed.
Determining Grid Point Elevation
An important export setting is the method for determining elevation at each point. You can choose to either sample the surface elevation at the grid point, or compute the average elevation from surrounding points. The latter method (averaging) is more time consuming. For greater efficiency, use the surface sampling option, as shown in figure 4.
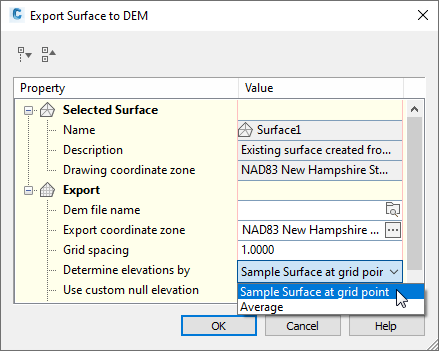
Figure 4: Optimizing settings for an exported DEM file