Mattes can be used for several purposes. For instance, use a matte to remove colour spill, hue shift an object in an image for artistic effect, or match colours in a specific range. Use mattes to define the range of colour you want to modify in the result clip.
You can generate up to three mattes using the Selective menu.
To generate a matte for selective colour correction:
- Enable Plot and then sample the image.
A black dot representing the sample appears on the hue cube. A red line also appears in the luma range and the sample is outlined in the 2D or 3D vectorscope. When you create the matte, you can modify the softness and tolerance boundaries to include or exclude the plotted colour.
- From the Work On box, select a selective (Sel 1, Sel 2, or Sel 3). With each selective, you define a range for a matte by selecting colours in the front clip.
- From the Selective View box that appears, select Sel.

The front clip is displayed as a greyscale image.
- Click one of the Define controls to set the initial softness and tolerance for the matte.
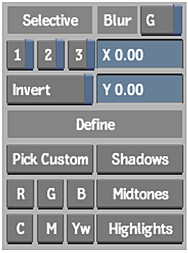
Click: To define: Pick Custom The tolerance range based on a sample from the image. You must drag the cursor over the image to define initial tolerance. R, G, B, C, M, or Yw The tolerance range based on the selected colour channel. For example, click Yw to use the yellow channel to set the tolerance. The luma range is set to default tolerance and softness values. Shadows, Midtones, Highlights The tolerance range based on the selected luma range. These buttons expand the tolerance and softness boundaries to include all ranges of colours in the image. The initial softness and tolerance is set for the matte. The range you use to define the matte becomes visible through the greyscale image. The unselected colours remain greyscale.

(a) Original colour visible through the greyscale display.
The Active button associated with the selective is enabled when you set the initial softness and tolerance. When an Active button is enabled, the selective's matte will be applied to the result clip. You can disable the Active button at any time if you do not want to apply this matte to the result clip.
Tip: To redefine a matte based on a different Define control, click the control you want to use. The matte is reset according to your selection. - Enable Tolerance and Softness.
The range of colour used to define the matte is shown on the hue cube with tolerance and softness indicators. The light grey outline shows tolerance and the black outline shows softness. When you define a matte with a luma range, it is shown in the luma range—the white line indicates the tolerance and the yellow line indicates softness.
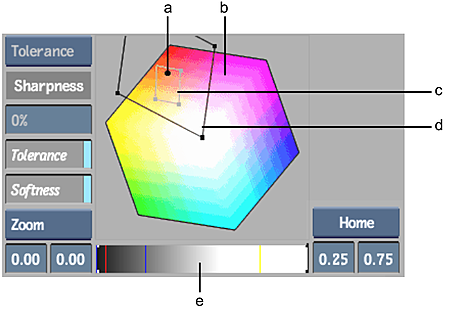
(a) Plotted colour (black dot) (b) Hue cube (c) Tolerance range (d) Softness range (e) Luma range
Tip: Select Home from the Frame Options box to reset the hue cube to its original size and position. - To view the matte while you refine it, select Matte from the Selective View box.

(a) Work On box (b) Selective View box
The matte appears in the image window. The black and grey areas of the matte can be colour corrected. The white areas will remain unaffected.
Tip: Select Matte view to output a matte for use in another tool in Batch or Batch FX. The selective must also be selected in the Work On box. - To refine the matte, do any of the following:
- Adjust softness and tolerance by selecting options from the Adjusting box and then sampling the result clip.
Select: To: Tolerance Add tolerance to the matte. +Softness Add softness to the matte. -Softness Remove softness from the matte. - Adjust softness and tolerance by selecting Move from the Move/Zoom box and then moving the handles of the tolerance or softness outlines on the hue cube. The Tolerance and Softness buttons must also be enabled.
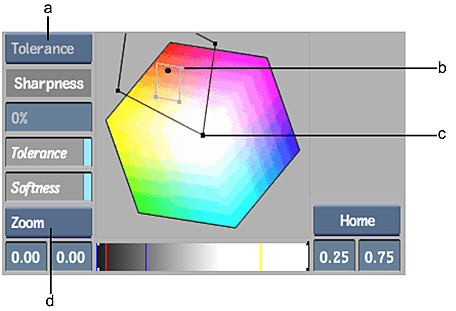
(a) Adjusting box (b) Tolerance handle (c) Softness handle (d) Move/Zoom box
Tip: You can zoom the hue cube by selecting Zoom in the Move/Zoom box and then dragging the cube. Alternatively, Ctrl+spacebar-drag to zoom. You can pan the hue cube by pressing spacebar and dragging.- Adjust the softness and tolerance in the luma range by dragging the Softness and Tolerance fields.

(a) Softness range (b) Low Softness field (c) Low Tolerance field (d) Low bracket (e) Tolerance range (f) Plot line (g) High bracket (h) High Tolerance field (i) High Softness field
When working with 16-bit floating point images, you can press spacebar to pan the gradient bar, and Ctrl+spacebar to zoom the gradient. Select Home from the Frame Options box to reset the gradient to the default 0:1 position. If you have softness or tolerance values out of the 0:1 range, select Autoframe from the Frame Options box to view the complete gradient range. Select Plot Colour from the Frame Options box to enlarge the gradient to include the plot and reference colours.
- If the matte appears grainy, drag the Sharpness field to adjust softness and reduce noise.
- To apply a Gaussian blur, enable G. To apply a box blur, disable G and set the width and height of the blur with the X and Y fields.
- To invert the matte, enable Inv Selection.
- Continue fine-tuning the matte until you are satisfied.
You can select the selective in the Work On box from any menu in the Colour Warper to perform advanced colour corrections on the range defined by the matte. You can also change the view in the Selective View box.
Tip: When you switch from the Selective menu to any other menu in the Colour Warper, Result appears in the Selective View box. Select Result to view the result clip.