Using the information from the analysis, you can modify components to eliminate the interference.
- On the ribbon, click
Inspect tab
 Interference panel
Interference panel  Analyze Interference .
Analyze Interference .
- In the Interference Analysis dialog box, click Define Set #1, and then select the first component or group of components to analyze in the graphics window or browser.
- Click Define Set #2, and then select the second component or group of components to analyze.
- Select Treat subassemblies as components to treat sub-assemblies as single components and ignore the interferences within the sub-assemblies.
- Click OK to check for interference.
- If interference is detected, the Interference Dialog box dialog box displays the following:
- The number of interferences detected and their total volume, and additional information about each interference. Double-click an entry in the list to zoom to the interference.
- Options to filter out the following interference types so that you can focus your attention on the information you need to analyze:
- General: Interferences that do not belong to any of the types below.
- Threads: Interference between 2 components, one of which is threaded.
If found, Matching Threads displays as an additional filter.
- Non-threaded Content Center parts: Interferences between 2 components one of which is from Content Center.
- AnyCAD reference components: Interferences within the AnyCAD reference component itself.
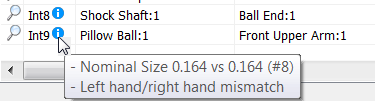
- Detailed information about the 4 types of mismatched thread interferences. Hover over the information tooltip to display the type of interference.
- Threaded components are misaligned.
- Thread designation doesn't match, including nominal diameter, pitch .
- Left/Right hand doesn't match.
- Thread depth mismatch indicates the external thread length and the internal thread depth do not satisfy the minimum thread engagement.
For example, interference is reported when the length of a component's external thread is shorter than the depth of the internal thread. The following illustration represents another example where minimum thread engagement is not met.

Note: The first set of numbers in the tooltip indicate Internal thread value. The second set indicate the External thread value. - Ignore and Un-ignore options. You can:
- Right-click an item and select to ignore the selected volume or ignore all interference volumes less than a selected value.
- Select or deselect the Ignored filter to show or hide the ignored interferences in the list.
Note: An ignored interference is displayed with a cross line.
- Right-click an ignored interference and select to Un-ignore the selected item, or Un-ignore all.

- Options to copy the values to the clipboard and print the list.
Note: The interference type is included in a new column called Note when you copy
 a thread interference value into Excel.
a thread interference value into Excel.
Tip: If you want to check all components for interference, use a crossing window to add all components to Set # 1 and then click OK to analyze.
Tip: By double clicking on a resultant interference, you can graphically focus on an individual interference region by zooming into a specified collision.