Use this option to define code parameters of a member type for the Italian CNR-UNI code. There are two ways to access this option:
- Click the New member type option in the Member Type dialog
- Click the Parameters button in the Definitions dialog dialog.
The following dialog displays:
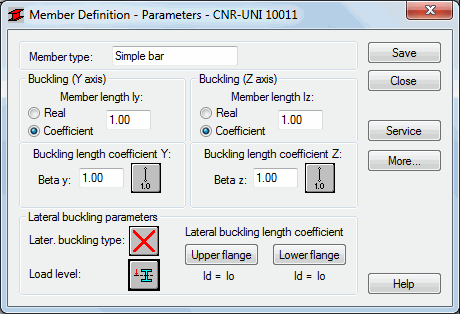
The Member Type field displays the name of the selected member type (enter the name of the defined bar type). The Buckling with respect to axis Y and Z fields displays the length of a member for the appropriate plane. There are two ways to define this length:
- Select the Real option, the introduced value is interpreted directly as member length
- Select the Coefficient option, the introduced value is interpreted as the coefficient by which the real member length should be multiplied to obtain the required value. For instance, introducing the value 0.25, means that the relevant member length equals 1/4 of the real length.
Choose the Coefficient option to define simultaneous members of different actual lengths, additional supports equally spaced, for example. Also, use the Coefficient option, if the set parameters are to be saved as a category. Introducing the value 1.0 guarantees that each member (defined using the category Ly) will have its actual length accepted.
The Member buckling length coefficients in both directions (Beta y and beta z) are described in the Buckling Length Coefficient dialog. The actual bar length (i.e. the sum of component member lengths) is entered automatically in the appropriate fields.
The Buckling length coefficient depends on the end-support condition of the bar nodes in the buckling plane. The Buckling length is also defined in the Buckling Diagrams dialog, opened by clicking the icon representing the selected buckling model type. After selecting a typical scheme, the coefficient value will be accepted or calculated automatically.
The icons in the dialog box are divided into two groups:
- The first group contains typical (code) methods of member support and corresponding values of buckling coefficients.
- The second group contains icons of options used for calculating buckling coefficient for columns of multi-story frames.
Buckling is always considered in calculations if a compression force appears in the member, even if it is negligible in comparison to the other internal forces. A separate analysis is not performed that would determine if buckling effects should be disregarded. To eliminate buckling effects from the calculations, the last icon must be chosen. If selected, buckling will be disregarded in the calculation process.
In the Lateral Buckling Parameter field select options used during the verification of the lateral buckling for the member: lateral buckling type, load level and the lateral buckling length coefficient. Clicking the appropriate icon opens the dialog for the definition of corresponding parameters.
The Lateral Buckling Type option defines the corresponding code lateral buckling parameters depending on the static pattern of the member. As required by the code, one of the patterns included in the code should be accepted. Patterns in the shape of icons mirror the appropriate items from the code. Select the last icon to exclude lateral buckling effects during calculations.
Lateral buckling calculations require you to provide for a bar the distance between sections blocked against twisting (lateral buckling length). It is necessary to distinguish two buckling lengths (for the upper and for the lower flange) as it is possible to attach the upper and lower flanges separately, which results in the appearance of different load cases of compression forces. You should provide the value of the coefficient by which the base bar length should be multiplied to obtain the lateral buckling length. The length IZ is taken as the base length. The coefficient value may be entered directly or by selecting the icon representing typical attachment case for which the coefficient will be automatically chosen.
Click the More button to open an additional dialog. You can then define the remaining bar type parameters described in the code as: Anet/Agross ratio.
Click the Service button to open an additional dialog. You can then define the parameters of bar type (limit displacements, initial deflection).
Click the Add button to add the bar type with a defined name and parameters to the list of previously defined steel member types.