Use this dialog to determine the appropriate distances between member sections protected against torsion according to the NBR 8800:2008 code.
Access
- Click Upper flange or Lower flange in the Member Definitions - Parameters dialog.
Dialog elements
To calculate the lateral buckling coefficient properly, it is necessary to define the lateral buckling length. The dialog contains typical methods of member support which determine appropriate values of lateral buckling length coefficients.
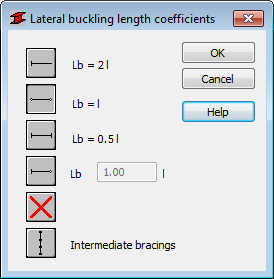
- Lateral buckling length coefficients
- Due to the possibility of supporting the upper or lower flange separately and the occurrence of compressive stresses in upper or lower flange for different load cases, two lateral buckling lengths are distinguished. There is a coefficient provided, by which the base member length should be multiplied to obtain lateral buckling length. As base length, the l length is assumed.
- Enter a coefficient value or choose an icon with typical support case to select the coefficient automatically.
- No lateral buckling

- Select this icon to ignore the lateral buckling effects during the calculation process.
- Internal bracings

- Opens the Internal bracings dialog, which allows you to define the parameters of lateral stiffening.
- This option allows you to consider bars with internal bracings during the calculations. Internal bracings include: lateral stiffening of the analyzed bars, or limiting the buckling length.