Robot can analyze various types of structures. These structures are listed in the following table, along with their coordinates system and their nodal degrees of freedom.
Open Structure Type dialog window, which selects a structure type to be created, using either method:
- Click Geometry menu > Structure Type.
- Click
 .
.
|
STRUCTURES |
COORDINATES |
NODAL DEGREES OF FREEDOM |
|---|---|---|
|
2D frames 
|
|
UX , UY , - , - , - , RZ , |
|
2D trusses 
|
|
UX , UY , - , - , - , - , |
|
Grillages 
|
|
- , - , UZ , RX , RY , - , |
|
3D trusses 
|
|
UX , UY , UZ , - , - , - , |
|
3D frames 
|
|
UX , UY , UZ , RX , RY , RZ, |
|
Plates 
|
|
- , - , UZ , RX , RY , - , |
|
Shells 
|
|
UX , UY , UZ , RX , RY , RZ, |
|
Plane stress structures 
|
|
UX , UY , - , - , - , - , |
|
Plane deformation structures 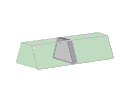
|
|
UX , UY , - , - , - , - , |
|
Axisymmetric structures 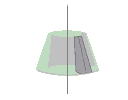
|
|
UX , UY , - , - , - , - , |
|
Volumetric structures 
|
|
UX , UY , UZ , - , - , - , |
 is not a structure type, but a template which facilitates defining this structure type. The available coordinates and nodal degrees of freedom for the building type are the same as the ones for shells.
is not a structure type, but a template which facilitates defining this structure type. The available coordinates and nodal degrees of freedom for the building type are the same as the ones for shells. See also:
 X, Y
X, Y  X, Y
X, Y  X, Y
X, Y 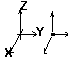 X, Y, Z
X, Y, Z 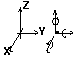 X, Y, Z
X, Y, Z 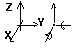 X, Y
X, Y 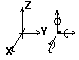 X, Y, Z
X, Y, Z