The SLS Parameters tab allows you to define parameters for the calculation of cracking and deflections of the Slab-shell structure.
Access
- Click
Design
 Required Reinforcement of Slab/Walls - Options
Required Reinforcement of Slab/Walls - Options  Code parameters to open the Slab and Shell Reinforcement Type dialog, and then click
Code parameters to open the Slab and Shell Reinforcement Type dialog, and then click
 .
.
- Click
 (Slab and Shell Reinforcement Type) to open the Slab and Shell Reinforcement Type dialog, and then click
(Slab and Shell Reinforcement Type) to open the Slab and Shell Reinforcement Type dialog, and then click
 .
.
Dialog elements
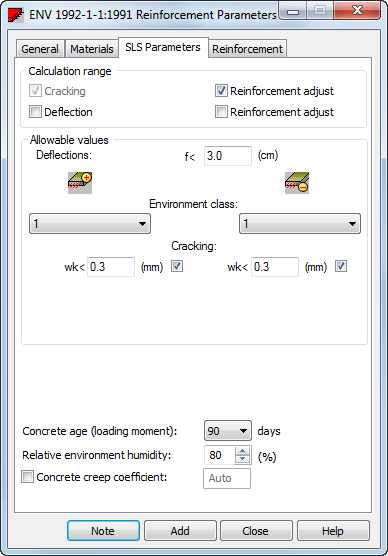
- Calculation range
-
Define the range of calculations in the Serviceability Limit State (SLS) while designing an RC slab (panel).
- Cracking. Calculations of the cracking width.
- Reinforcement correction (cracking). Automatic correction of cracking width by increasing reinforcement area.
- Deflection. Calculations of the RC slab deflection with cracking considered.
- Reinforcement correction (deflections). Automatic correction of deflections by increasing reinforcement area.
- Allowable values
-
You can define the allowable values of cracking width and/or of deflection. If these values are exceeded, the results table will report relevant information.
Cracking width is defined in two ways (separately for the top and bottom areas).
- Choose the environment class resulting in a cracking width in accordance with code requirements.
- Enter a value of cracking width. A change of the environment class has no effect on the adopted value of the cracking width.
If the Reinforcement correction option is selected, the defined values are also the limit values. Reinforcement area is increased for these values to be reached.
- Additional parameters
-
You can determine the ratio of variable loads to long-term loads.
-
Variable loads may be divided into short-term and long-term loads. The long-term to variable coefficient specified in the Ratio of loads is used to split variable loads into a short-term part and a long-term part according to the following formula.
variable load = (1 - c) * variable load + c * variable load = short-term load + long-term load,
where c is a coefficient of the participation of long-term loads in variable loads.
You can also specify:
- Concrete age (loading moment) is used in calculations of modulus of elasticity of the concrete.
- Environment humidity may also be entered.
- Concrete creeping coefficient The concrete creeping coefficient may be selected automatically in compliance with code requirements after defining the concrete age at the loading moment.
Note: Cracking is calculated independently in two directions on the basis of equivalent moments (see: Cracking of Slabs and Shells - Calculations).Deflection in slabs is calculated on the basis of the ratio of elastic stiffness to the stiffness determined on the basis of the phase of RC element work (see: Deflections of slabs and shells - calculations).
Deflection of RC slabs is identified with displacement. While working in 3D with slabs and shells or while using elastic supports in the 2D slab module, pay attention to the displacement of supports that may change the value of actual deflections.
The dialog may include additional RC code specific parameters such as the following.
- American code: how long a long-term load is acting on the structure, x coefficient.
- UK code: concrete age (part 7.2 of BS 8110), concrete creeping coefficient (fi according to Figure 7.1 in BS 8110), relative environment humidity (Figure 7.1 in BS 8110).
- Polish code: concrete age, concrete creeping coefficient.
- Eurocode 2: allowed nonlinear creep - according to the EN 1992-1-1:2004 AC:2008 code with all National Annexes [point 3.1.4(4)].
-