About the Geometry Editor
Scene > Geometry Editor
The Geometry Editor contains functions for modifying scene geometry. Use it to adjust/flip normals and re-tessellate NURBS surfaces.
Normals
These parameters affect the normals of the selected geometry.
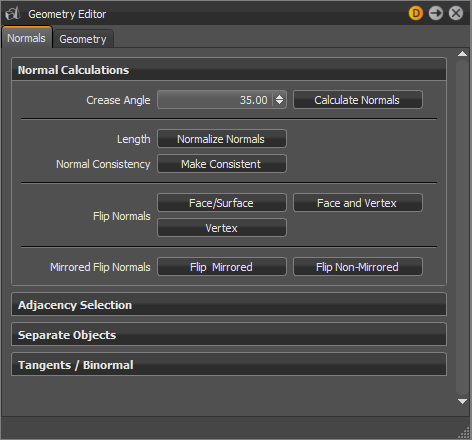
Normal Calculations
- Crease Angle - Determines the hardness of the shading between geometry edges. A lower value gives a harder look to the edges. While values around the default of 35 degrees give a smoother appearance.
- Calculate Normals - Starts to recalculate the normal orientation for the selected objects.
- Length - Normalizes the normal vector lengths in the geometry to a value of one.
- Normal Consistency - Removes the inconsistencies with surface normals that can occur when importing geometry; some normals point inside and others outside (the Vertex/Face Normal Rendering Mode helps to identify affected objects). This option sets all normals so they are pointing on the same side of the surface geometry.
- Flip Normals - Enables you to flip all types of normals.
- Face/Surface - Switches the direction of the face or surface normals of the selected geometry.
- Vertex - Switches the direction of the vertex normals of the selected geometry.
- Face and Vertex - Switches the direction of both the face and vertex normals of the selected geometry.
- Mirrored Flip Normals - Allows the flipping of the normals for instanced geometry, such as a mirrored surface. The Flip Mirrored button flips the normals for the instanced object, while the Flip Non-Mirrored button flips the normals for the original object.
Adjacency Selection
Selects the triangles of the geometry that have neighboring vertex normals less than the given Crease Angle value. This function, along with the Separate Objects function, can be useful when selecting portions of an object to separate it.
Crease Angle - Defines the angle used for identifying neighboring vertex normals.
Select - Starts the identification and selection process.
Separate Objects
Separates geometry into discrete objects, when the angle between the vertex normals is larger than the value specified by the Separation Angle.
Separation Angle - Defines the angle used for separation.
Separate - Starts the separating process.
Tangents/Binormal
Calculates the tangents and binormals of the given UV texture coordinates.
Source - Shows the texture coordinates that should be used to calculate the tangents & binormals.
Tangent - Shows the texture coordinate slot that the tangent values are saved in.
Binormal - Shows the texture coordinate slot that the binormal values are saved in.
Calculate - Executes the calculation using the selected values from Source, Tangent, and Binormal.
Geometry
These parameters affect the selected geometry.
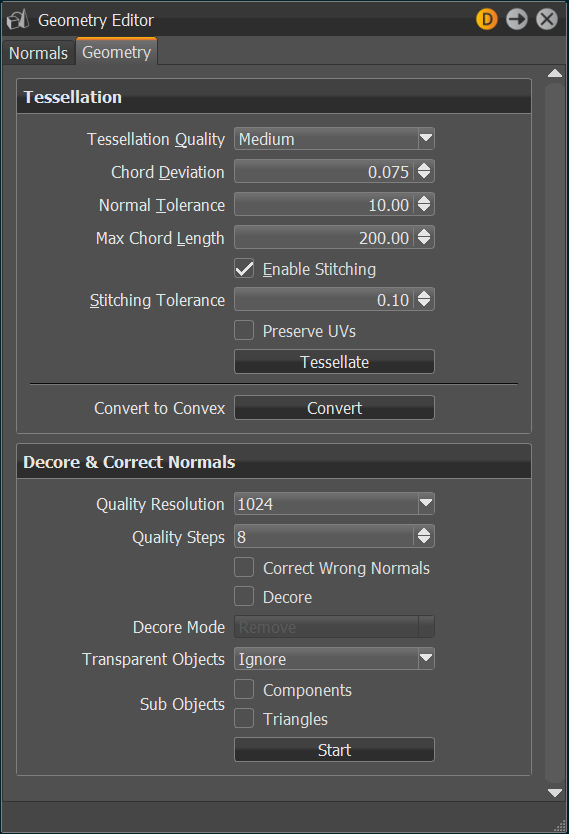
Tessellation
Provides the functionality for re-tessellation of surface (NURBS) data in the scene.
Tessellation Quality - Displays different presets to help you choose reasonable settings, if you are a casual user.
Tesselation Quality Coarse Low Medium High Chord Deviation 1.00 0.15 0.075 0.0375 Normal Tolerance 30.00 20.00 10.00 7.50 Max Chord Length 400.00 300.00 200.00 100.00 Enable Stitching Yes Yes Yes Yes Stitching Tolerance 0.10 0.10 0.10 0.10
- Chord Deviation - Describes the maximum deviation between the NURBS surface and the tessellated surface. A low value results in more accurate polygon model but it also increases the number of triangles.
- Normal Tolerance - The normal tolerance is the allowed normal deviation between the normals on the ends of a tessellated edge.
- Max Chord Length - Defines the maximum edge length of the generated polygons. Long polygon edges are not shaded smooth within the Render Window. This setting is helpful to avoid such faceted effects.
- Enable Stitching - Rebuilds existing topology and makes edges of selected shells align to each other, when enabled on tessellation. It avoids ragged edges on tessellated representation within the Stitching Tolerance.
- Stitching Tolerance - Sets the tolerance where two adjacent edges are considered to be touching and should be stitched together.
- Preserve UVs - Preserves the existing UV layout for surfaces if the geometry is re-tessellated.
- Convert to Convex - Converts concave polygon primitives into convex polygons, which are polygons with interior angles more than 180 degrees. Concave polygons may cause problems during rendering.
Decore & Correct Normals
Decoring removes redundant geometry that is inside other geometry, like screws and mountings inside a door covering. Since it is not visible, won't be seen when rendered, decoring makes the file lighter and reduces render time. A virtual camera flies around the selected object, takes screenshots, and depending on your settings, removes or ignores non-visible geometry, or sets the normals to bside.
Access geometry normals (or use vrdGeometryNode, set/getNormals), set the correct face normals (or use vrDecoreService), and select your decore settings.
- Quality Resolution - Defines the resolution of the images taken. A higher resolution gives more precise results.
- Quality Steps - Defines the number of images taken during the analysis. A higher value gives more accurate results.
Correct Wrong Normals - Flips polygon normals pointing away from the camera, if they are encountered during the analysis.
Note:As of 2022.3, you can flip normals at the triangle level without "removing" other triangles.
- Decore - Enables the decoring and parameters for defining this behavior.
Decore Mode - Defines the action to be taken, when geometry is determined to be inside another and non-visible. Choose from the following:
Transparent Objects - Determines how objects behind transparent objects are handled. Select from the following:
Ignore - Transparent objects are ignored (i.e., they do not occlude other objects and they are not occluded by other objects). (Fastest mode)
Treat as Transparent - Transparent objects will not occlude other objects, but they can be occluded by non-transparent objects. (Slower, but most accurate mode)
Treat as Opaque - No special handling for transparent objects, they are treated as opaque.
Sub Objects - Determines how sub-objects are factored in when decoring. When neither is enabled, sub-objects are not changed and decoring only happens at the object level.
- Components - Works on the component level for shells.
- Triangles - Works on the triangle/polygon level for meshes.
Start - Once all parameters are set, click Start to begin the decoring process.
For Python for decoring, see vrDecoreService, vrdDecoreSettings, and vrGeometryTypes.