About the UV Editor
Scene > UV Editor
Video captions: In VRED 2021.1, we have implemented a completely reworked UV Editor. First, we removed the Texture Editor, and all projection methods are available within the new editor, which makes working with textures more seamlessly. You can now also copy a UV layout from one object to another, which is a massive time saver when having identical objects in the scene. We also implemented the option to preserve the UVs when doing your retesselation of an object, so you don't need to create the UVs again. When creating a new UV layout, you can now enable Sew on Unfold, which simplifies the creation process. And we implemented and replaced the old unfold algorithm with a best-in-class Unfold3D library, which gives you much better results now and offers much more layout and optimize options. We also added a Select Shortest Path, which makes edge selection very easy now. Another new feature is the ability to constrain edges horizontally or vertically to make the UV layout fit to a rectangular texture. Just select the edges you want to constrain and apply the U or V constraint to it and unfold again. Now, you can apply your rectangular texture much better to your 3D models. Like here for the tire or for a seat belt, for example. For Show Texture, we added the option to choose between different channels of the material. If you're doing a selection in the UV Editor, you can now sync the 3D viewport, which makes orientation easier. You can also now export the UV layout as a snapshot with transparency, which is very helpful for the texture creation process. Find also many UV Editor settings in the preferences, like loading your own checkerboard texture or changing the color of your selections.
The UV Editor, available in both VRED Professional and VRED Design, is the primary tool for arranging and laying out UVs for optimal texture placement. Create and manipulate UVs (texture coordinates) of geometries within the scene.Correct the placement and orientation of your UV maps, then deal with the textures. The UV Editor works with any triangle geometry, either triangle meshes or NURBS data (surfaces and shells) that has been tessellated in VRED. If the geometry is re-tessellated, its UV coordinates are not preserved, and changes to the UVs will need to be redone.
An easy way to apply textures to a geometry with no UVs is to use a material with a texture projection, such as triplanar mapping. With triplanar mapping, there is a blend zone where the projections overlap on the surface. If this does not give the desired result, actual UV coordinates need to be created, and UV must be used as the Mapping type for the texture in the material.
Use the UV Editor to create UV coordinates (a.k.a, texture coordinates) for a geometry.
UV coordinates can be created in the UV Editor using Unfold & Layout in the Object selection mode. Unfold is an algorithm that tries to flatten the surface in UV space. This can only succeed if the surface is not a closed object, or has been cut beforehand (see Select UV Edges > Cut Edges). Cuts appear as UV seams in the texture mapping.
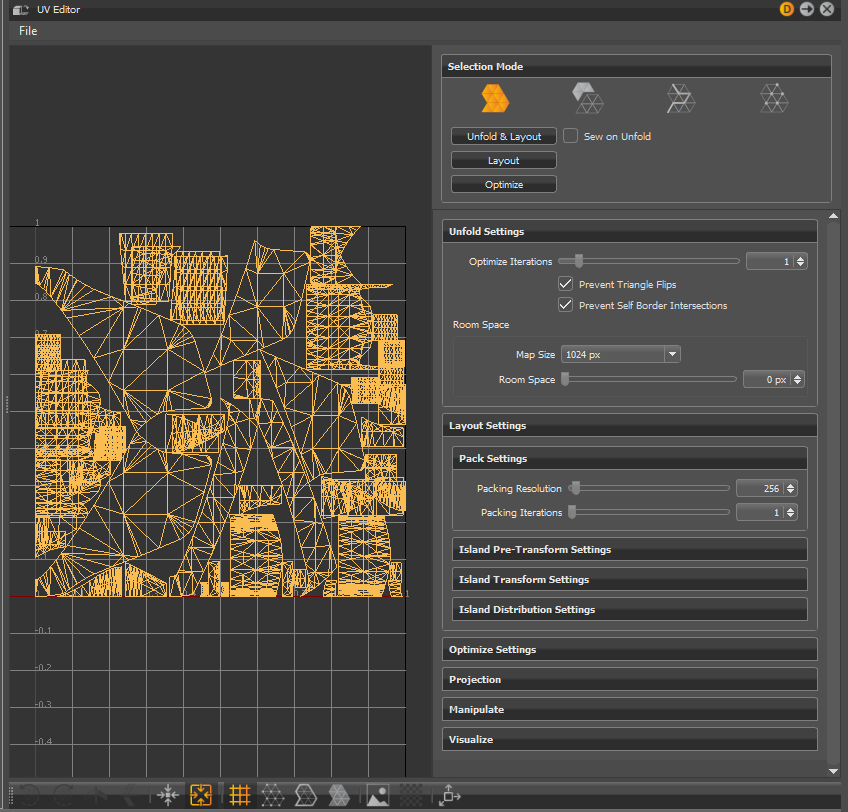
The UV Editor displays the UVs of selected geometry to the left and assorted options to the right. Along the bottom is a toolbar with icons for working in the UV Editor.
Terminology
Here are some definitions of terms you will need to know:
-
UV island - These are UVs that are connected, directly or indirectly. In Maya, they are called UV shells.
-
UV border - This refers to an island border, UV cut, or UV seam.

When unfolding a shell geometry for the first time, each of its surface patches will be treated as a separate UV island. Unfold flattens each surface as an island in UV space, and Layout packs the islands next to each other into UV space. If islands should be merged together (treated as one connected entity) in UV space, use Sew Islands, or Unfold Islands with Sew on Unfold enabled.
How this all comes together is when you return to the Material Editor. When the same geometry is selected, under Diffuse Texture, change the Mapping Type to UV.
File
This menu contains options for exporting an image of the UV layout and resetting UV preferences.
Save UV Snapshot
Exports a snapshot of the UV Layout as an image with alpha channel. When selected, the Save UV Snapshot dialog opens.

Set the dimensions of the image, choose from 0 to 1 UV Space or Bounding Box for the UV area, then click OK.
To set a preference for this, see Snapshot.
Reset Settings to Preferences
Changes the current settings for the UV Editor to those set in the UV preferences. Use this whenever you need to use consistent UV settings applied to your content.
UV Sets
This menu contains options for viewing, copying and pasting, and deleting UV sets, as well as selecting nodes not contained within a UV set.
Material UV Set
Changes the UV Editor viewport to display the material UV sets, since VRED can display lightmap UV sets, as well.
Lightmap UV Set
Changes the UV Editor viewport to display the lightmap UV sets, since VRED can display material UV sets, as well.
Copy to Lightmap UV Set/Copy to Material UV Set
Copies the UV set of the current active UV set (seen in the UV Editor viewport) and pastes it onto the other UV set. For example, if the Lightmap UV set is visible in the UV Editor viewport, then VRED would copy its UV set and paste it onto the Material UV set, making the UV sets identical.
Delete Material UV Set/Delete Lightmap UV Set
Deletes the current active UV set (seen in the UV Editor viewport). For example, if the Material UV set is displayed, this is deleted.
Select all Nodes Without UV Set
Selects nodes in the Scene Graph without UV sets. This is handy when you want a good lightmap result, have manually created a UV set, and want to ensure all nodes are part of the UV set.
Selection Mode
Sets the selection criteria for the UV Editor (Objects, Islands, Edges, and Vertices) and Render Viewport.
Once a Selection Mode is set, select your content in the Scene Graph to load it into the UV Editor.
Making Selections in the UV Editor
To select islands, edges, or vertices in the UV Editor, first select the geometry in the scene that you want to work with. Then go to a UV selection mode, such as Select UV Islands, and select islands in the UV view.
These UV islands, edges, and vertices can also be selected in the viewport in 3D rendering. We recommend to enable  Wireframe Selection to display the current selection. Wireframe Selection can be toggled in the main toolbar.
Wireframe Selection to display the current selection. Wireframe Selection can be toggled in the main toolbar.

Colors in the UV Editor
Colors play an important role in the UV Editor. They help distinguish one thing from another and whether something is selected or not.
To identify or set the colors for selected or unselected islands, island borders, vertices, edges, and U and V constraints, visit Edit > Preferences > Selection > UV.
Select Objects
 Nodes in the scene can be selected in the Render Window. Nothing can be selected in the UV Editor view.
Nodes in the scene can be selected in the Render Window. Nothing can be selected in the UV Editor view.
Unfold & Layout
Unfold creates UV coordinates for the selected geometries, with the current Unfold settings. It tries to flatten the surface in UV space. This can only succeed if the surface is not a closed object or has been cut beforehand (see Select UV Edge > Cut Edges). Cuts appear as UV seams in the texture mapping. Afterwards, the UV islands are layed out (see Layout).
Unfold & Layout can be used on geometries without UV. It uses the 3D data of the surface as input.
If you experience an unexpected unfold result (a circular-shaped UV island), try to deactivate the Prevent Triangle Flips option.

-
Sew on Unfold - Sews together all UV islands of geometry before unfolding.
Warning:Do not use on closed objects, as it can produce a single merged UV island that cannot be flattened with Unfold.
Layout

Lays out the selection, based on the Layout Settings established below. It automatically repositions UV islands, so as not to overlap in UV texture space and maximize the spacing and fit between them. This is useful for ensuring that the UV islands occupy their own separate UV texture space.
In general, you should keep UV islands separated for convenience and clarity, but it is not absolutely necessary. For example, you may want the UV islands to overlap so different faces use the same region of a texture.
You can also use the Layout feature to scale or stretch the UV islands to fit within the 0 to 1 coordinates of the UV Editor. This is useful if you need to maximize the texture space used when creating a texture map.
If you perform a Layout and see that the padding isn't correct, either Undo and make the changes or make the changes, then click Layout.
Before using Layout, you should already have performed the necessary UV mapping. That is, the Layout feature will only arrange existing UV texture coordinates, it will not create them.
Optimize
Smoothes out areas of distortion in the existing UV layout.
Select UV Islands
 UV islands of selected geometry nodes can be selected. If an island is selected, its corresponding sub-mesh is highlighted white.
UV islands of selected geometry nodes can be selected. If an island is selected, its corresponding sub-mesh is highlighted white.

Sew Islands
Attempts to join the selected islands.
- Only Borders between Islands - Only attempts to join borders between different islands (does not attempt to join internal borders). Enable it before clicking Sew Islands.
Unfold Islands
Unfolds selected islands. The new UV coordinates for the selected islands are scaled to be approximately as large as the originals and placed in the original locations.
Sew on Unfold
Sews selected objects together, once Unfold is clicked. Enable this option before clicking Unfold.
Layout Islands
Lays out the islands, based on the Layout Settings established below.
Optimize Islands
Smoothes out areas of distortion in the selected islands, according to the Optimize settings.
Select UV Edges
![]() Edges of selected geometry nodes can be selected. Holding the Shift or Shift+Ctrl keys and hovering the cursor over an unselected edge, highlights it the color set in the Selection Preferences. Same can be said for hovering over a selected edge. Selected edges are green by default, butcan also be customized.
Edges of selected geometry nodes can be selected. Holding the Shift or Shift+Ctrl keys and hovering the cursor over an unselected edge, highlights it the color set in the Selection Preferences. Same can be said for hovering over a selected edge. Selected edges are green by default, butcan also be customized.

Only Select Borders
Filters the non-border edges from the new edge selection.
Select Shortest Path
Helps with selecting a path of edges, by clicking, then select at least two points. When picking is complete, the shortest path is created, connecting each way point in the order it was picked and adding it to the current edge selection. See How to Select Edges of Selected Geometry Nodes for more information.
Select Shortest Path will never cross a border.
Double Click Selection
Controls at which edge the selection stops. For example, with Max 3D Angle = 89°, the selection cannot go around a cube (because its faces have a 90° angle).
- Max 2D Angle - The angles made by the surface topology, regardless of the surface’s shape.
- Max 3D Angle - The angles made by the surface’s shape, as measured in world or local space.
Double Click Selection will never cross a border.
In the following example, the highlighted edge was double-clicked. The tool looks for neighboring edges to the left and right. It takes into account the Max 3D Angle and Min 2D Angle. Since Max 3D Angle is set to 90 degrees, the border cannot be crossed. Since Min 2D Angle is set to 30 degrees, the selected edge can't go along the border. Instead, it traveled around the torus, making it appear as if the selection crossed the border.

If there is another border and the edge is double-clicked, it will not cross that border.

In this example, the highlighted edge was double-clicked. The edge to the right stops as there is no further matching edge, but the left can continue.

If Stop At Border is enabled, the result is different. The selection stops at the border, even though there are more matching edges.

Stop At Border
Prevents continuous selection from crossing a UV border.
In the following example, you will see how Stop At Border affects the path selected by Select Shortest Path. Instead of traveling a shorter distance to connect these points, a longer path is taken. This is because the tool cannot cross the border.

Automatic Seam Selection
Automatically selects a generated edges set for opening the chosen mesh type. When Select UV Edges is selected, the Automatic Seam Selection options are accessible. This option can be a time saver for generating UVs.
Selection Type > Manufacturing
Selects a generated edges set to open a manufactured mesh. Use Angle to define the angle between two consecutive polygons and Area Ratio to define the ratio between the smaller and larger patch area.
Selection Type > Organic
Selects a generated edges set to open an organic mesh. It tries to detect feature points of the mesh, such as finger tips or toes, links them together, and segments the mesh, if the Segmentation Amount is greater than 0.0. Use the Use Pipecutter option to force linking of all holes, to suppress all pipes of mesh.
Selection Type > Bake
Selects a generated edges set to open a mesh for baking. It makes patches, according to a defined angle between polygons, and defines the size of the smallest patch by merging the smaller patches until the minimum size is reached.
Angle
Sets the angle between two consecutive polygons and is used with Manufacturing and Bake selection types.
Use Pipecutter
Forces linking of all holes to suppress all pipes of mesh for the Organic selection type.
Segmentation Amount
Segments the mesh for the Organic selection type, if the amount is greater than 0.0.
Size of Min Patch
Defines the size of the smallest patch. For the Bake selection type, it merges the smaller patches until minimum size is reached.
Area Ratio
Defines the ratio between the smaller and larger patch areas for the Manufacturing selection type.
Select
Processes the nodes to select the type of automated generated edges set, based on the set parameters.
Cut Edges
Cuts the mesh along the selected edges.
Sew Edges
Joins two borders together, making the border edges a normal edge.
Constrain U
Constrains the selected edges to the U direction (horizontal).
Constrain V
Constrains the selected edges to the V direction (vertical).
Edge constraints are taken into account when applying Unfold or Optimize to a UV island. The unfolded/optimized island should then have a straight horizontal or vertical edge where the constraint had been set. This can be used, for example, to force UVs into a rectangular shape.
An edge can be constrained either horizontally, or vertically, not both at the same time.
Edge constraints are not kept when re-tessellating geometry.
Unconstrain
Removes any edge constraints from selected edges.
Select Vertices
![]() Vertices of selected geometry nodes can be selected.
Vertices of selected geometry nodes can be selected.
Optimize
Specifies the number of unfold calculations performed. Higher values can produce better quality but increases unfolding time.
Show All Vertices
 Displays all vertices in the UV map in magenta.
Displays all vertices in the UV map in magenta.
Unfold Settings
Use these options to set how objects or UV islands are unfolded in the UV Editor.
Models with degenerate triangles (zero area triangles) show a warning when attempting to unfold. If you confirm the dialog and proceed, those triangles are removed from the mesh or from the shell tessellation. You can also do the cleanup using Scene > Optimize > Filter > Remove Degenerate Triangles. The removal is not undoable.
Method
Lets you specify the method VRED uses to unfold UVs. Depending on the Method you select, different options display in the Unfold UVs Options window. Select from the following methods:
Unfold3D
(Default) VRED uses the Unfold3D algorithm. This method eliminates degeneracy and distortion, even at complex corners, in one unfold operation. For more information about the unfold options see Solver Options below.
Optimize Iterations
Specifies the number of times the Optimize algorithm is performed after the Unfold process completes (i.e., a value of 0 will unfold the mesh without any optimizations) to give you a smooth UV layout.
A very high number of iterations may produce undesirable results.
Prevent Triangle Flips
When on (default), prevents degenerate UV maps. Degeneracy can occur when a UV is moved in such a way that a face overlaps itself.
This is an example of how a triangle flip look.

Prevent Self Border Intersections
When on (default), prevents self-intersections on the border of the unfolded UV islands. For example, this option automatically untangles the border of a UV island when a border edge has looped around itself.
This is an example of self border intersections.

Room Space
Map Size
Select a preset that corresponds to your texture map size (in pixels) for space calculation during unfolding.
Room Space
Specifies the distance between parts of the selected UV island in pixels.
When Room space is greater than 0, it prevents textures from bleeding past the UV borders. Avoid increasing this value past its default (0 pixels), because it can slow down the unfold calculations and create distortion.
The following example shows the fingers of a hand. When Room space is set to 0, some of the fingers overlap. When Room space is set to 2, the space between the fingers increases.
Prevent self-border intersections must be turned on to see the effects of the Room Space option.
Layout Settings
Use these options to set how objects or UV islands are laid out in the UV Editor.
Models with degenerate triangles (zero area triangles) show a warning when attempting to unfold. If you confirm the dialog and proceed, those triangles are removed from the mesh or from the shell tessellation. You can also do the cleanup using Scene > Optimize > Filter > Remove Degenerate Triangles. The removal is not undoable.
The default settings give the best results in most situations.
Pack Settings
These settings relate to how the selected objects' UV islands are packed into the specified UV space, overall.
Packing Resolution
Determines the resolution of the packing grid used to place UV islands next to each other in the UV space. Higher values are slower, but produce better results when there are a lot of smaller islands. Default value is 256.
Packing Iterations
Determines the number of trials the packing algorithm will take to achieve the desired result. More iterations are slower, but can increase accuracy. Default value is 1.
Island Pre-Transform Settings
These settings determine the UV islands' start positions/orientations before packing begins.
Island Pre-Rotation
Allows islands to be rotated before packing occurs.
- Off - No pre-rotating occurs.
- Horizontal - Orient UV islands horizontally (via their bounding box) before packing.
- Vertical - Orient UV islands vertically (via their bounding box) before packing.
- Align X to V - Orient UV islands such that their X axes in 3D space are aligned to the V axis in UV space.
- Align Y to V - Orient UV islands such that their Y axes in 3D space are aligned to the V axis in UV space.
- Align Z to V - Orient UV islands such that their Z axes in 3D space are aligned to the V axis in UV space.
Island Pre-Scaling
Allows islands to be scaled before packing occurs.
-
Off - No pre-scaling occurs.
-
Preserve 3D Ratios - Scale UV islands to preserve their surface areas in 3D space.
-
Preserve UV Ratios - Scale UV islands to preserve the total UV area. Ratios between the selected islands is preserved, as well as their original total area in UV space.
Island Transform Settings
These settings relate to how UV islands can be transformed during the packing operation. Both translation and rotation are heavily influenced by the Layout Settings, but rotation can be further customized by specifically outlining the possible step sizes within a min/max range.
Translate Islands
Determines whether UV islands can be moved during the packing process. These are useful if you just want to rescale/reorient without affecting your packing arrangement or vice versa.
Rotate Islands
Determines whether UV islands can be rotated during the packing process. These are useful if you just want to rescale/reorient without affecting your packing arrangement or vice versa.
Rotation Step
Determines the allowable orientations for UV islands during the packing process. During packing, rotation will begin at the Minimum Island Rotation, then progressively increase by the Rotation Step amount as necessary, up to the Maximum Island Rotation. As a result, smaller values incur slower packing speeds. Default value is 90.
Rotation Range
Determines the minimum/maximum allowable orientation for UV islands during the packing process.
Island Distribution Settings
Padding Units
Set the units used when setting the amount of space between UV islands. Choose from pixel or UV.
Texture Map Size
Specifies the size of the texture map from 32 px to custom to be used as a reference when setting the Padding Units in Pixel unit.
Island Padding
Determines the amount of space to leave between UV islands when packing. If you do not see an effect, turn on Translate Islands. Add this space to avoid texture bleeding across islands.
In the following example, the image on the left has an Island Padding of 5.00 px. The image on the right has a 20.00 px. Notice the extra spacing between the islands.

Tile Padding
Determines the amount of space to leave between the UV islands and the edges of the tile.
In the following example, the image on the left has an Tile Padding of 5.00 px. The image on the right has a 20.00 px. Notice the extra spacing (where the red arrows are) between the UV islands and edges of the tile.

Island Distribution
Determines how island placement is associated to UV tiles. Select from:
-
Distribute - The selected set of islands is automatically segmented into the available tiles specified by the Tiles U and V values.
-
Island Centers - UV island layout is determined by each island's bounding box center. islands are assigned to the tile currently containing their bounding box center. When using Island Center mode, you must ensure that the Packing Region is set to the bottom-left corner of where you want the tiling to start. For example, if you want the islands to line up with the entire visible grid in the UV Editor (so -1 to 1 in U and V), you would need to set Packing Region to Custom and its U and V ranges to -1, 0. then the number of Tiles in U and V to 2.
Tiles U/V
Specifies the number of working UV tiles for distribution.
Packing Region
Determines the portion of the tile space in which UV islands are packed (including the margin). When packing multiple tiles in U and V, this region represents the lower-left tile in UV space. Select from the following, then click Layout, when finished.
| Packing Regions | Results |
|---|---|
| Full Square |  |
| Top Half |  |
| Top Left |  |
| Top Right |  |
| Bottom Half |  |
| Bottom Left |  |
| Bottom Right |  |
| Left Half |  |
| Right Half |  |
| Custom (U 0.2 - 1.0) (V 0.5 - 1.0) |  |
U min/max
(Only available when Packing Region is set to Custom)
Sets the U range for island distribution when the packing region is set to custom.
V min/max
(Only available when Packing Region is set to Custom)
Sets the V range for island distribution when the packing region is set to custom.
Scale Mode
Determines the universal post-packing scale operation used. Choose from:
-
Off - No post-packing scaling occurs.
-
Uniform - (Default) Scale all islands so that their global bounding box fits best in the given packing region. U and V axes are scaled uniformly.
-
Non-Uniform - Scale all islands, in U and V independently, so that their global bounding box matches the given packing region. This allows you to maximize the space usage of the UV tile, but can potentially cause distortions if the corresponding texture is not adjusted to compensate.
Optimize Settings
Use these options to set how objects or UV islands are optimized in the UV Editor.
Models with degenerate triangles (zero area triangles) show a warning when attempting to unfold. If you confirm the dialog and proceed, those triangles are removed from the mesh, or from the shell tessellation. You can also do the cleanup with Scene > Optimize > Filter > Remove Degenerate Triangles. The removal is not undoable.
The following options are only available when Unfold3D is the selected method:
Optimize Iterations
Specifies the number of times the optimize algorithm is performed after the Unfold process completes (i.e., a value of 0 will unfold the mesh without any optimizations).
A very high number of Iterations may produce undesirable results.
Angle vs. Distance
Controls the strength of the surface and angular optimization, minimizing stretching and angular errors in your UV map. The default value is 1.
Power
Determines how strongly the selected UV maps are optimized. The higher the number, the larger the changes from the original geometry. The default value is 100.
Prevent Triangle Flips
Prevents degenerate UV maps. Degeneracy can occur when a UV is moved in such a way that a face overlaps itself.
Prevent Self Border Intersections
Prevents self-intersections on the borders of unfolded UV islands. For example, this option automatically untangles the border of a UV island when a border edge has looped around itself.
Room Space
Map Size (Pixels)
Select a preset that corresponds to your texture map size.
Room Space (Pixels)
Specifies the distance between parts of the selected UV island.
When Room space is greater than 0, it prevents textures from bleeding past the UV borders. Avoid increasing this value past its default (0 pixels), because it can slow down the unfold calculations and create distortion.
The following example shows the fingers of a hand. When Room space is set to 0, some of the fingers overlap. When Room space is set to 2, the space between the fingers increases.
Prevent self-border intersections must be turned on to see the effects of the Room Space option.
Projection
Only available for Objects.
Controls the projection shape and angle when projecting UVs onto the selected object in the scene.
This will recalculate the current UV Map.
Mode
Sets the type of projection to use:
Cylindrical

Use for cylindrical shapes, such as a screw.
Triplanar

Use for complicated shapes, such as a steering wheel or car seat.
Planar

Use for flat shapes, such as a hood or seat of a car seat.
When applying a projection to the geometry, the current projection settings are attached to the node. If you want to later continue to work on the projection, select the geometry and click “Project”. The last used settings will be used for the projection.
Project
Applies the selected projection mode to the UV texture mapping channels of the related material, when this button is clicked.
Manipulate
Only available once Project is pressed.
Click this button to display the manipulator in your scene. Click the button to hide it.
To reset the current projection settings for the selected object, click  . Use this to avoid manually refreshing every value when exiting and re-projecting UVs.
. Use this to avoid manually refreshing every value when exiting and re-projecting UVs.
This is an example of the triplanar texture manipulator, which appears in the scene, when the Triplanar mode is selected and Project is clicked.

For additional information, see Using Texture Manipulators.
Place Texture 3D
Place Texture 3D is for positioning and scaling the cylinder in 3D space. The projection is calculated from the world space positions of the vertices of the selected geometry.
Projection Center
-
For Cylindrical, it sets the center of the cylinder to the center of the selected geometries.
-
For Triplanar, it sets the center of the selected object.
-
For Planar, it specifies what to use as the center for the projection and where the center of the projection plane is placed.
Select from Object Center (to use the center of the object) or set custom coordinates.
- For Cylindrical, Center X, Y, Z, X, Rotate X, Y, Z, Scale X, Y, Z, and Projection Angle.
- For Triplanar, Center X, Y, Z and Rotate X, Y, and Z.
- For Planar, Center X, Y, Z, and Rotate values.
Once values are entered, use the Pick button and Shift+RMB to position the plane in the Render Window.
Fit to Bounding Box
Only available for Cylindrical mode.
Adjusts the scale and center of the cylinder to the bounding box of the selected geometry. If Keep Aspect Ratio is checked, this also respects the aspect ratio of the selected texture.
Center (X,Y,Z)
For Cylindrical mode, it sets the position of the cylinder’s center in the 3D scene.
For Planar, it enables more accurate placement of the texture projection, using numerical input for the X,Y, and Z texture coordinates.
Rotate
Only available for Planar mode.
Determines the degree of rotation for the texture, rotated away from the projection plane orientation.
Rotate (X,Y,Z)
Only available for Cylindrical mode.
Sets the rotation of the cylinder in the 3D scene.
Keep Aspect Ratio
Only available for Cylindrical mode.
Locks the aspect ratio of the texture projection, when changing scale or projection angle, via the UI or manipulator.
Scale (X,Y,Z)
Only available for Cylindrical mode.
The Y scale value scales the cylinder along its main axis (changes its height). The unscaled cylinder height is 1.0. Therefore, if the cylinder height should be 1000 scene units, set the Y scale to 1000. X and Z scale values scale the base of the cylinder. The base cylinder radius is 1.0. To have a regular cylinder with a circular base and diameter of 200 scene units, set X and Z to 100.0. Keep X and Z scale at identical values for a circular base. With unequal X and Z values, the cylinder base is stretched to an ellipse.
Projection Angle
Only available for Cylindrical mode.
Use this angle value to set how often the texture should wrap around the cylinder. The angle value defines the segment on the cylinder onto which the texture is projected once, horizontally. With 360 degrees, the texture wraps exactly once around the cylinder. With 180 degrees, the texture is projected two times, once onto each half of the cylinder, etc.
Place Texture 2D
Rotation
Only available for Cylindrical mode.
Sets the angle the texture is rotated on the cylinder surface.
Fit Size
Only available for Triplanar and Planar modes.
Adjusts the projection size to the selected geometry.
The aspect ratio of the selected texture (see the drop-down next to the Visualize > Show Texture option) is respected.
Keep Aspect Ratio
Only available for Planar mode.
Locks the aspect ratio of the current size values and current repeat values, when changing these with the numeric input controls in the GUI or with the manipulator.
Size
Only available for Planar mode.
Base size of the projection plane in scene units.
Repeat
Only available for Planar mode.
Sets how many times to repeat the 2D texture in the X and Y directions. When Keep Aspect Ratio is enabled, the texture will be uniformly repeated in both directions. Disable it to repeat the texture more in one direction.
Offset
Only available for Planar mode.
Defines how far the texture is shifted from the projection center position on the X- or Y-axis.
Rotation
Only available for Planar mode.
Defines the angle the texture is rotated within the projection plane.
Manipulate
For the following options, use the field to the right for how many degrees vertices, edges, or islands are rotated or flipped.
Apply World Scale
Scales the UV coordinates according to the average triangle area in scene units. Use in combination with Use Texture Size in the material to get a real world scaling of your textures. Real world scaling displays a texture on an object where UV islands correspond to the size of the in-scene object parts, so the texture appears with a specified width and height on the object in the scene, for example, 200 mm x 100 mm.
Rotate Left
 Rotates the selected vertices/edges/islands to the left (counter-clockwise), using the set rotation value.
Rotates the selected vertices/edges/islands to the left (counter-clockwise), using the set rotation value.
The UV preference, Rotation Step Size, sets the rotation size used for the Rotate Left (Rotate Left) and Rotate Right (Rotate Right) toolbar button in the UV Editor.
Rotate Right
 Rotates the selected vertices/edges/islands to the right (clockwise), using the set rotation value.
Rotates the selected vertices/edges/islands to the right (clockwise), using the set rotation value.
The UV preference, Rotation Step Size, sets the rotation size used for the Rotate Left (Rotate Left) and Rotate Right (Rotate Right) toolbar button in the UV Editor.
Use UV Lattice
Enables the 2D UV lattice deformer for modifying the layout of multiple UVs, all at once.
Columns/Rows
The number of columns/rows of the current lattice manipulator.
Falloff
The lattice manipulator's level of influence or falloff value.
Use Bounding Box
When selected, the current lattice manipulator cannot extend past the outer edge or boundary of the target geometry.
Visualize
When checked, these are enabled by default. Uncheck to have them disabled by default.
Show Grid
 Displays the grid in the UV Editor view.
Displays the grid in the UV Editor view.
In the following example, the image on the left only displays UV islands. The image on the right displays them with the grid added.

Show All Vertices
 Displays all vertices in the UV map in the editor view in magenta.
Displays all vertices in the UV map in the editor view in magenta.
In the following example, the image on the left only displays UV islands. The image on the right displays them with blue borders surrounding them.

Show Borders
 Displays borders on UV islands.
Displays borders on UV islands.
In the following example, the image on the left only displays UV islands. The image on the right displays them with blue borders surrounding them.

Show Shading
 Shows if any UVs or UV islands overlap when viewed in the Render Window and UV Editor view. When activated, all selected UV islands appear shaded in a semitransparent way. However, areas that appear more opaque than normal indicate regions of overlap. Overlapping UVs are often undesirable because any associated texture maps will also overlap on the related surface meshes.
Shows if any UVs or UV islands overlap when viewed in the Render Window and UV Editor view. When activated, all selected UV islands appear shaded in a semitransparent way. However, areas that appear more opaque than normal indicate regions of overlap. Overlapping UVs are often undesirable because any associated texture maps will also overlap on the related surface meshes.

Show Wireframe
 Shows or hides wireframe rendering. When enabled, wireframe rendering is displayed in the Render Window and UV Editor view. When disabled, wireframe rendering is not displayed.
Shows or hides wireframe rendering. When enabled, wireframe rendering is displayed in the Render Window and UV Editor view. When disabled, wireframe rendering is not displayed.
Show Texture
 Displays any textures used by the materials of the selected nodes in the Render Window and UV Editor view.
Displays any textures used by the materials of the selected nodes in the Render Window and UV Editor view.

-
The texture selected in the drop-down next to Show Texture is displayed in the background. It is scaled according the to UV repeat, UV offset, and rotate values from the material where this texture is used.
-
If there are multiple textures used by the materials, only one of them displays in the UV Editor.
If the selected texture has Use Texture Size enabled, the grid uses 0-100 mm labels on the U and V axes, instead of 0.0 to 1.0 labels. This is to help with the world scale texture workflow.
Show Checkerboard
Only available when Show Texture is enabled.
 Overwrites the existing object material in the Render Window and UV Editor view with Checkerboard. You can input values for the height and width of the checker pattern (to the right of the option). The colors and detail of the checkerboard make it easier to identify distortions, map direction, check details, and display repeats. Select Show Texture to return to the original material.
Overwrites the existing object material in the Render Window and UV Editor view with Checkerboard. You can input values for the height and width of the checker pattern (to the right of the option). The colors and detail of the checkerboard make it easier to identify distortions, map direction, check details, and display repeats. Select Show Texture to return to the original material.

In the following example, the image on the left only displays UV islands. The image on the right displays them with the checkerboard material.


Show Manipulator
 Displays the selected manipulator in the Render Window and UV Editor view: Translate, Rotate, Scale, Rotate Pivot, or Scale Pivot.
Displays the selected manipulator in the Render Window and UV Editor view: Translate, Rotate, Scale, Rotate Pivot, or Scale Pivot.
The manipulator only works when Select UV Island, Select UV Edge, or Select UV Vertex is active. If one of these is selected, the manipulator is not displayed, even if Show Manipulator is selected.

Quick Access Bar
These shortcuts are found at the bottom of the UV Editor:
Rotate Left
 Rotates the selected vertices/edges/islands to the left (counter-clockwise), using the set rotation value.
Rotates the selected vertices/edges/islands to the left (counter-clockwise), using the set rotation value.
The UV preference, Rotation Step Size, sets the rotation size used for the Rotate Left (Rotate Left) and Rotate Right (Rotate Right) toolbar button in the UV Editor.
Rotate Right
 Rotates the selected vertices/edges/islands to the right (clockwise), using the set rotation value.
Rotates the selected vertices/edges/islands to the right (clockwise), using the set rotation value.
The UV preference, Rotation Step Size, sets the rotation size used for the Rotate Left (Rotate Left) and Rotate Right (Rotate Right) toolbar button in the UV Editor.
Flip in U Direction
 Flips the UV coordinates of selected vertices/edges/islands in the U direction.
Flips the UV coordinates of selected vertices/edges/islands in the U direction.
Flip in V Direction
 Flips the UV coordinates of selected vertices/edges/islands in the V direction.
Flips the UV coordinates of selected vertices/edges/islands in the V direction.
Zoom To
![]() Zooms to selected UVs in the Render Window and UV Editor view. If none are selected, it frames all UVs.
Zooms to selected UVs in the Render Window and UV Editor view. If none are selected, it frames all UVs.
Zoom To Selected UVs
 Zooms into the selected UVs in the Render Window and UV Editor view.
Zooms into the selected UVs in the Render Window and UV Editor view.
Show Grid
 Displays the grid in the UV Editor view. See the Show Grid section above.
Displays the grid in the UV Editor view. See the Show Grid section above.
Show All Vertices
 Displays all vertices in the UV map in magenta in the Render Window and UV Editor view. See the Show All Vertices section above.
Displays all vertices in the UV map in magenta in the Render Window and UV Editor view. See the Show All Vertices section above.
Show Borders
 Displays borders on UV islands in the Render Window and UV Editor view. See the Show Borders section above.
Displays borders on UV islands in the Render Window and UV Editor view. See the Show Borders section above.
Show Shading
 Use to identify overlapping parts of your UV layout, selected islands, and islands in the Render Window and UV Editor view. See the Show Shading section above.
Use to identify overlapping parts of your UV layout, selected islands, and islands in the Render Window and UV Editor view. See the Show Shading section above.
Show Wireframe
 Displays the wireframe of the selected nodes in the Render Window and UV Editor view. See the Show Wireframe section above.
Displays the wireframe of the selected nodes in the Render Window and UV Editor view. See the Show Wireframe section above.
Show Texture
 Displays any textures used by the materials of the selected nodes in the Render Window and UV Editor view. See the Show Texture section above.
Displays any textures used by the materials of the selected nodes in the Render Window and UV Editor view. See the Show Texture section above.
Show Checkerboard
 Overwrites the existing object material in the Render Window and UV Editor view with Checkerboard. See the Show Checkerboard section above.
Overwrites the existing object material in the Render Window and UV Editor view with Checkerboard. See the Show Checkerboard section above.
Show Manipulator
 Displays the selected manipulator in the Render Window and UV Editor view: Translate, Rotate, Scale, Rotate Pivot, or Scale Pivot. See the Show Manipulator section above.
Displays the selected manipulator in the Render Window and UV Editor view: Translate, Rotate, Scale, Rotate Pivot, or Scale Pivot. See the Show Manipulator section above.