Isotropic Material Temperature Dependence
Description: Specifies temperature-dependent table references for MAT1 material properties. This entry is used if a MAT1 entry is specified with the same MID.
Format:
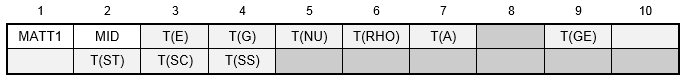
Example:

| Field | Definition | Type | Default |
|---|---|---|---|
| MID | Material identification number that matches the MAT1 identification number. | Integer > 0 | Required |
| T(E) | TABLEMi identification number for Young's modulus. | Integer ≥ 0 or blank | |
| T(G) | TABLEMi identification number for shear modulus. | Integer ≥ 0 or blank | |
| T(NU) | TABLEMi identification number for Poisson's ratio. | Integer ≥ 0 or blank | |
| T(RHO) | TABLEMi identification number for mass density. | Integer ≥ 0 or blank | |
| T(A) | TABLEMi identification number for thermal expansion coefficient. | Integer ≥ 0 or blank | |
| T(GE) | TABLEMi identification number for damping coefficient. | Integer ≥ 0 or blank | |
| T(ST) | TABLEMi identification number for tensile stress limit. | Integer ≥ 0 or blank | |
| T(SC) | TABLEMi identification number for compressive stress limit. | Integer ≥ 0 or blank | |
| T(SS) | TABLEMi identification number for shear stress limit. | Integer ≥ 0 or blank |
Remarks:
- Temperature-dependent material properties are only calculated when a temperature distribution for materials is defined by using TEMPERATURE, TEMPERATURE(MATERIAL), or TEMPERATURE(BOTH) Case Control commands.
- Fields 3, 4, etc., of this entry correspond, one-by-one, to fields 3, 4, etc., of the MAT1 entry referenced in field 2. The value in a particular field of the MAT1 entry is replaced or modified by the table referenced in the corresponding field of this entry. In the example shown, E is modified by TABLEMi 56. A blank or zero entry means no temperature dependence of that field on the MAT1 entry.
- Any quantity modified by this entry must have a value on the MAT1 entry. Initial values of E, G, or NU may be supplied according to Remark 3 on the MAT1 entry. If a table is specified for E and not for G, the E table reference will be used in the determination of G.
- Table references must be present for each item that is temperature-dependent.