FBScene - The Scene Class
The MotionBuilder Scene
The FBScene class provides access to the MotionBuilder scene. It contains a list of all the scene elements including cameras, lights, models, characters, actors, poses, materials, textures, devices, constraints, etc. There is only one instance of FBScene available for manipulation at any given time, accessible via FBSystem.Scene.
from pyfbsdk import *
sys = FBSystem()
scene = sys.Scene
# Print the camera names in the scene.
for camera in scene.Cameras:
print camera.Name
The scene may be cleared by calling FBApplication.FileNew(). This will reset the scene to its default state, similarly to selecting File > New in the application menu.
app = FBApplication()
app.FileNew()
Example: Adding Objects to the Scene
Sample Viewport Output:
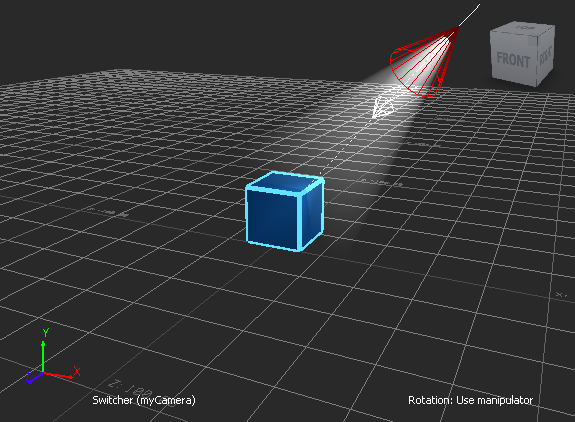
Program Summary: The following program presents a broad overview of how to add various objects to the scene, including cameras, lights, materials, shaders, i/o devices, and constraints.
from pyfbsdk import *
###############################################################
# Helper Function(s). #
###############################################################
# Create a cube primitive using FBCreateObject(). You can also create
# a unit cube (1x1x1) using FBModelCube('cubeName').
def createCube():
# (!) Note: When you are creating PRIMITIVES using FBCreateObject(),
# the custom name of the object (3rd parameter) must have the same
# name as the EntryName (2nd parameter)
cubePrimitive = FBCreateObject( 'Browsing/Templates/Elements/Primitives', 'Cube', 'Cube' )
cubePrimitive.Name = 'myCube'
# Move the cube up by 10 units along the y axis.
cubePrimitive.Translation = FBVector3d(0, 10, 0) # (x, y, z) translation vector.
# Show the cube in the scene.
cubePrimitive.Show = True
return cubePrimitive
# Apply a blue material to the model.
def applyMaterial(pModel):
# FBMaterial() adds a material to the scene's list of materials.
material = FBMaterial('myMaterial')
# Define the material's color channels
material.Ambient = FBColor(0, 0.32, 0.66) # (red, green, blue) color
material.Diffuse = FBColor(0.17, 0.47, 0.8)
material.Specular = FBColor(0, 0.7, 0.86)
material.Shininess = 100
# The material must be assigned to a model to modify the way it is rendered.
pModel.Materials.append(material)
# Apply a cartoon edge shader to the model.
def applyShader(pModel):
shader = FBCreateObject('Browsing/Templates/Shading Elements/Shaders', 'Edge Cartoon', 'myShader')
shader.Name = 'myShader'
# (!) Note: Shader properties must be accessed using shader.PropertyList.Find(<propertyName>)
# The actual value of the property must be changed using its .Data field.
colorProp = shader.PropertyList.Find('EdgeColor') # Obtain the shader's EdgeColor FBProperty.
colorProp.Data = FBColor(0.38, 0.89, 1) # Turquoise edges
widthProp = shader.PropertyList.Find('EdgeWidth') # Obtain the shader's EdgeWidth FBProperty.
widthProp.Data = 5 # Make the edges sufficiently thick.
# Assign a shading mode to the model, along with the default shader
# and the cartoon shader we just created.
# The default shader is required to display the cartoon shader.
pModel.ShadingMode = FBModelShadingMode.kFBModelShadingDefault
defaultShader = FBSystem().Scene.Shaders[0]
pModel.Shaders.append(defaultShader)
pModel.Shaders.append(shader)
# Create a camera looking at the model.
def createCamera(pModel):
# FBCamera() adds a camera to the scene's list of cameras.
# We use the camera switcher to change the view to our own camera.
camera = FBCamera('myCamera')
camera.Translation = FBVector3d(85, 80, 180)
camera.Show = True
# Set the camera's interest point to the model.
camera.LookAt = pModel
# Enable camera switching.
scene.Renderer.UseCameraSwitcher = True
# Set our view to the newly created camera.
cameraSwitcher = FBCameraSwitcher()
cameraSwitcher.CurrentCamera = camera
return camera
# Create a light pointing at pModel.
def createLight(pModel):
# FBLight() adds a light to the scene's list of lights.
# The light will be parented to the cube - when the cube moves, so will the light.
light = FBLight('myLight')
# Make the light a spotlight.
light.LightType = FBLightType.kFBLightTypeSpot
light.Intensity = 100 # Value between 0 and 200
light.ConeAngle = 50 # Value between 0 and 160
light.FogIntensity = 50 # Value between 0 and 200
light.DrawGroundProjection = False # Don't show the light on the ground.
# Point the light at the model.
light.Parent = pModel # Set the light's parent model.
light.Translation = FBVector3d(60, 75, 30) # The light's local translation from its parent.
light.LookAt = light.Parent # Point the light at the parent.
light.Show = True # Show the light in the scene.
return light
# Create a keyboard i/o device.
def createKeyboard():
# (!) Note: If FBCreateObject() is used to create an i/o device, this
# device must be added to the scene's list of devices manually.
keyboard = FBCreateObject('Browsing/Templates/Devices', 'Keyboard', 'myKeyboard')
scene.Devices.append(keyboard)
# The i/o device's Online and Live properties must be set to True so its input
# can be used.
keyboard.Online = True
keyboard.Live = True
return keyboard
# Create an empty constraint relation.
def createConstraintRelation():
# The newly created constraint must be explicitly activated.
constraintRelation = FBConstraintRelation('myConstraintRelation')
constraintRelation.Active = True
return constraintRelation
# Recursively print the model's children.
def printSceneGraph(pModel, pLevel):
tabs = ''
for i in range(0, pLevel):
tabs += '\t'
print tabs + pModel.Name + ' - ' + pModel.ClassName()
for child in pModel.Children:
printSceneGraph(child, pLevel + 1)
# Print the list of FBPlugs.
def printList(pPlugList):
print pPlugList.Name
for element in pPlugList:
print '\t' + element.Name + ': ' + element.ClassName()
print ''
###############################################################
# Main. #
###############################################################
# Clear the scene and obtain a reference to it.
FBApplication().FileNew()
scene = FBSystem().Scene
# Create our scene elements.
cube = createCube()
applyMaterial(cube)
applyShader(cube)
createCamera(cube)
createLight(cube)
createKeyboard()
createConstraintRelation()
# Print the scene graph.
print '-------------------------'
print 'Scene graph:'
print '-------------------------'
printSceneGraph(scene.RootModel, 0)
print ''
# Print the scene's contents by type.
print '-------------------------'
print 'Scene contents by type:'
print '-------------------------'
printList(scene.Materials)
printList(scene.Shaders)
printList(scene.Cameras)
printList(scene.Lights)
printList(scene.Devices)
printList(scene.Constraints)
###############################################################
# Output. #
###############################################################
'''
>>>
-------------------------
Scene graph:
-------------------------
Scene - FBModel
myCube - FBModel
myLight - FBLight
myCamera - FBCamera
-------------------------
Scene contents by type:
-------------------------
Materials
DefaultMaterial: FBMaterial
myMaterial: FBMaterial
Shaders
Default Shader: FBShaderLighted
myShader: FBShader
Cameras
Producer Perspective: FBCamera
Producer Front: FBCamera
Producer Back: FBCamera
Producer Right: FBCamera
Producer Left: FBCamera
Producer Top: FBCamera
Producer Bottom: FBCamera
myCamera: FBCamera
Lights
myLight: FBLight
Devices
myKeyboard: FBDevice
Constraints
Shot Track: FBStoryTrack
myConstraintRelation: FBConstraintRelation
>>>
'''