You can choose to import Inventor objects as either Body Objects or Editable Mesh objects. Various other options control Inventor file import.
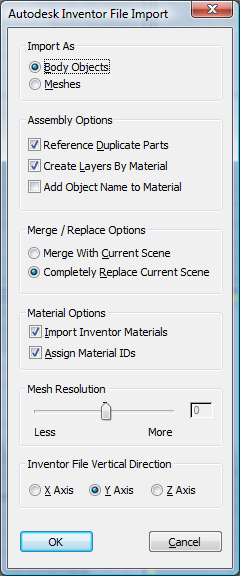
Import As group
Choose the format in which the Inventor file is imported:
- Body Objects Imports the Inventor file as Body Objects, which retain all ACIS solids information (Body Objects are also used when you import SAT files). To save these objects as solids, use the SAT exporter.
- Meshes Imports the Inventor file as editable mesh objects. Use the Mesh Resolution setting (see following) to determine the fineness or coarseness of the imported mesh.
Assembly Options group
- Reference Duplicate Parts
- When on, the importer treats duplicate parts in the Inventor file as references of each other.
- Create Layers by Material
- Generates layer information based on incoming materials. All objects sharing a material will be placed on the same layer.
- Add Object Name to Material
- When importing materials, uses the imported material name as part of the object name.
Merge / Replace Options group
Choose how the importer treats current scene contents:
- Merge With Current Scene Incoming geometry is merged with any existing geometry in the scene. This setting is useful for combining components from separate files into a single scene.
- Completely Replace Current Scene (The default.) The imported data completely replaces any existing geometry in the current scene. If the current scene has not been saved, you are given the opportunity to save the scene before proceeding with the import process.
Material Options group
- Import Inventor Materials
- When on, all Inventor materials and texture maps are translated and imported into the scene. When off, no materials are imported with the model.
- Assign Material IDs
- Lets you control whether material IDs are assigned to objects that are imported from Inventor. You can assign different materials to different surfaces of the same object while working in Inventor. When these objects are imported to 3ds Max, material IDs are assigned to the faces of single objects to which multiple materials are applied.
For example, say you've created a single object that represents a knob with a threaded shaft and you've applied a black, plastic material to the knob and a silver, metal material to the threaded shaft. If Assign Material IDs is on when you import the model into 3ds Max, the imported faces that have the plastic material are assigned material ID #1 and the faces that have the metal material are assigned material ID #2. If you choose to try different materials while working in 3ds Max, you can quickly make sub-object selections based on the material IDs or apply a Multi/Sub-Object material that contains materials that correspond to the IDs assigned to the faces.
Mesh Resolution group
- Mesh Resolution slider
-
When importing as meshes, this slider lets you determine the degree of refinement applied to the mesh objects. When set to 0 (zero), the geometry is imported as it appears in Autodesk Inventor. When set less than zero, the mesh is optimized with fewer faces, thus reducing detail. If the mesh resolution is set higher than zero, the mesh is tessellated with more faces, providing greater detail.
The Mesh Resolution slider is always set to 0 when you initiate an import.

Left: Mesh Resolution=–7
Center: Mesh Resolution=0
Right: Mesh Resolution=+7
Note: The option to adjust mesh resolution is available only for models imported from Autodesk Inventor 10 or later.
Inventor File Vertical Direction group
This option determines the model's orientation upon import. You can choose which axis of the Inventor model is vertical.
Choose the axis option:
- X Axis The X axis of the model, as seen in Inventor, is rotated so it is vertical when the model is imported.
- Y Axis The model is imported with the Y axis oriented as the vertical axis.
- Z Axis The imported model is rotated so its Z axis is the vertical axis.