About rational vs. non-rational geometry
Non-rational geometry is a sum of polynomials. Rational geometry is a ratio of sums of polynomials. Rational geometry is considerably more complex mathematically. Therefore:
- It may not be transferable to downstream CAD packages that can’t deal with complex descriptions
- It can be slower to manipulate when modeling, and slower to render.
The following tables lists the differences between the two types of geometry.
| Nature | Pros | Cons |
|---|---|---|
| Non-rational | More flexibility for transformations.Faster. | Sacrifices some precision for modeling flexibility. |
| Rational | Precise geometry (that is, exact conics). | Weighted CVs not supported by many CAD packages. Weighted CVs harder to manipulate.Creates multi-knots.Slower to display and render. |
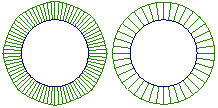
This illustration shows two circles drawn with the two types of geometry.
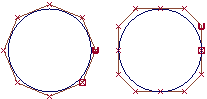
- The circle on the left is a non-rational curve with CVs that are all weighted equally. To have a non-rational curve, all weights must be 1.0.
- The circle on the right is a rational curve with different weights applied to the CVs, and multi-knots.
You can see the difference in two ways:
If you attach a radius measurement to the circles, the non-rational circle is not a perfect circle (although it is close): it has different radii depending on where you measure. The rational circle is a perfect circle.
Attach curve curvature combs to the circles. The curvature on the non-rational circle on the left varies. The curvature of the rational circle on the right is constant.