About surface textures
Surface textures are two-dimensional textures that simulate various types of surface materials by using either an image file (File and Stencil textures) or a computer graphic procedure (Bulge, Checker, Cloth, Curvature, Fractal, Grid, Highlight, Mountain, Noise, Ramp, and Water textures).
There are 13 different types of surface textures.
Environment textures map to directions. Surface textures and solid textures map to positions.
Do not map a surface texture to the Reflection parameter of a shader because it does not produce realistic-looking reflections.
File texture

The File texture lets you use an image file as a surface texture. You can create an image file using a paint package, using Alias’s integrated sketching tools (see the Sketching book), using a scanner to scan in a photograph, or by rendering a scene.
Bulge texture
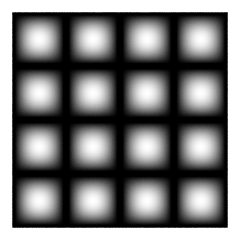
The Bulge texture represents a grid of white squares which fade to grey toward their edges. Use the Bulge texture as a bump or displacement map to create surface bulges, as a transparency map to simulate windows that are dirty around the edges, or as a color map to simulate tiles.
Checker texture
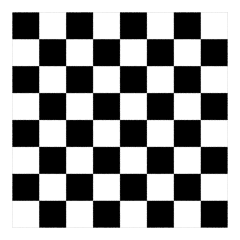
The Checker texture represents a checkerboard pattern.
You can modify the colors and size of the squares.
Cloth texture
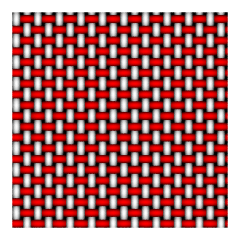
The Cloth texture simulates fabric or other woven materials.
When using cloth texture, remember the following:
- Rendering is faster if all three randomizing parameters (Randomness, Width Spread, and Bright. Spread) are set to 0.
- Very fine cloth textures may produce aliasing or moiré patterns, especially when viewed from a distance. If this occurs, set the Randomness value to a small non-zero value, or use Convert Solid Tex to convert the cloth texture into an image file.
- If you apply the cloth texture as a bump or displacement map, set the U Thread Color and V Thread Color to white, and the Gap Color to black, and use the Intensity parameters (Amult and Aoffset) to control the intensity of the bump/displacement effect. Decrease the Blurmult value to provide greater definition in the bump/displacement effect. Generally, the Amult and Blurmult values should be very low (less than 0.1).
Fractal texture

The Fractal texture represents a random function with a particular frequency distribution (a fractal) and can be used to create many different types of effects. Use the Fractal texture as a bump or displacement map to simulate rock or mountains, or as a transparency map to simulate clouds or flames. The Fractal texture has the same level of roughness at different levels of magnification (that is, at different distances from the camera).
Grid texture
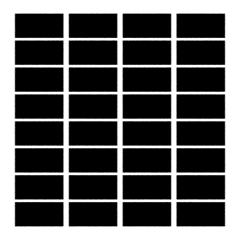
The Grid texture represents a scalar grid pattern.
Mountain texture
The Mountain texture simulates rocky terrain using a two-dimensional fractal pattern. Use the Mountain texture as both a color map and a bump or displacement map (on a flat surface) to simulate snow capped mountains.
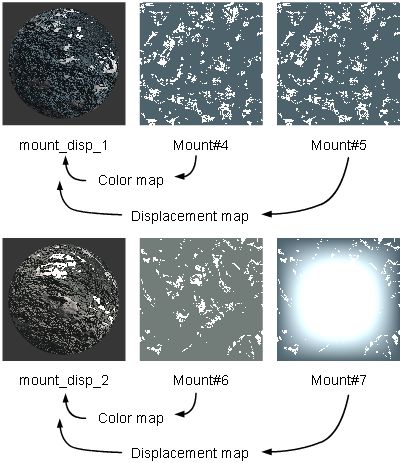

If you do apply the Mountain texture as both a color map and a bump or displacement map, note the following:
- The texture calculates the color map based on the bump/displacement map, so, for example, the location of snow is based on the displacement of the surface.
- The color parameters (Snow_color and Rock_color) of the Mountain texture relate only to the color map, and have no effect on the bump/displacement map. Similarly, all non-color parameters of the Mountain texture relate only to the bump/displacement map, and have no effect on the color map.
- The values of the Boundary parameter, the Snow Levels parameters, and the Recursion Depth parameter (Level_max) of the bump/displacement map override the values of the color map. For example, the Boundary value of the bump/displacement map controls the raggedness of the snow/rock boundary of the color map.
Noise texture

The Noise texture represents a random pattern of two colors. The Noise texture appears smoother the closer it is to the camera.
Ramp texture

The Ramp texture represents a gradation through a series of colors. The ramp texture can be used to create many different types of effects (stripes, geometric patterns, mottled surfaces).
The default ramp texture is blue/red/black unless the texture is mapped to certain single-channel parameters (for example, Reflectivity, Bump, Displacement). In these cases the ramp is black/white/black.
Use a ramp texture:
- as a two-dimensional environment background
- as the source file for an environmental sphere texture to simulate a sky and horizon
- as the source file for a projection texture to simulate wood grain, marble, or rock.
Very complex ramp textures may experience aliasing during an animation. If this occurs, use Convert Solid Tex to convert the ramp texture into an image file.
Stencil texture

The Stencil texture is like File texture. It lets you use an image file as a surface texture; however, it also lets you mask the image file to control how it covers a surface. Use the Stencil texture to overlay different textures (and control which parts of the textures are visible), or for label mapping.

Water texture
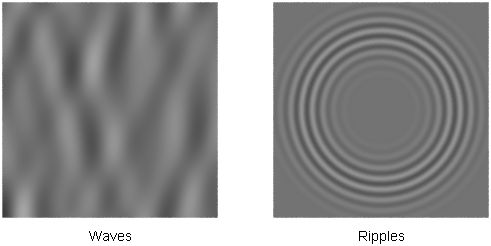
The Water texture simulates linear water waves, concentric water ripples (for example, caused by an object falling into water), or a combination of waves and ripples. Use the Water texture as a bump or displacement map to simulate water, or as a color map to simulate light reflections or refractions from a water surface.
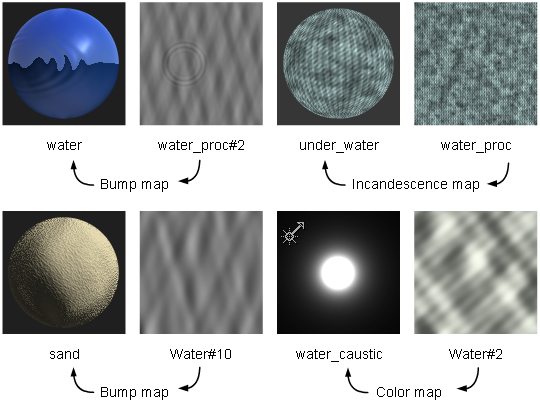

The Water Texture Parameters include the Linear Wave Parameters which control the appearance of linear water waves, and the Concentric Ripple Parameters, which control the appearance of concentric water ripples.
Uses for surface textures
- The File and Stencil textures are used to specify an image file.
- The Curvature texture is used by the Surf curvature and Surf curv params tools.
- The Highlight texture is used by the Highlight and Highlight params tools.