You can shorten or lengthen objects to meet the edges of other objects.
In practice, this means you can first create, copy, or offset an object such as a line or an arc, and then later adjust it to fit exactly between other objects.
Quick Mode Operation - Default
After you start the TRIM or EXTEND commands, simply select the objects near the ends to be trimmed or extended. There are three default options for selecting the objects:
- Two-point fence selection. Click two points that define a segment crossing through the objects near the ends to be trimmed or extended. In this case, the lines are being extended:
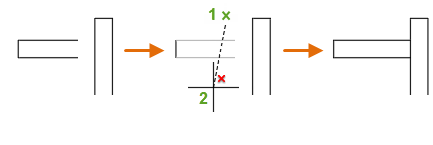
- Individual selection. Simply click one or more objects near the ends to be trimmed or extended. In this case, the selected line is being trimmed:
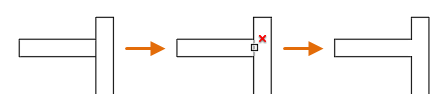
- Freehand selection. Click and hold down the left mouse button in an empty area and drag the cursor through one or more objects near the ends to be trimmed or extended. In this case, the lines are being trimmed:
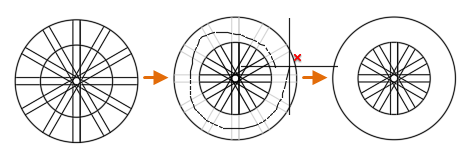
Standard Mode Operation
When you use Standard mode, objects you select as cutting edges or boundary edges are not required to intersect the object being trimmed. You can trim or extend an object to a projected edge or to an extrapolated intersection; that is, where the objects would intersect if they were extended.
If you do not specify a boundary and press Enter at the Select Objects prompt, all displayed objects become potential boundaries.
Trim Objects
You can trim objects so that they end precisely at the edges of selected objects. An object can also be one of the cutting edges and one of the objects being trimmed. For example, in the illustrated light fixture, the circle is a cutting edge for the construction lines and is also being trimmed.
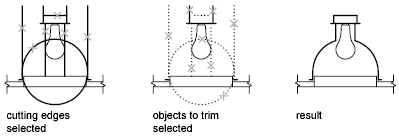
When you trim several objects, the different selection methods can help you choose the current cutting edges and objects to trim. In the following example, the cutting edges are selected using crossing selection.

The following example uses the fence selection method to select a series of objects for trimming.
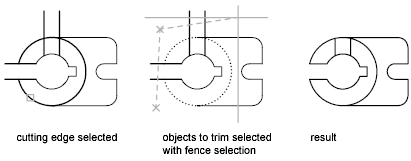
You can trim objects to their nearest intersection with other objects. Instead of selecting cutting edges, you press Enter. Then, when you select the objects to trim, the nearest displayed objects act as cutting edges. In this example, the walls are trimmed so that they intersect smoothly.

Extend Objects
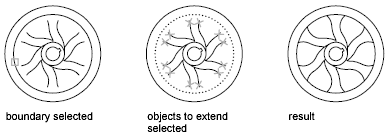
You can extend objects so that they end precisely at boundary edges defined by other objects. In this example, you extend the lines precisely to a circle, which is the boundary edge.
Trim and Extend Wide Polylines
2D wide polylines trim and extend at their centerlines. The ends of wide polylines are always squared off to the end of the polyline, not rounded or at a diagonal.
If you trim or extend a tapered 2D polyline segment, the width of the extended end is corrected to continue the original taper to the new endpoint, if possible. Otherwise, the ending width is forced to 0, a sharp point.

Trim and Extend Spline-Fit Polylines
Trimming a spline-fit polyline removes the curve-fit information and changes the spline-fit segments into ordinary polyline segments.
Extending a spline-fit polyline adds a new vertex to the control frame for the polyline.
Extend a Spline
Extending a spline preserves the shape of the original portion of the spline, but the extended portion is linear and tangent to the end of the original spline.
Trim or Extend in 3D
You can trim or extend an object to any other object in 3D space, regardless of whether the objects are on the same plane or parallel to the cutting or boundary edges. In the TRIM and EXTEND commands, use the Project and Edge options to select one of three projections for trimming or extending:
- The XY plane of the current UCS
- The plane of the current view
- True 3D, which is not a projection