|
|
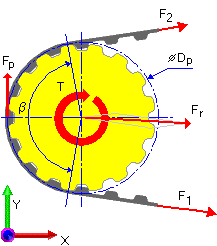
For each pulley |
|
F 2 - F 1 + F p = 0 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
For the driver pulley
![]()
|
|
v ≤ v max |
|
|
f b ≤ f max |
![]()
F c = mv 2
F Tmax = k 1 F p + F c
F 1 = F tmax
F 2 = F 1 - F p
For individual driven pulleys and idlers
i-index of the pulley
F Pi = P xi F p
![]()
![]()
![]()
F 1i = F 2i-1
F 2i = F 1i + F p i
where:
![]() for synchronous pulley
for synchronous pulley
![]() for flat pulley
for flat pulley
For entire belt drive
![]()
Required belt installation tension is determined from forces at driver pulley as follows
![]()
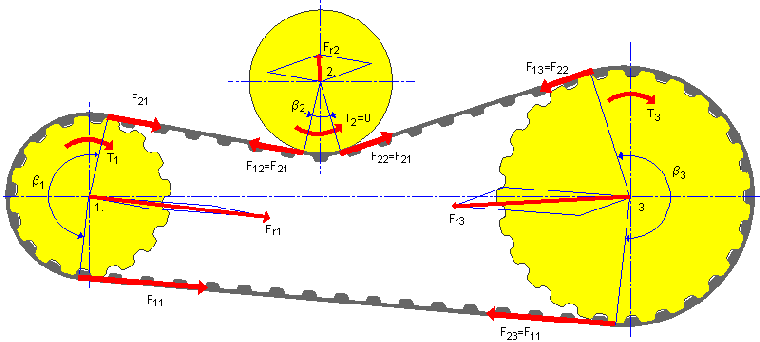
Example of power transmission with idler
|
Driver pulley |
Flat idler |
Driven pulley |
|
P x1 = 1 |
P x2 = 0 |
P x3 = 1 |
|
|
|
F P3 = P x3 F p |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
F 12 = F 21 |
|
|
|
F 22 = F 12 + F p2 = F 12 |
|
|
F c = m v 2 |
|
|
|
F Tmax = k 1 F p + F C |
- |
F 13 = F 22 |
|
F 11 = F Tmax |
- |
F 23 = F 13 + F p3 = F 11 |
|
F 21 = F 11 - F p |
- |
|
|
|
- |
- |
Meaning of used variables:
|
F p |
Effective pull [N] |
|
F 1 |
Belt tension on input side of the given pulley [N] |
|
F 2 |
Belt tension on output side of the given pulley [N] |
|
z |
Number of teeth of given pulley/ Number of belt teeth [-] |
| β |
Arc of contact / tooth angle of side inclination [deg] |
|
P |
power to transmit [W] |
|
P R |
Belt power rating for given transmission layout [W] |
|
c L |
Service factor [-] |
| β |
Arc of contact [deg] |
|
T |
Torque acting on given pulley [Nm] |
|
n |
Speed of given pulley [rpm] |
|
D p |
Pitch pulley diameter [m] |
|
v |
Belt speed [m/s] |
|
k |
Number of pulleys within belt transmission [-] |
|
L |
Belt pitch length [m] |
|
P |
power to transmit [W] |
|
m |
Specific belt weight for given width [Kg/m] |
|
k 1 |
Belt tension factor [-] |
|
F p |
Effective pull [N] |
|
F c |
Centrifugal force [N] |
|
F t |
Minimum belt installation tension [N] |
|
P xi |
Power ratio of given pulley [-] |
|
D pi |
Pitch pulley diameter [m] |
|
i |
Transmission ratio (speed ratio) of given pulley [-] |
|
T i |
Torque acting on given pulley [Nm] |
| η |
Efficiency [-] |
|
p b |
Circular pitch [m] |
|
D |
Nominal flat pulley diameter [m] |
|
H |
Belt height [m] |
|
h T |
Belt tooth height [m] |
|
a |
Pitch line offset [m] |