This material type is not supported for Explicit analyses. After selecting Orthotropic 3D from the Type drop-down, the following material sections will be available: General, Stiffness, Shear, Poisson’s Ratio, Thermal Expansion, Allowables, and Thermal.
Material stability requires that:
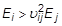
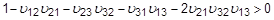
If either condition is not met, a warning message will be issued.
It may be difficult to find all nine orthotropic constants. In some practical problems, the material properties may be reduced to normal anisotropy in which the material is isotropic in a plane (i.e., plane 1-2) and has different properties in the direction normal to this plane. In the plane of isotropy, the properties are reduced to:
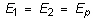
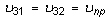
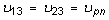
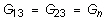
with
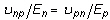 and
and
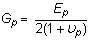 .
.
There are five independent material constants for normal anisotropy (i.e.,
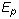 ,
,
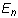 ,
,
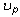 ,
,
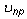 ,
,
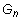 , and
, and
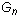 ). In case the material has a planar anisotropy, in which the material is orthotropic only in a plane, the elastic constants are reduced to seven (i.e.,
). In case the material has a planar anisotropy, in which the material is orthotropic only in a plane, the elastic constants are reduced to seven (i.e.,
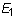 ,
,
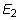 ,
,
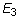 ,
,
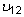 ,
,
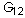 ,
,
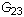 , and
, and
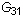 ).
).
-
General
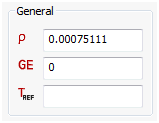
- Mass density, material damping coefficient, and reference temperature are input here for an Orthotropic 3D material.
- The mass density, RHO, will be used to automatically compute mass for all structural elements.
- To obtain the damping coefficient GE, multiply the critical damping ratio C/C0 by 2.0. If a dominate frequency is not defined for Material Structural Damping (see Dampings section), GE is ignored in transient response analyses.
- TREF is used only as the reference temperature for the calculation of thermal loads in linear solutions. If an initial temperature load is specified, TREF will be ignored.
-
Stiffness
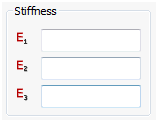
- You can input Young’s modulus for the longitudinal, lateral and thickness directions.
-
Shear
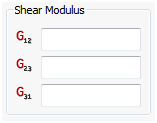
- You can input the in-plane, lateral transverse, and longitudinal transverse shear moduli.
- An approximate value for G2z and Gz1 is the in-plane shear modulus G12. If test data is not available to accurately determine G23 and G31, the value to G12 may be supplied for G2z and Gz1.
-
Poisson’s Ratio
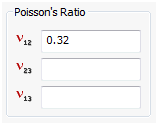
- The three dimensional Poisson’s ratios are input here.
-
Thermal Expansion

- The three dimensional thermal expansion coefficients are input here.
-
Allowables
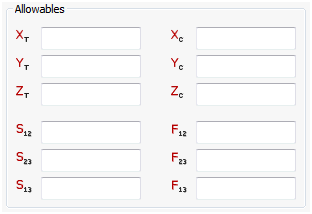
- Tension and compression allowables for all three directions are input here as well as the shear allowable and interaction terms used for the Tsai-Wu failure criteria.
- Xt, Yt, Zt, S12, S23, and S31 are required for composite element failure calculations when requested in the FT field of the PCOMP entry. Xc, Yc, and Zc are also used but not required.
- The interaction terms F12, F23, and F31 are experimentally determined from test specimens under multiaxial loading. This inconvenience along with the constraint that F12, F23, and F31 satisfy stability criteria of the form:
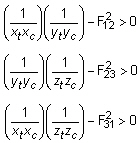
creates complications in the use of this theory. For this reason, it is recommended that F12, F23, and F31 be set to zero.
-
Thermal
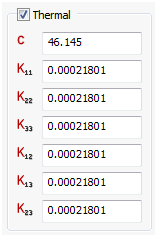
-
For thermal analyses, you can input values for a conductivity matrix, specific heat, and mass density under the Thermal section. Mass density is repeated since it may be a requirement in thermal analysis as well as in structural analysis.
- Kij defines a conductivity matrix.
-