This material type is not supported for Explicit analyses. After selecting Anisotropic 3D from the Type drop-down, the following material sections will become available: General and Thermal.
-
General
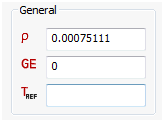
- Mass density, material damping coefficient, and reference temperature are input here for an Anisotropic 3D material.
- The mass density, RHO, will be used to automatically compute mass for all structural elements.
- To obtain the damping coefficient GE, multiply the critical damping ratio C/C0 by 2.0. If a dominate frequency is not defined for Material Structural Damping (see Dampings section), GE is ignored in transient response analyses.
- TREF is used only as the reference temperature for the calculation of thermal loads in linear solutions. If an initial temperature load is specified, TREF will be ignored.
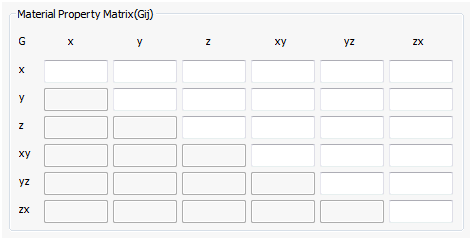
- Material Property Matrix: This button activates the following window where you can define the Gij matrix as well as the thermal expansion coefficient terms.
-
Thermal Expansion
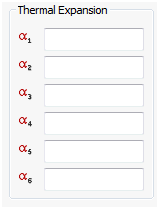
- The subscripts 1 through 6 refer to x, y, z xy, yz, zx of the material coordinate system. The stress-strain relationship is:

- The subscripts 1 through 6 refer to x, y, z xy, yz, zx of the material coordinate system. The stress-strain relationship is:
-
Thermal
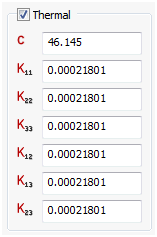
- For thermal analyses, you can input values for a conductivity matrix, specific heat, and mass density under the Thermal section. Mass density is repeated since it may be a requirement in thermal analysis as well as in structural analysis.
- Kij creates a conductivity matrix.