On the Material form, under the Analysis Specific Data section, click the Nonlinear button. Then select the Nonlinear Elastic option under Type. The following window pops up:
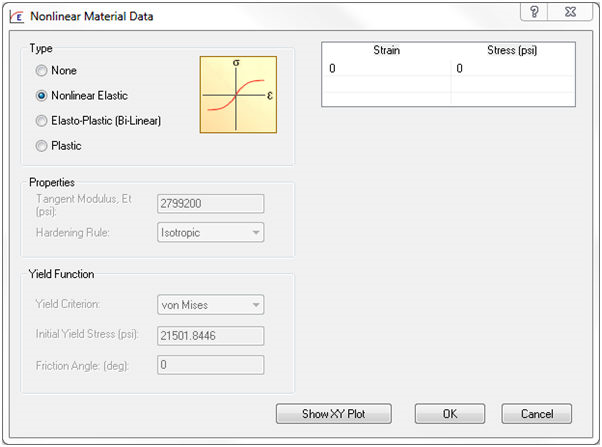
- Nonlinear elastic materials spring back elastically. There is no permanent deformation created when the material goes plastic.
- The stress vs. strain data must be true stress vs. true strain. The slope between any two points must not be negative.
- This option requires you to enter the full stress-strain data in the form of a table that will be used to model the material’s nonlinear elastic behavior.
- An example of such a material would be rubber.
- Values can be entered for both first and the third quadrant i.e., tension and compression, passing through (0, 0). If the values for compression are not given, it will be assumed to be identical to tension values and the first row has to be (0, 0).
- You can input the table values by double-clicking the fields, copied from either a text file like Notepad (tab separated columns of values) or from a table in Excel.
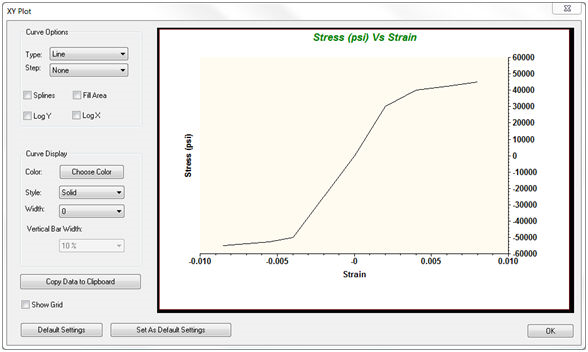
Here is a nonlinear elastic material example:

- Clicking Show XY Plot displays the data:
 Temperature dependent elastic and plastic analysis capabilities will be available in later versions.
Temperature dependent elastic and plastic analysis capabilities will be available in later versions.