A
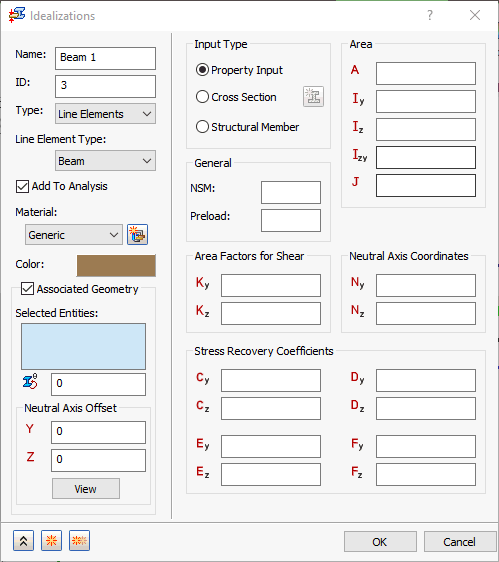
Beam is a 1D element with six degrees of freedom per node, where the shear center can be offset. It has the options to use
Property Input, Cross Section, or
Structural Member under
Input Type.

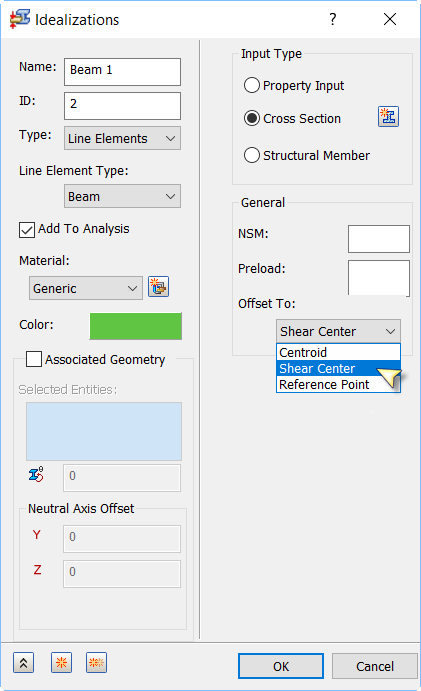
- NSM: Defines non-structural mass for this element type.
- Preload: A preload value can be input on the Beam element. Used for modeling connections that have preload.
- Offset To: These options refer to the actual mesh (numerical representation) of the model.
- Centroid: Will always mesh to the centroid of the library part used no matter how it looks on the screen.
- Shear Center: Will mesh the selected structural members to the offset shear center.
- Reference Point: Used for cross section definition. A reference point can be assigned to a location on the cross-section and then the section offset to this reference point location.
- Offset vectors are treated like rigid elements and are therefore subject to the same limitations.
- Offset vectors do not affect thermal loads.
- The specification of offset vectors is not recommended in solutions that compute differential stiffness because the offset vector remains parallel to its original orientation (differential stiffness is computed in buckling, prestress, and nonlinear analysis with large displacement effects ON).
- The following figures define beam element geometry:
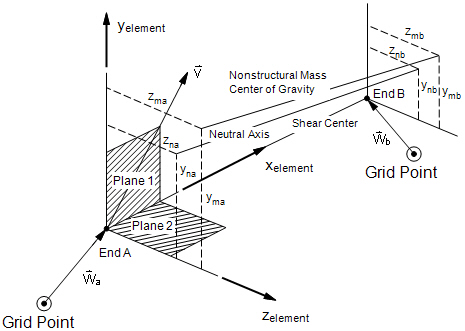
Beam Element Geometry System
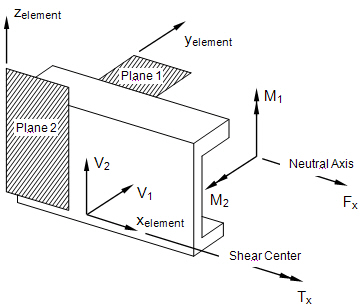
Beam Internal Element Forces and Moments
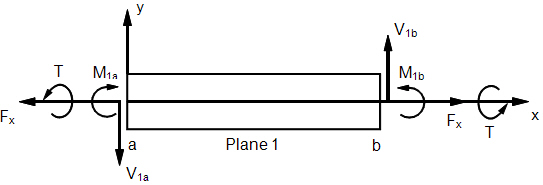
Beam Element Internal Forces and Moments (XY Plane)
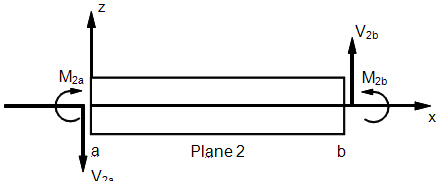
Beam Element Internal Forces and Moments (XZ Plane)