Element Stress Output Request
Description: Request element stress output.
Format:

Example:
STRESS(SHEAR) = ALL
| Option | Definition | Type | Default |
|---|---|---|---|
| Element stresses will be output to both the Model Results Output File and the results neutral file system. | Character | ✓ | |
| PLOT | Element stresses will be output only to the results neutral file system. | Character | |
| PUNCH | Element stresses will be output additionally to the Model Results Punch File. | Character | |
| CENTER | Output shell and solid element stresses at the center only. | Character | ✓ |
| CORNER | Output shell and solid element stresses at the center and corner nodes. | Character | |
| GAUSS | Output shell and solid element stresses at the center and gauss/integration points. | Character | |
| SHEAR | Maximum shear stress request for shell elements and octahedral shear stress request for solid elements. | Character | |
| VONMISES | Von Mises stress request for shell and solid elements. | Character | ✓ |
| TRESCA | Tresca stress request for shell and solid elements. | Character | |
| REAL or IMAG | Requests complex output in rectangular format (real and imaginary). | Character | ✓ |
| PHASE | Requests complex output in polar format (magnitude and phase). Phase output is in degrees. | Character | |
| PSDF | Power spectral density function, RMS, and number of positive crossings output request. | Character | |
| ATOC | Autocorrelation function output request. | Character | |
| RALL | Both PSDF and ATOC will be output. | Character | |
| VRMS | RMS von Mises output request. | Character | |
| BIAX | Biaxiality ratio output request. | Character | |
| VALL | RMS von Mises, RMS principal, RMS maximum shear, and biaxiality ratio will be output. | Character | |
| ALL | Element stresses for all elements will be output. | Character | |
| n | Set identification of previously appearing SET command. Only stresses for elements whose identification numbers appear on this SET command will be output. | Integer > 0 | |
| NONE | Element stresses will not be output. | Character | ✓ |
Remarks:
- ELSTRESS is an alternate form and is identical to STRESS.
- Both STRESS and STRAIN cannot be requested in the same subcase.
- Shell elements must be referenced on a SURFACE and solid elements must be referenced in a VOLUME. (See the SURFACE and VOLUME commands in Section 3, Case Control.)
- Solid element invariants are defined as follows:
Mean pressure:

Octahedral shear stress:

von Mises equivalent stress:
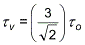
Tresca stress:
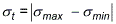
- Shell element invariants for plane stress analysis are defined as follows:
Maximum shear stress:
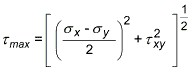
von Mises equivalent stress:

Tresca stress:

- Shell element Tresca stress is defined using the maximum and minimum of three stress measures:
- Inplane major principal stress
- Inplane minor principal stress
- Through thickness stress defined as the negative of the applied pressure at the element surface
- VRMS, von Mises RMS stress, is calculated by evaluating the PSD response of the peak RMS stresses calculated at each frequency step in a frequency or random response analysis. It is used as a measure of the total component stress.
- BIAX, Biaxiality Ratio, is the ratio of the minimum and maximum principal stress and is used in conjunction with the von Mises RMS stress to assess the nature of stress components in a frequency or random response analysis. Values that tend towards -1 indicate a pure shear state, 0 indicates uniaxial state, and 1 indicates equal biaxial loading.