Assign Texture to a Material
You can assign textures to a material's color.
Each texture type has a unique set of controls, or channels, that adjust properties such as reflectivity, transparency, and self-illumination. Within each of these channels, you can assign, hide, or delete a texture. When you assign textures to a material's color, the texture colors replace the material's diffuse color.
After you apply the texture, you can realign it with a face or shape by adjusting the material mapping. Using this feature is recommended for advanced users only.
There are two types of textures; image and procedural.
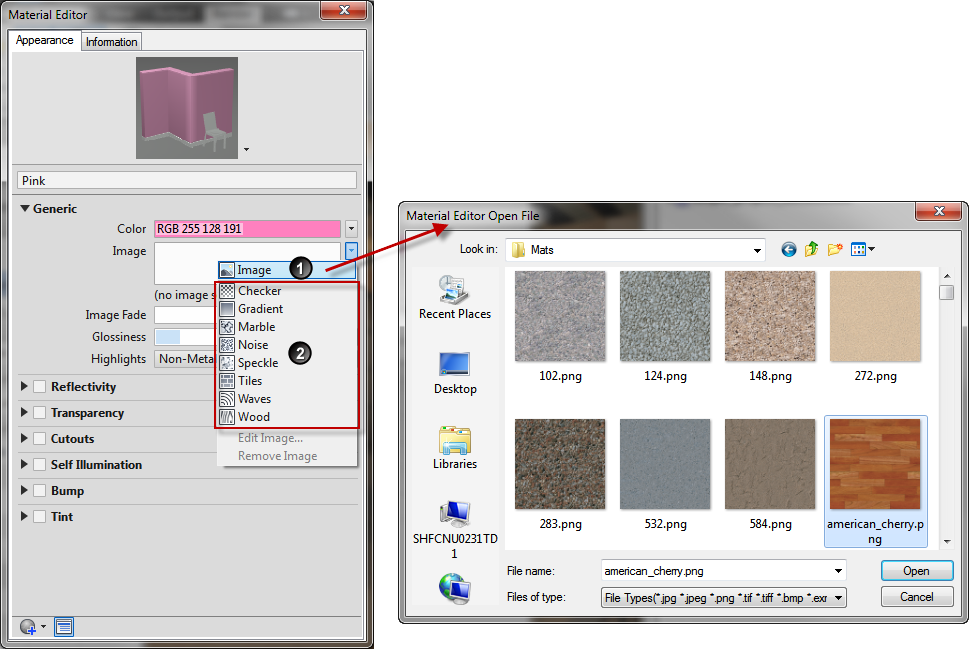
Image Textures
Image textures use an image to represent a texture. For example, you can use an image of wood, concrete conglomerate, metal, carpet, or basketry.

You can edit the texture scale and other properties to customize it to your model. The product provides a library of images that you can use with textures. You can also add your own textures using the following file types:
- BMP, RLE, or DIB
- GIF
- JFIF, JPG, or JPEG
- PCX
- PNG
- TGA
- TIFF
Procedural Textures
Procedural textures are generated by a mathematical algorithm to represent repetitive textures such as tiles or wood. You can adjust the texture properties for the effect you want. For example, you can adjust tile size and mortar spacing for a brick material or change the spacing of the grain in a wood material.
The types of settings for a procedural texture vary. You nest them to add depth and complexity to the material.







