Use the Functions tab to enter expressions using functions.
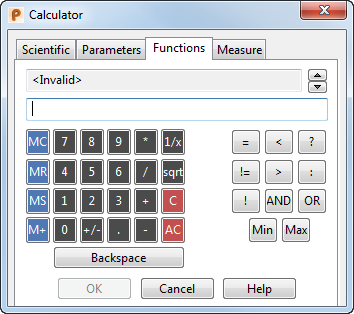
The result of a logical expression is 0 or 1, where 0 is false and 1 is true. You can combine buttons to give more operators.
Each logical operator is discussed below.
A == B outputs 1 if A equals B and 0 otherwise
A != B outputs 1 if A does not equal B and 0 otherwise
A < B outputs 1 if A is less than B and 0 otherwise
A <= B outputs 1 if A is less or equal to B and 0 otherwise
A > B outputs 1 if A is greater than B and 0 otherwise
A >= B outputs 1 if A is greater or equal to B and 0 otherwise
A AND B outputs 1 if A and B are true and 0 otherwise
A OR B outputs 1 if either A or B is true and 0 otherwise
! A outputs 1 if A is false and 0 if true. This is known as the not operator.
test ? result_true : result_false if test is true then output result_true otherwise output result_false.
Example 1
a>=b ? a+b : a-b
This outputs a+b if a>=b and a-b if a<b.
Example 2
a= (b>20)?10:((b>30)?20:30)
This example uses a nested expression to determine the value of a, based on the value of b
if b > 20 then
a = 10
else if (b > 30) then
a = 20
else
a = 30
Min — This determines the minimum value of a list of values in the expression.
The list of values in the expression must be of the form:
A1; A2; … ; AN
Max — This determines the maximum value of a list of values in the expression.
The list of values in the expression must be of the form:
A1; A2; … ; AN