After clicking New Vehicle icon in the Moving loads dialog, the following displays.
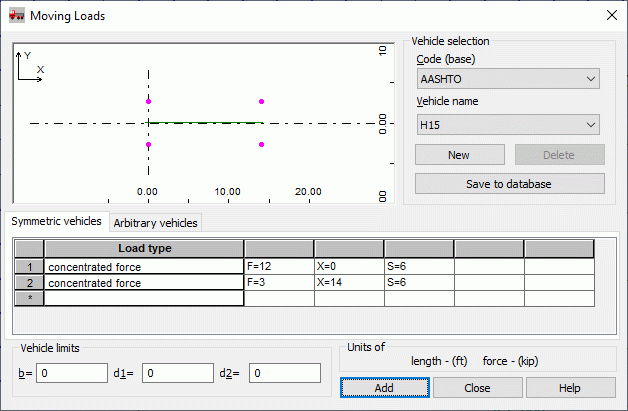
A vehicle is a set of forces that constitutes the load in a moving load case. The vehicle moves along a defined route by a distance referred to as a step in the route of a moving load case. Each individual position of the vehicle is saved in the successive case component.
A vehicle definition can include concentrated, linear forces or planar forces acting on a linear contour.
The dialog lets you select a vehicle to add to the active list of vehicles in the Moving Loads dialog. There are 2 vehicle types available:
- Symmetric vehicles - Loads are defined as pairs of forces with a defined spacing, symmetrical to the vehicle axis at any point over the axis length. Forces are defined as vertical loads (horizontal forces caused by braking can be obtained by defining values of route coefficients). Vehicles of this type are used for modeling bridge loads.
- Arbitrary vehicles - Loads defined as forces at any point over the length of a vehicle axis and at any distance from it. Concentrated forces can be defined in the directions X, Y, and Z of the local coordinate system of the vehicle. Route coefficients are not applied for this vehicle type. This type of vehicles is used for modeling loads caused by overhead traveling cranes. (An example definition of such a vehicle is shown in the following image.)
The dialog has several parts. The upper right corner of the dialog has the Vehicle selection field, where there are 2 selection fields: Code (database) and Vehicle name. In addition, there are 3 buttons:
- New - Defines a new vehicle. Clicking New opens an additional dialog, where you can define the name of a new vehicle. There are 2 ways:
- If you click Add after defining the loads for a new vehicle, the vehicle is added only to the list of active vehicles in the Moving Loads dialog.
- If you click Save (to database) after defining the loads for a new vehicle, a new dialog displays, where you can select the database (folder) of vehicles for storing the new vehicle.
- Save to database - Lets you save the new vehicle to a selected vehicle database. Clicking Save to database opens the dialog, where you can select the database (folder) of vehicles for storing the new vehicle.
- Delete - Deletes a selected vehicle from the vehicle database.
The upper left corner displays a diagram of the selected vehicle.
The middle of the dialog has a table displaying a description of the loads for the selected vehicle. Robot provides 3 types of loads: concentrated load, linear load, and planar load. You can change the load parameters that are defined for a vehicle.
The following parameters must be defined for individual load types (dimensions are displayed diagrammatically in the following images for load types):
|
Concentrated force 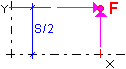 |
Symmetric vehicles: F- value of a concentrated force (unit: force) X - Coordinate value of the point where the force is applied (along the vehicle axis) S - Width of the force spacing Asymmetric vehicles: FX, FY, FZ - values of a concentrated force X - Coordinate value of the point where the force is applied (along the vehicle axis) Y- Coordinate value of the point where the force is applied (perpendicularly to the vehicle axis) |
|
Linear load  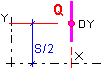 |
Symmetric vehicles: Q - Value of a linear load (unit: force/length) X - Coordinate value of the line along which the force is applied (along a vehicle axis) S - Width of the linear load spacing (only in the Y axis direction) Dx - Length of a segment along which a load is acting (along a vehicle axis) Dy - Length of a segment along which a load is acting (perpendicularly to the vehicle axis) Asymmetric vehicles: Compared to symmetric vehicles, instead of the S value there is Y - coordinate value of the point where the force is applied (perpendicularly to the vehicle axis) |
|
Planar load 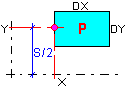 |
Symmetric vehicles: P- Value of a planar load (unit: force/length^2) X - Coordinate value of the line along which the force is applied (along the vehicle axis) S - Width of the planar load spacing (only in the Y axis direction) Dx - Length of a rectangle side upon which a load is acting (along the vehicle axis) Dy - Length of a rectangle side upon which a load is acting (perpendicularly with respect to the vehicle axis) Asymmetric vehicles: Compared to symmetric vehicles, instead of the S value there is Y - Coordinate value of the point where the force is applied (perpendicularly to the vehicle axis) |
The lower part of the dialog has 2 fields:
- Vehicle dimensions:
b - Vehicle width
d1 - Distance between the load and the vehicle contour (from the vehicle front)
d2 - Distance between the load and the vehicle contour (from the vehicle back)
- Units:
forces - The units in which the values of forces are displayed (the units can be modified in the Job Preferences dialog)
length - The units in which the values of length are displayed (the units can be modified in the Job Preferences dialog)
Note: The units of force and length also determine a unit for a linear and planar load: a linear load unit is expressed by the force per length unit; a planar load unit is expressed by the force per area unit (the length squared).