A sliding analysis may be required if there is a large participation of horizontal forces acting on a foundation as compared to vertical ones. Such a situation results in possible soil damage caused by sliding of the foundation footing on the soil or sliding between the layers of soils when the lower-positioned layers are weaker than those in direct contact with the footing.
In order to avoid the loss of sliding stability, the following solutions are recommended.
- Increase of a foundation weight.
- Preparation of a non-cohesive soil bed with controlled compaction ratio.
- Design of the so-called key (the option is not accessible in the foundation module).
During sliding analysis, note that the cohesion of soil directly adjacent to a foundation may be changed in the course of preparation works or because of varying location of the water level. In such cases a value of the soil cohesion should be reduced.
For all codes (except ACI, CSA, DTU 13.12 and Fascicule No 62 - Titre V) you can select the Sliding with soil pressure considered option. The soil pressure Pa and the passive pressure Pp will be calculated additionally.
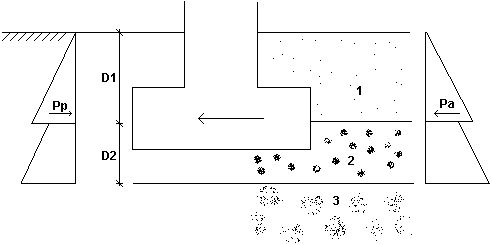
The height of the pressure model is equal to the following distances.
- From the soil level to the shear plane (for continuous footings).
- From the top surface of the spread footing base to the shear plane (for spread footings).
The passive pressure is calculated according to the following formula.
which for the second layer is understood as
![]() .
.
The total passive pressure of the soil is as follows.
If the backfill is loaded, the following term should be taken into account in calculations.
The load q must be constant and is multiplied by the augmentation factor. The algorithm for calculation of P a is identical as for P p .
You can define a load acting on a specified quarter of a spread footing. The soil pressure acting from a determined side will be calculated in proportion to the length of a selected quarter.

Sliding with soil pressure considered may be calculated for both directions simultaneously, or for each separately. It is selected from the list for X and Y directions, for X direction, or for Y direction.
Calculations for individual codes
- ACI \ CSA
Sliding design is not available for these codes. If required, check this value manually.
- BS 8004:1986
The general condition of sliding stability is presented as follows.
H ≤ H FRICTION
where:
H FRICTION = V * tg(φ) + c * Ac
V - vertical force
j - internal friction angle of the soil
c - cohesion
Ac - foundation-soil contact area.
Design of this limit state results in the safety factor of a structure: H FRICTION / H. The value of which is greater than or equal to 1.0.
Options in the Geotechnical options dialog enable the analysis of this limit state as well as determining the limit value of the factor.
- DTU 13.12
The general condition of sliding stability is presented as follows.
Qtf ≤ Qf = N * tg(ϕ) + c*Ac
where:
Qtf - horizontal force
N - vertical force
ϕ - internal friction angle of the soil, assuming that the adopted value of tg(ϕ) is not greater than 0.5
c - soil cohesion (though not greater than 75 kPa)
Ac - foundation-soil contact area.
When a seismic impact occurs, the soil cohesion is disregarded (according to studies), resulting in the reduction of the sliding formula to the following form.

During analysis of sliding between the foundation and the lean concrete ( not connected to the foundation by means of the dowel bar reinforcement), concrete - lean concrete friction coefficient is introduced, equaling 0.75.

If dowel bars ensure permanent connection between the foundation and lean concrete, this condition is not checked.
Design for this limit state results in obtaining the safety factor of a structure: Qtf / Qf. The value of which is greater than or equal to 1.0.
Turning on the analysis of this limit state as well as determining the limit value of the factor are enabled in the Geotechnical options dialog.
- ENV 1997-1:1994 (EC 7)
The analysis of sliding is performed according to point 6.5.3.
- For the conditions with drainage - formula (6.3):
 Note: It is assumed that the parameter d d is adopted as for foundations cast in situ, which means δ d = φd - 6.5.3 (8).
Note: It is assumed that the parameter d d is adopted as for foundations cast in situ, which means δ d = φd - 6.5.3 (8).Since EC7 code does not preclude accounting for the soil cohesion in the analysis of sliding 6.5.3 (8), there is a possibility to apply the soil cohesion partially or completely by extending the formula with an additional part for the reduced cohesion.

where:
the coefficient j included in the interval <0.0, 1.0> may be defined in the Geotechnical options dialog.
A' - Working area of the foundation (foundation-soil contact area).
c' - Design value of effective soil cohesion.
If the coefficient 0.0 is introduced, this formula assumes the form exactly as specified in code (6.3).
- For the conditions without drainage - formula (6.4):
Sd = A' * cu.
Note: The soil parameter: Cohesion without drainage - cu is applied here.If the working area is not equal to the foundation area (an uplift occurs), the following condition (6.5) is checked:
Sd < 0.4 Vd.
- For the conditions with drainage - formula (6.3):
- EN 1997-1:2004 (EC 7)
The analysis of sliding is performed according to point 6.5.3.
The general condition is described by formula (6.2):
Hd ≤ Rd + Rp;d
- For the conditions with drainage - formula (6.3):
Rd = V'd * tgδ d
Basing on point A.2(2) which refers to the γ φ coefficient it was assumed that the calculation value of the coefficient of friction amounts:
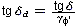
The tan d parameter which is a characteristic coefficient of friction soil - foundation is a soil property saved in the soil base called Coefficient of friction.
The tan d parameter is taken for the foundation formed directly on soil, in accordance with the soil database, where it should be defined according to the code on the base of the friction angle in critical condition tan δ = tan φ cv 6.5.3 (10) i A.2(2). After the Smooth precast foundation 6.5.3(10) option is activated in the Geotechnical options dialog according to 6.5.3 (10) and A.2(2), the value of the coefficient is calculated in the following way:

The EC7 code does not recommend to consider soil cohesion in the sliding analysis 6.5.3 (10) though the program allows such a possibility. Partial or complete use of the cohesion is possible by entering an additional element to the formula (6.3a):
Rd = V'd * tgδ d + ξ * A c * c u
where:
the coefficient included in the interval <0.0, 1.0> may be defined in the Geotechnical options dialog
A' - working area of the foundation (foundation- soil contact area)
c' - Design value of effective soil cohesion
Default value of the reduction coefficient ξ = 0.0.
- For the conditions without drainage - formula (6.4):
Rd = A c * c u;d
Note: The soil parameter: Cohesion without drainage - cu is applied here.If the working area is not equal to the foundation area (an uplift occurs), the following condition (6.5) is checked:
Rd < 0.4 Vd.
- For the conditions with drainage - formula (6.3):
- Fascicule 62 Titre V
The general condition of sliding stability is presented as follows.
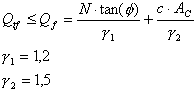
where:
Qtf - Horizontal force.
N - Vertical force.
φ - Internal friction angle of the soil.
c - Soil cohesion (though not greater than 75 kPa).
Ac - Foundation-soil contact area.
If a seismic impact occurs, the soil cohesion is disregarded (according to studies), resulting in the reduction of the sliding formula to the following form.

During analysis of sliding between the foundation and the lean concrete ( not connected to the foundation by means of the dowel bar reinforcement), concrete - lean concrete friction coefficient is introduced, equaling 0.75.

If dowel bars ensure permanent connection between the foundation and lean concrete, this condition is not checked.
Design for this limit state results in obtaining the safety factor of a structure: Qtf / Qf. The value of which is greater than or equal to 1.0.
Turning on the analysis of this limit state as well as determining the limit value of the factor are enabled in the Geotechnical options dialog.
- PN-81/B-03020
The condition for foundation sliding is not provided directly in the code PN-81/B-03020 [A3]. The following refers directly to the code PN-83/B-03010 [A4]. The general condition of sliding stability according to this code and studies is presented as follows.
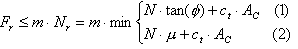
for the layer positioned below the contact level:

where:
F r - Design value of a displacing force.
N - Design value of a vertical force at the reference level.
A' c - Reduced area of the foundation base.
ϕ - Design value of the internal friction angle of the soil.
A c - Foundation-soil contact area (reduced area of the foundation base).
μ - Foundation-soil friction coefficient.
c t - Reduced value of cohesion = (0.2 do 0.5) * cu.
c u - Design value of soil cohesion.
m - Correction factor.
As a result of the design of this limit state, the following safety factor of a structure is obtained:

Turning on the analysis of this limit state as well as determining the limit value of the factor are enabled in the Geotechnical options dialog.
- SNiP 2.02.01-83
The general condition of sliding stability is presented as follows.

where:
H - Horizontal force.
γc - Environment coefficient.
γ n - Reliability factor taking account of the use for which a structure is intended.
V - Vertical force.
φ - Internal friction angle of the soil.
c - Soil cohesion.
Ac - Foundation-soil contact area.
As a result of design of this limit state, the following safety factor of a structure is obtained:

Turning on the analysis of this limit state as well as determining the limit value of the factor are enabled in the Geotechnical options dialog.