Opening the Snow/Wind Load dialog and clicking the Wind tab displays the following dialog.
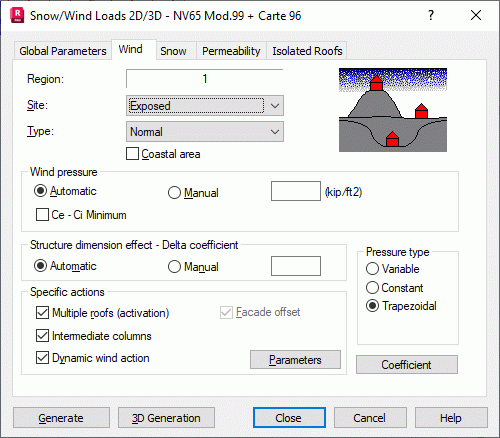
The dialog is divided into several fields with groups of specific options.
At the top of the dialog are the following options:
- Region - A list of available wind regions. A wind region is one of the factors that determine basic wind pressure over consecutive structure elements.
- Site - A list of structure site classes, subjected to wind actions, that are available for a specific snow/wind code. Clicking the arrow on the right side of the dialog opens a dialog with a list of site classes based on wind action.
The site, exposure, or structure location class are factors that determine the wind pressure on walls. The region where the structure is located (mountainous, flat, built over, unbuilt, and so on) is specified.
- Type - A list of wind types (such as normal and extreme) that are available for the snow/wind code. The wind type determines the value of the coefficient used for the wind pressure, the building location, and so on.
Below are the following fields:
- The Wind Pressure field has the following:
- Automatic - Automatically defines basic wind pressure according to structure site parameters.
- Manual - Lets you manually define basic wind pressure. Such parameters as Department, Region, or Type are not considered in the manual definition.
-
Ce - Ci Minimum
Loads applied to structure bars are calculated according to the following formulae:
Load = (Ce - Ci) * Qh * Ks * Delta * Envelope, where C = Ce - Ci
If the Ce-Ci Minimum option is selected, it is assumed that the absolute value C = Ce - Ci cannot be less than 0.3 (unless Ce - Ci = 0).
0.0 < C < 0.3 => C = 0.3
-0.3 < C < 0.0 => C = -0.3
If the Ce-Ci Minimum option is cleared, then the coefficient C = Ce - Ci can use arbitrary values.
- The Structure Dimension Effect - Delta Coefficient field has the following:
- Automatic - Automatically defines the DELTA coefficient according to predefined structure dimensions.
- Manual - Lets you manually define the global DELTA coefficient for the entire structure. It is the dynamic wind pressure reduction coefficient.
- The Specific Actions field has the following:
- Multiple Roofs - Accounts for the multiple roof effect, where roofs shield each other. It is related to the aerodynamic coefficient reduction on hidden elements.
- Facade Offsets - Accounts for pressure changes on flat roofs (change from wind suction to wind thrust).
- Dynamic Wind Action - When you select this option and click Parameters, a dialog opens for defining Beta, period (s), and decrement. When calculating the dynamic wind effect for a snow/wind code that accounts for vibration frequency or pulsations (instead of the structure vibration period), Robot automatically recalculates the period value for the required quantities. Dynamic wind effects are considered, if the Period field contains a value greater than 0.
In addition, you can specify the logarithmic damping decrement in the Decrement field. If a value is not entered in this field, Robot automatically assigns the proper value.
Note: Parameters is currently unavailable. - After clicking Intermediate columns, you can generate wind loads for intermediate columns positioned between main frames, for 3D frames built from repeating 2D frames. This option is available for all French snow and wind codes implemented in Robot. Intermediate columns are assumed to be positioned at the midpoints of spacings between frames. Loads for intermediate columns accounted for:
- in a 2D frame - as concentrated forces applied to the frame
- in a 3D frame - as a linear load on columns
- The Pressure type field has the following:
- Variable
- Constant
- Trapezoidal.
During snow and wind load calculations, loads on structure bars are calculated in the following manner:
Load = (Ce - Ci) * Qh * Ks * Delta * Envelope
Structure bars are divided into groups of snow and wind load surfaces, that is, a sequence of colinear bars.
Snow and wind load surfaces can be structure walls or roofs.
When Pressure type: constant is selected, for all bars of a given snow/wind load surface, 1 pressure value Qh is assumed, which is calculated for the highest point of the snow/wind load surface. In other words, the load value for each bar of a snow/wind load surface is identical.
When Pressure type: variable is selected, the Qh value is calculated separately for each bar of the snow/wind load surface (for h = height of the highest bar point). The load value for bars of a snow/wind load surface increases as the height increases.
When Pressure type: trapezoidal is selected, the Qh value is calculated separately for each bar of the snow/wind load surface using the height h of the beginning and end nodes. The result is a linear load varying along the height on each bar.